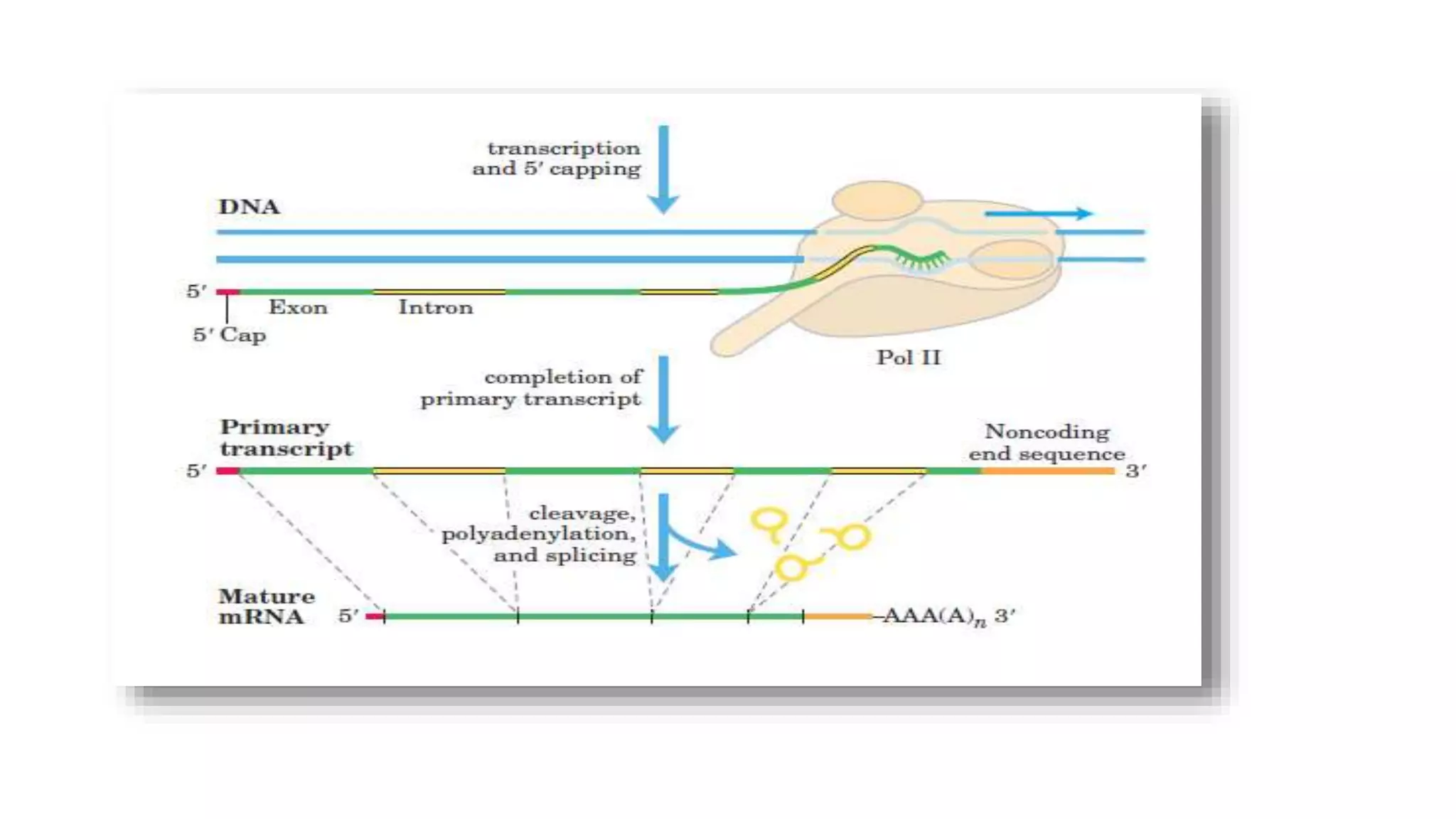
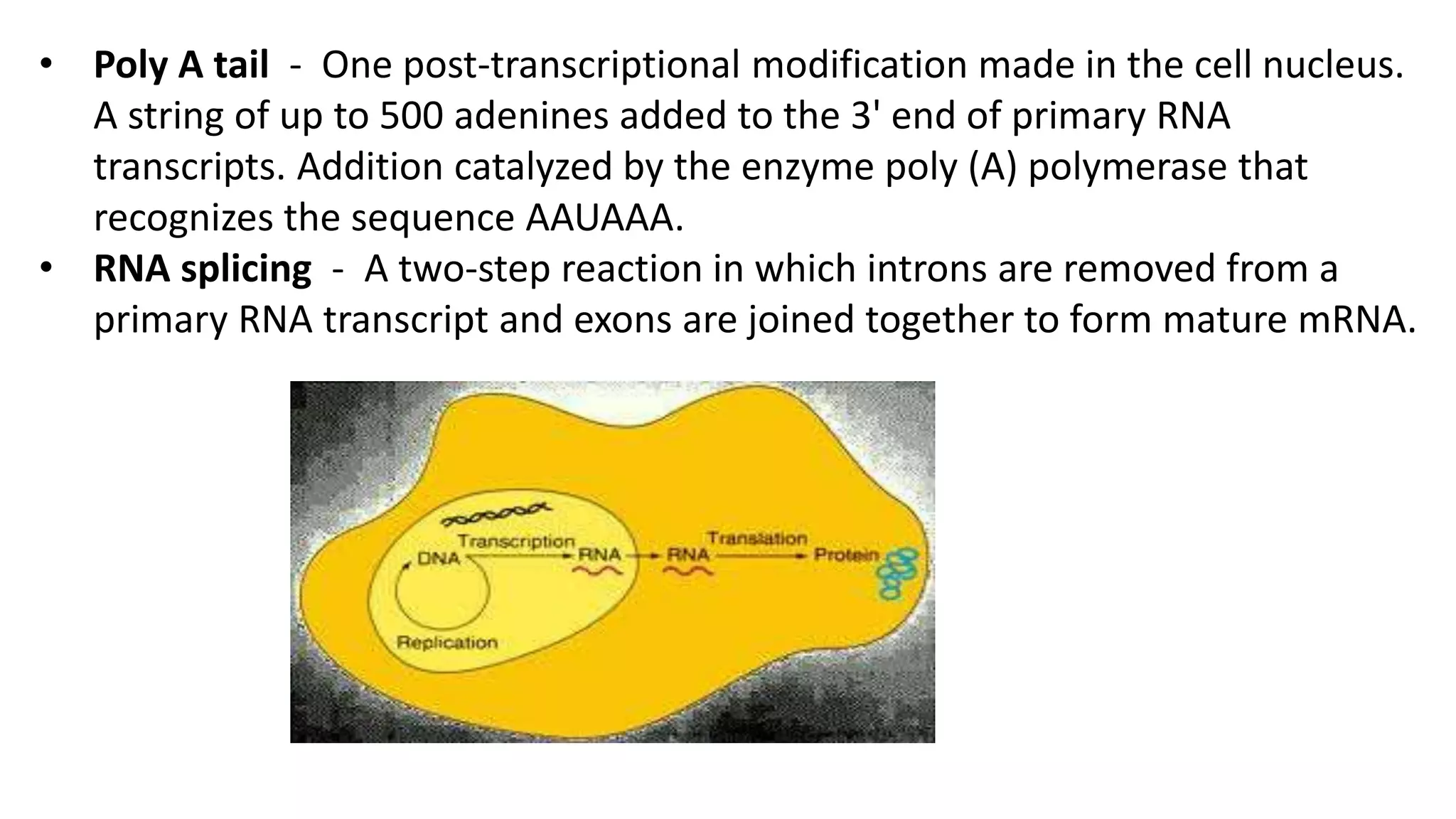
