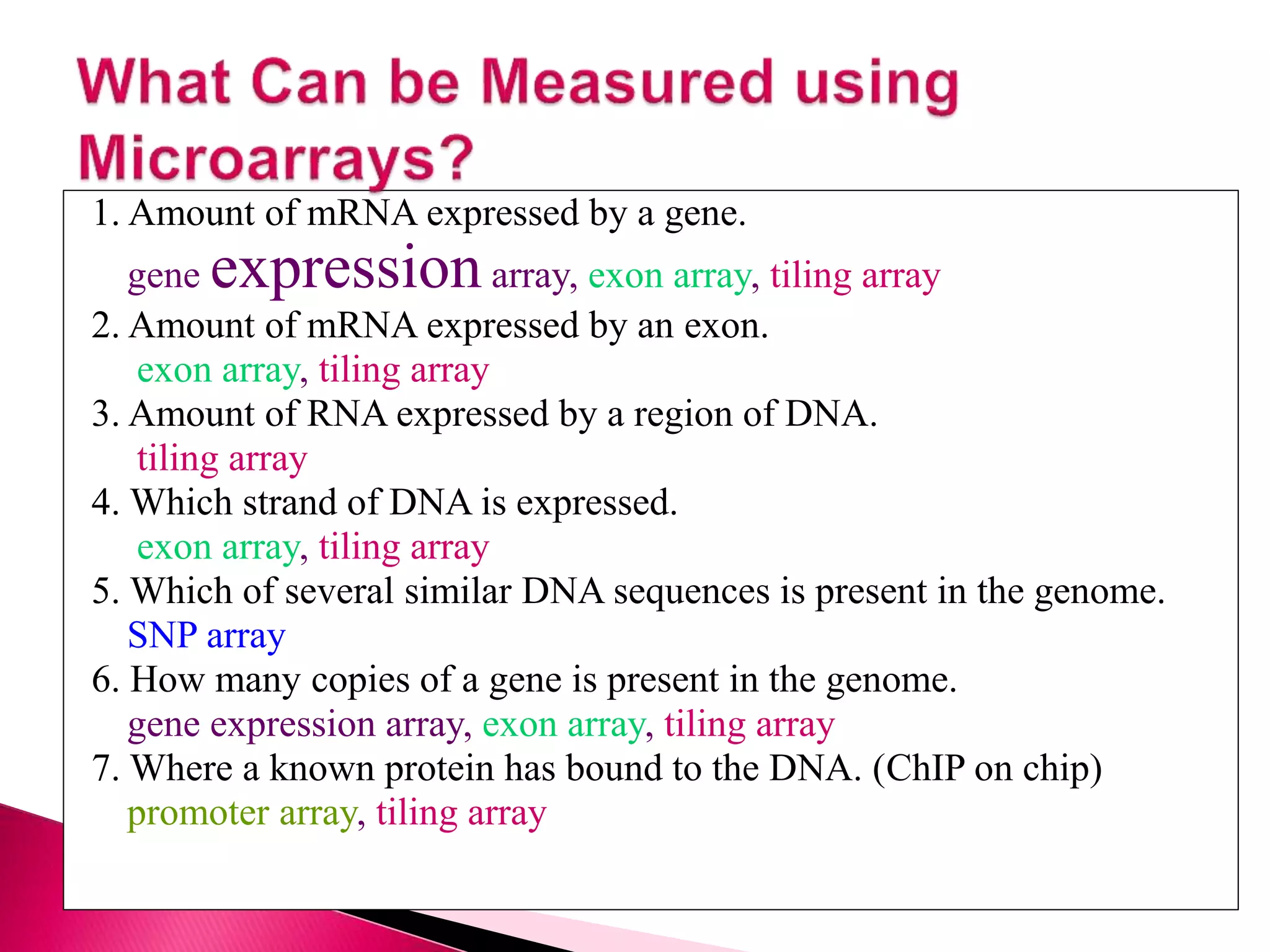
