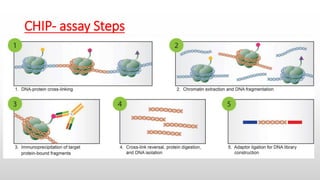
This document summarizes the steps of a ChIP-Seq (Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing) assay. The key steps are: 1) cross-linking proteins to DNA, 2) fragmenting chromatin, 3) immunoprecipitating the DNA-protein complex using antibodies specific to the protein of interest, 4) purifying and analyzing the DNA. ChIP-Seq allows researchers to identify the genomic binding sites of transcription factors and histone modifications genome-wide.


 .
Chromatin fragmentation : The chromatin is fragmented or “sheared” to
mononucleosome sized fragments (150-300 bp), which is important for obtaining
high resolution sequencing data. Chromatin shearing is accomplished by
sonication or enzymatic digestion using micrococcal nuclease (MNase) and
monitored by gel (e.g. agarose) or capillary electrophoresis .
Immunoprecipitation using specific Anti-bodies : Selected Abs should be highly –
specific Abs and show highly effective binding with chromatin associated
proteins . The amount of primary antibody required for good signal in a ChIP is
usually 2–5 μg . The antibody is coupled to magnetic beads , and incubate at 4°C
for at least 12 h, with rotation such that the samples mix and the beads remain
suspended . the antibody-bound chromatin is isolated from bulk chromatin using
a magnet, followed by a series of stringent washes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chip-seqimmunoprecipitation-230210215058-fa3f6455/85/ChIP-Seq-Immunoprecipitation-pptx-5-320.jpg)