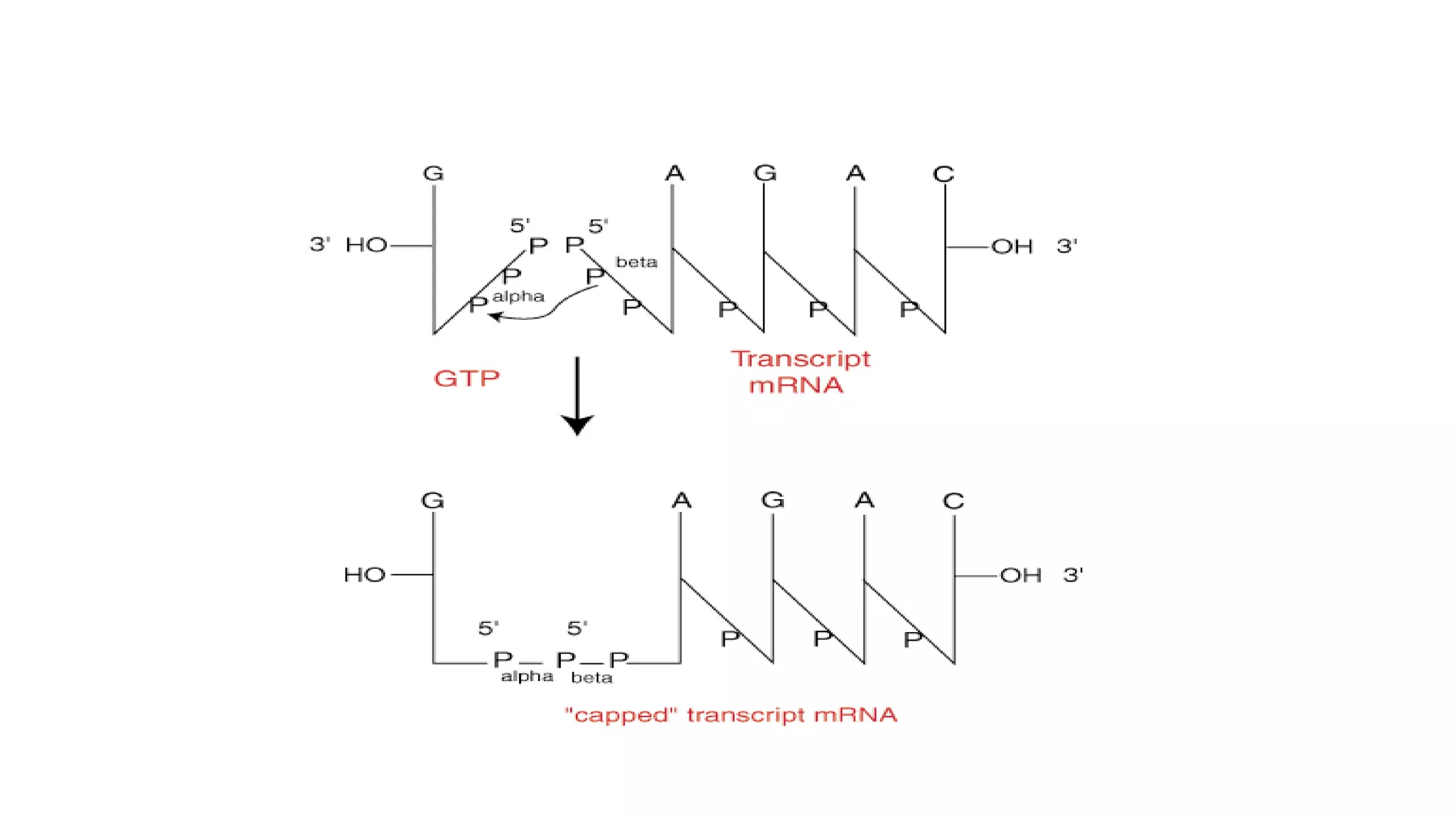
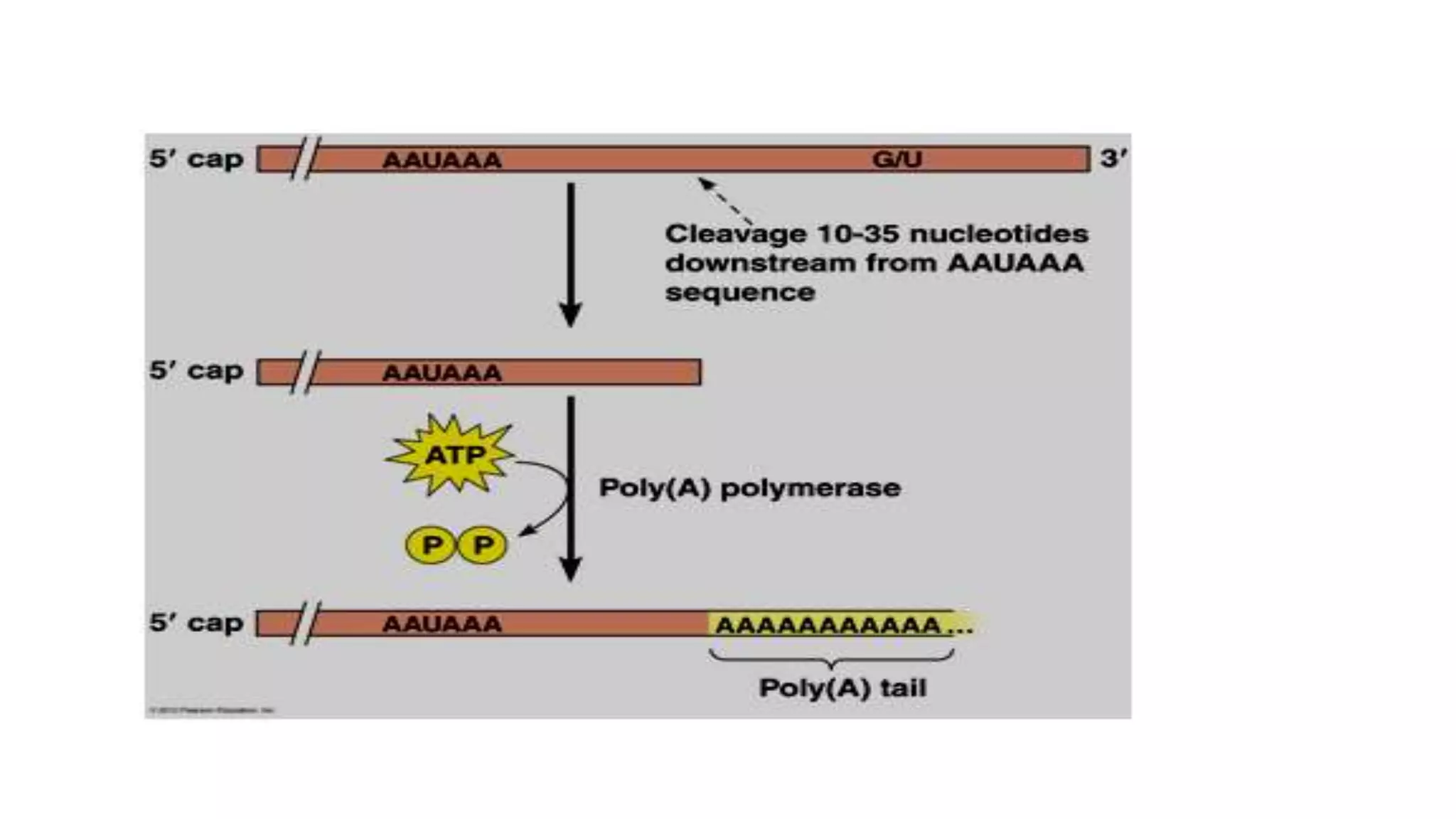
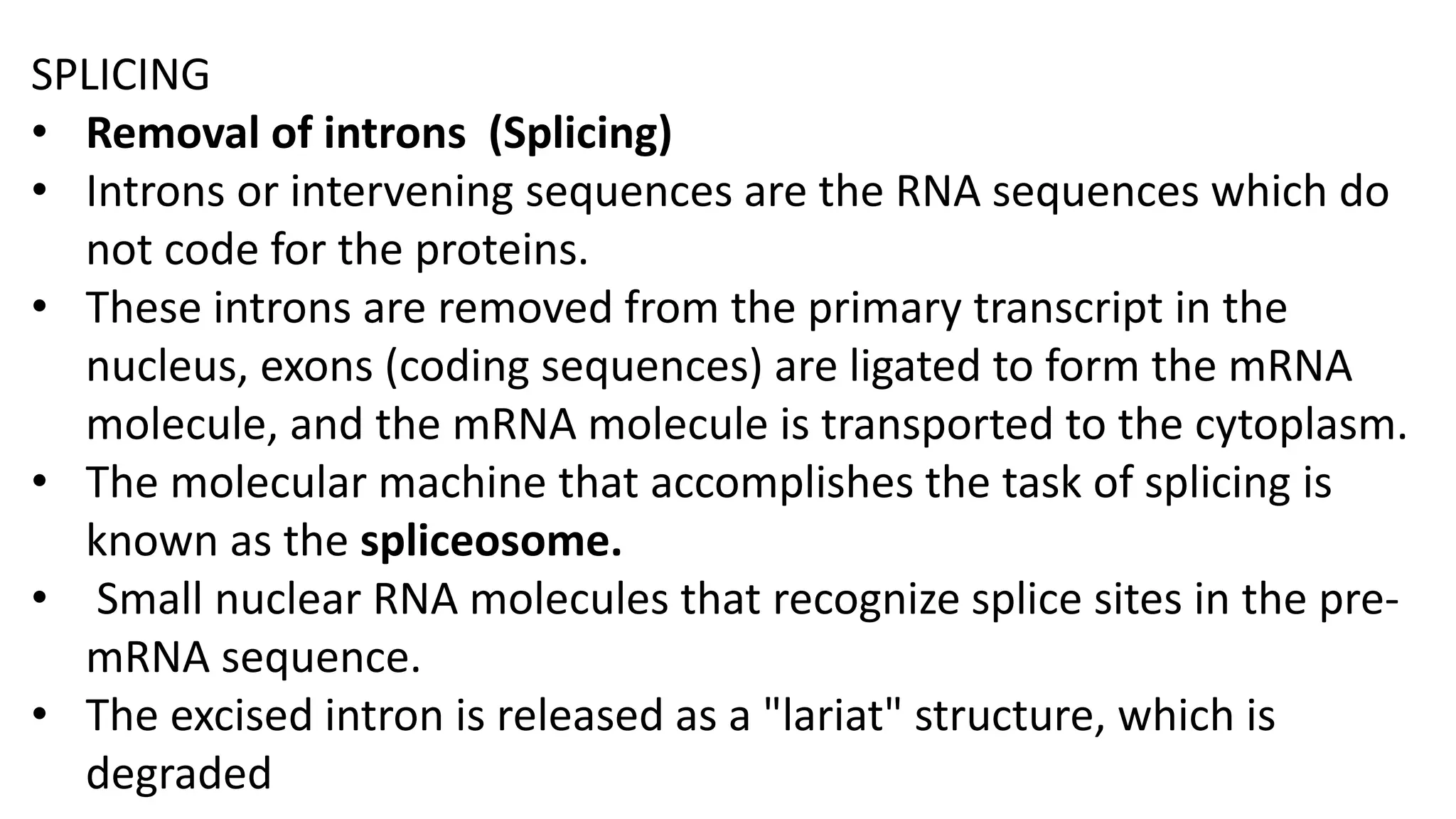