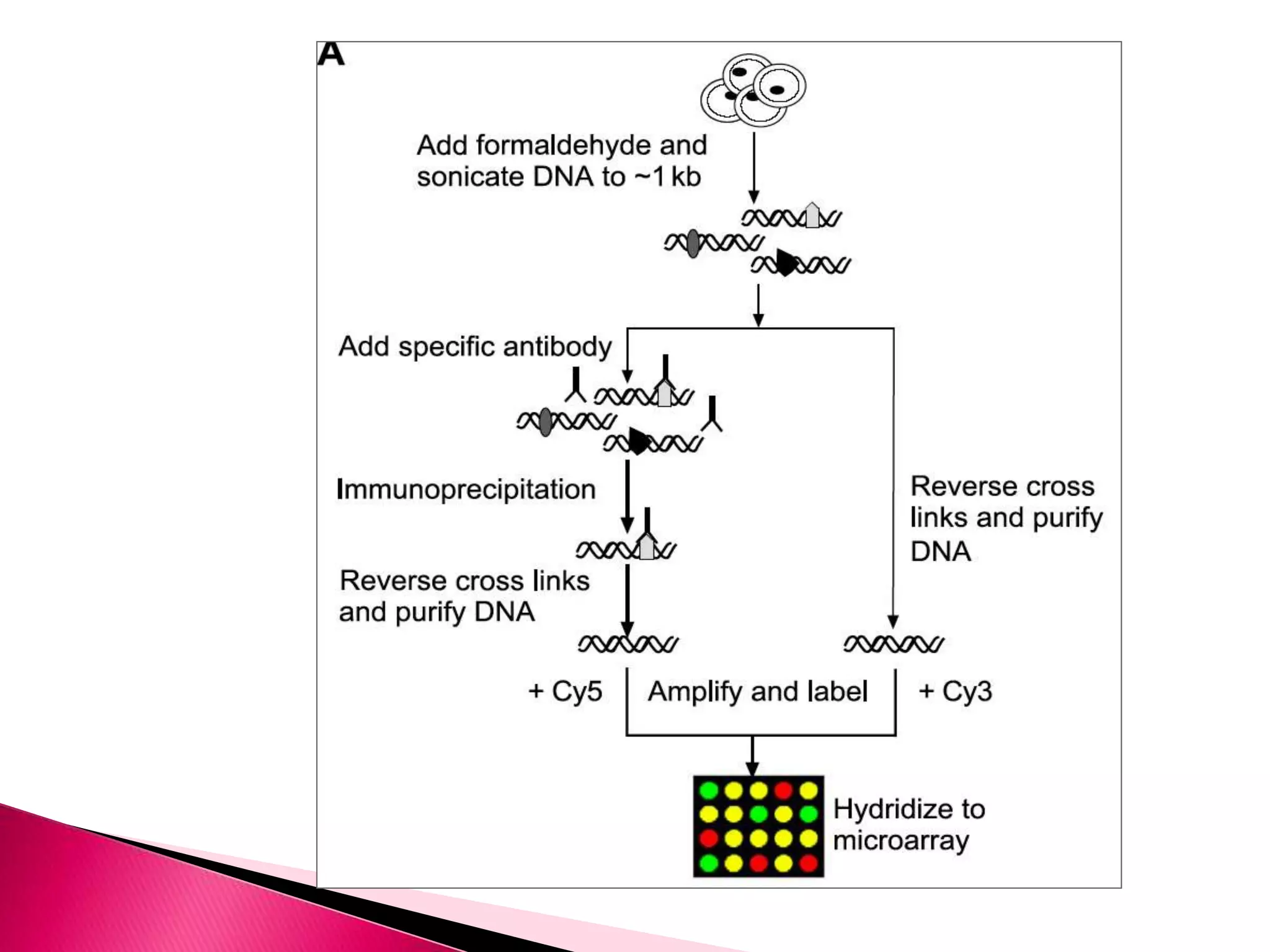
