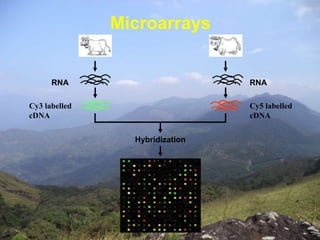
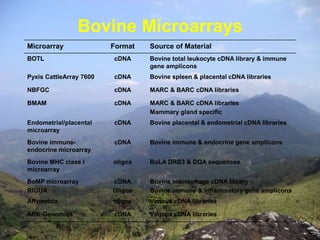
Microarrays are tools used to analyze gene expression. They consist of small glass slides containing samples of many genes arranged in a regular pattern. The genes are used to detect mRNA species present in a cell or tissue at a given time, allowing analysis of which genes are actively being expressed. Major uses of microarrays include analysis of gene expression, single nucleotide polymorphisms, and identification of pathogens or tumors. They provide a way to detect differences in gene expression across large numbers of genes in different cell populations on a genome-wide scale.