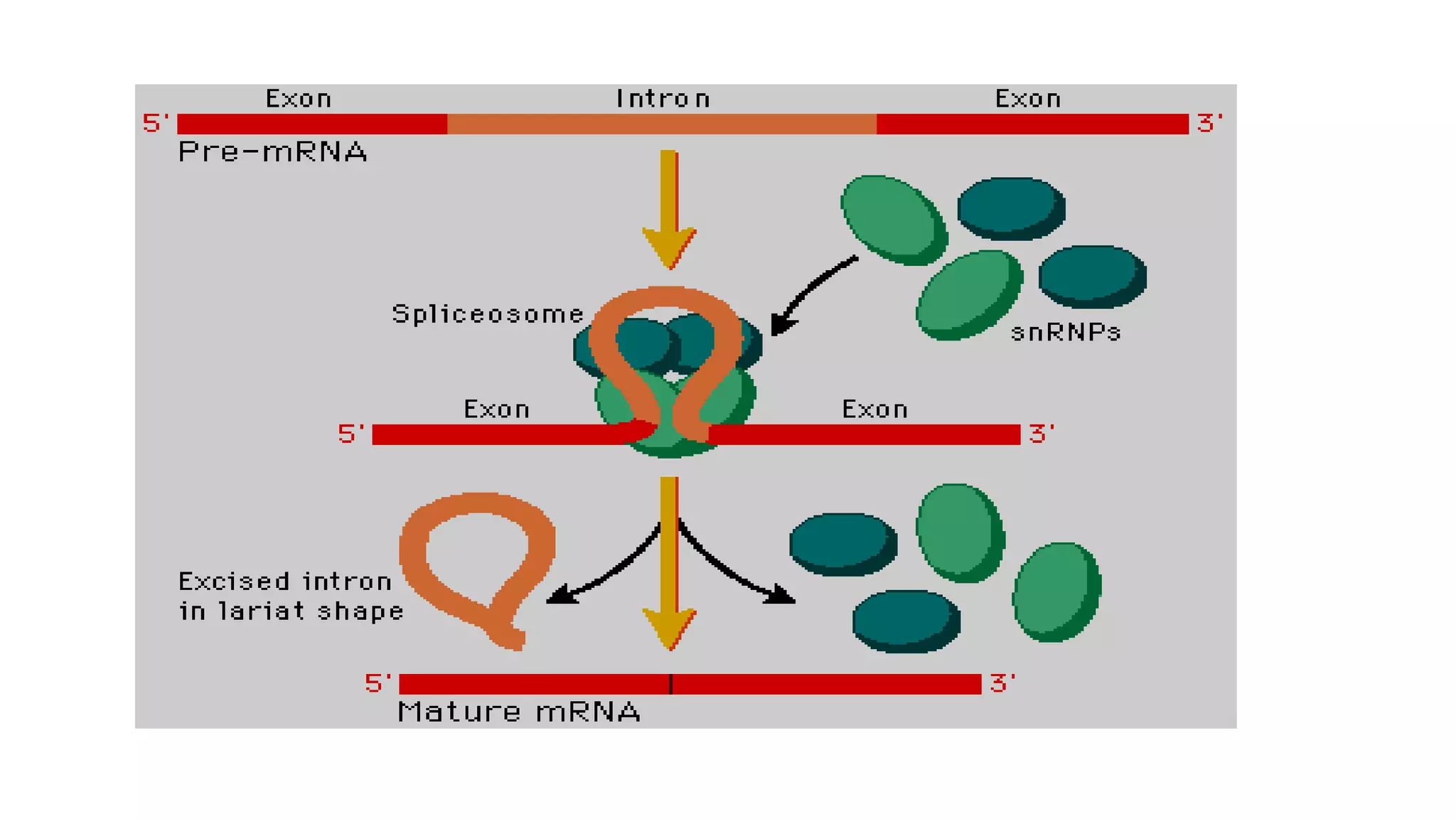
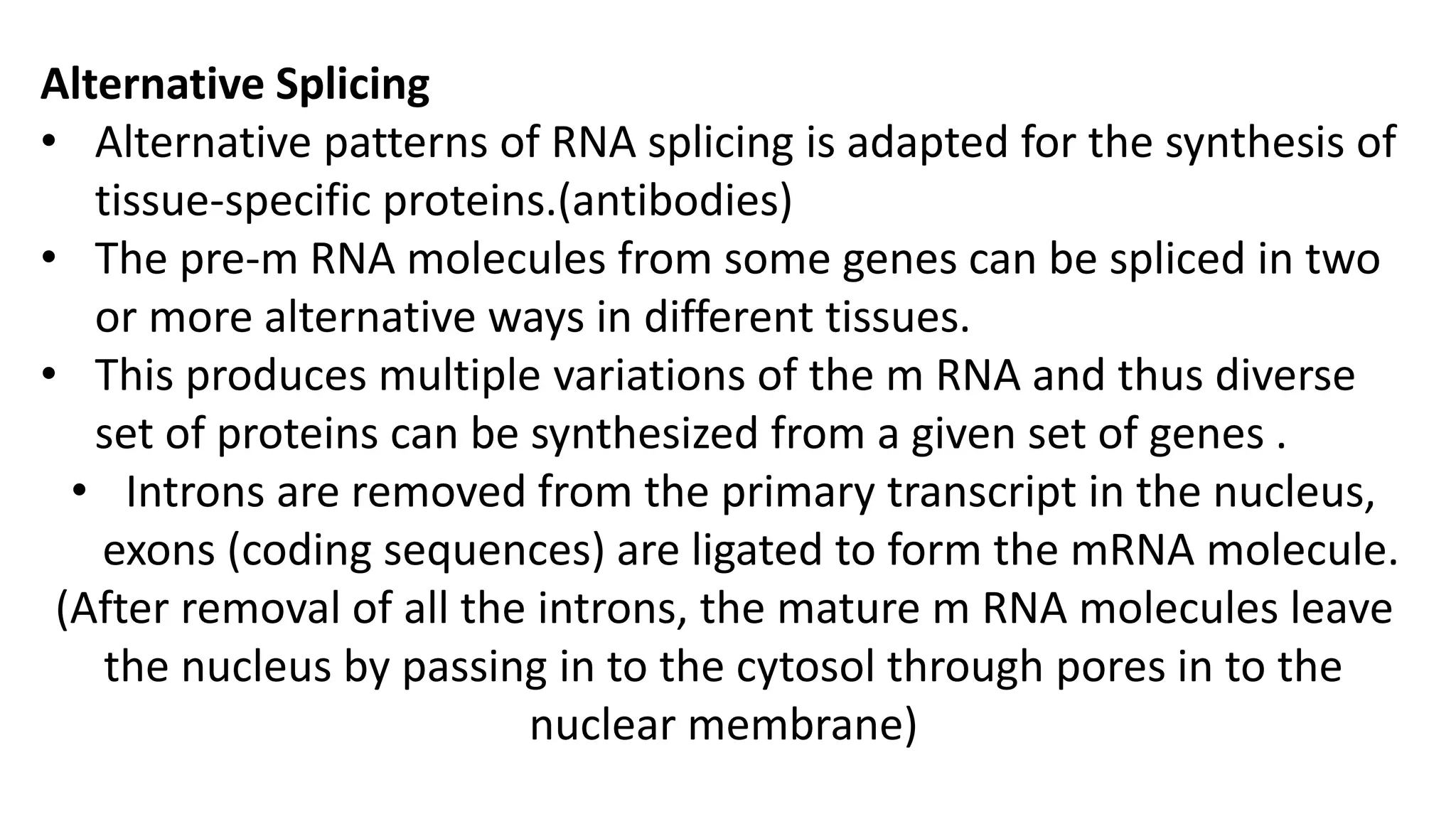