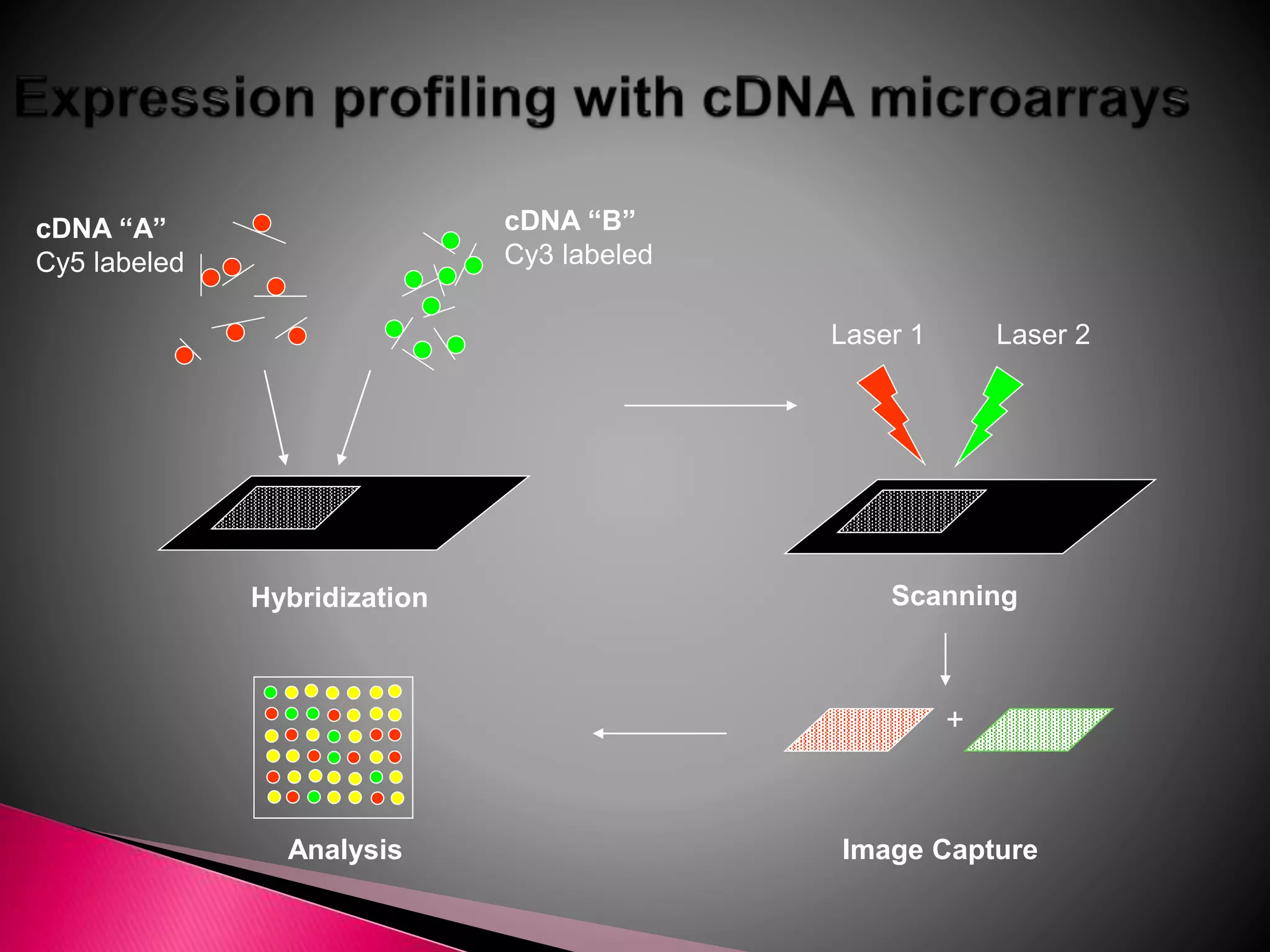
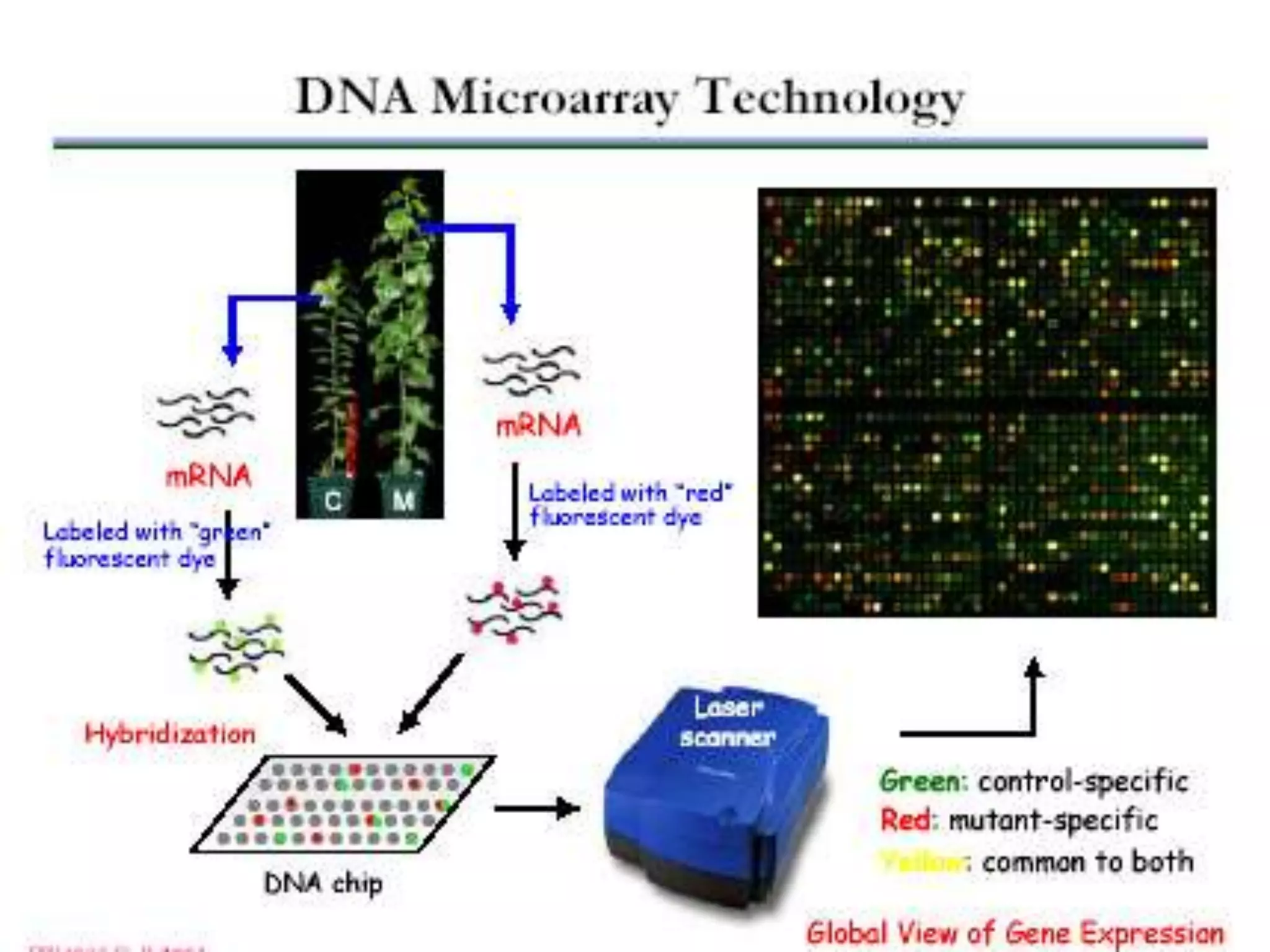