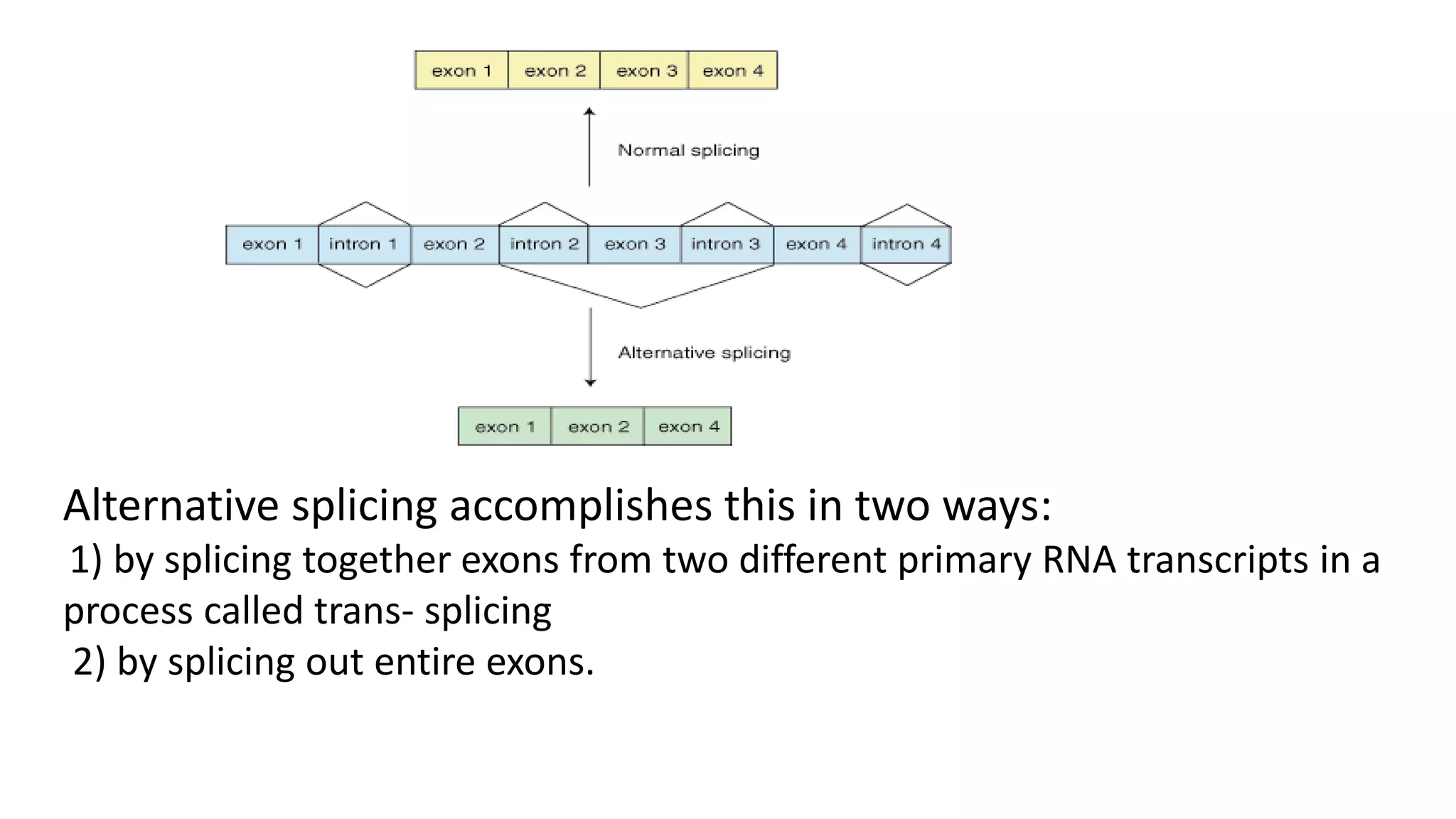
Post-transcriptional modifications help process primary transcripts into mRNA in three main ways: 1) 5' capping protects the transcript and aids export from the nucleus, 2) Polyadenylation aids stability and transport, and 3) Splicing removes introns and ligates exons to form mature mRNA. In eukaryotes, this occurs in the nucleus and is essential for efficient translation. It can also result in alternative splicing to increase protein diversity from a single gene.