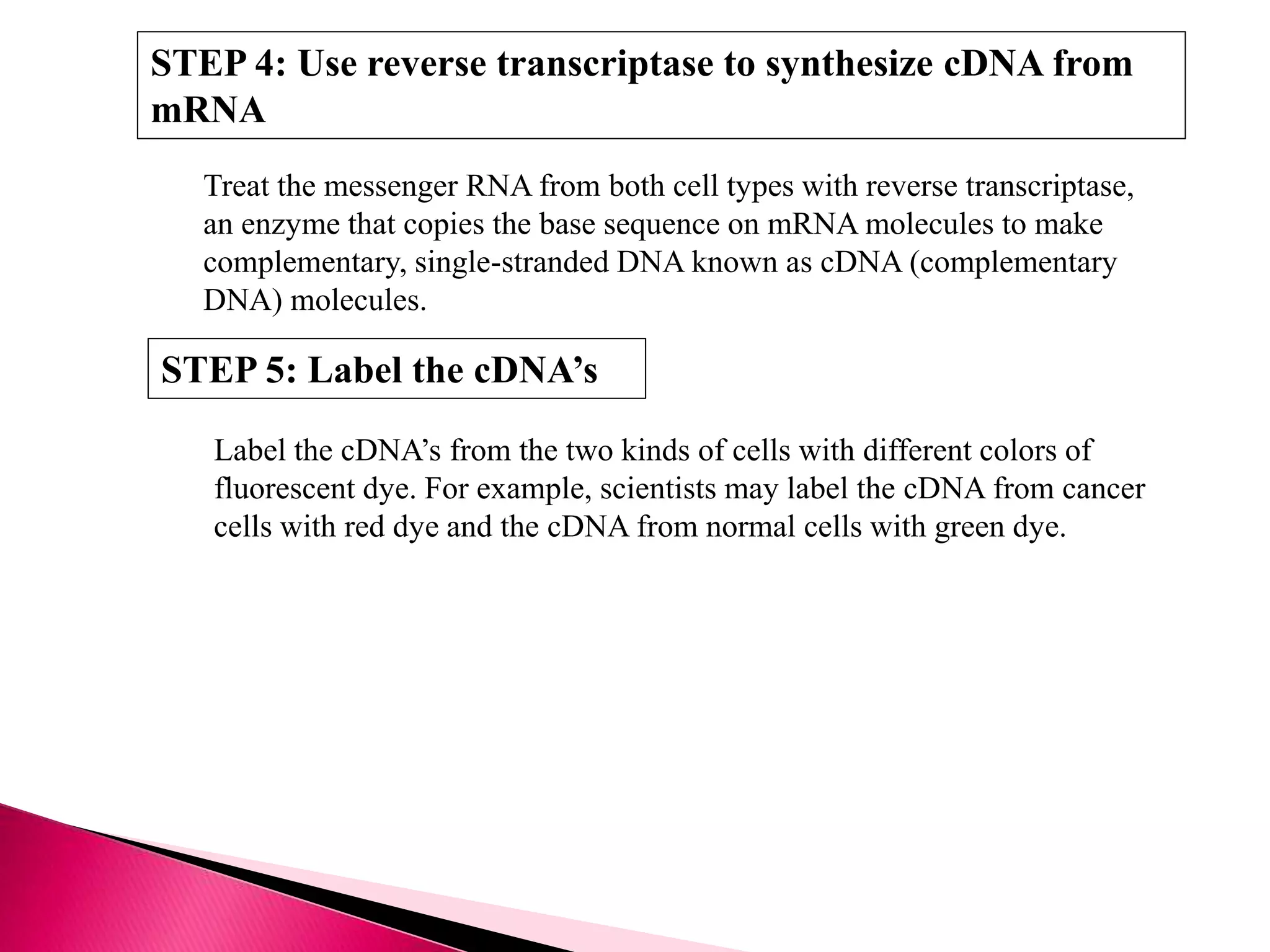
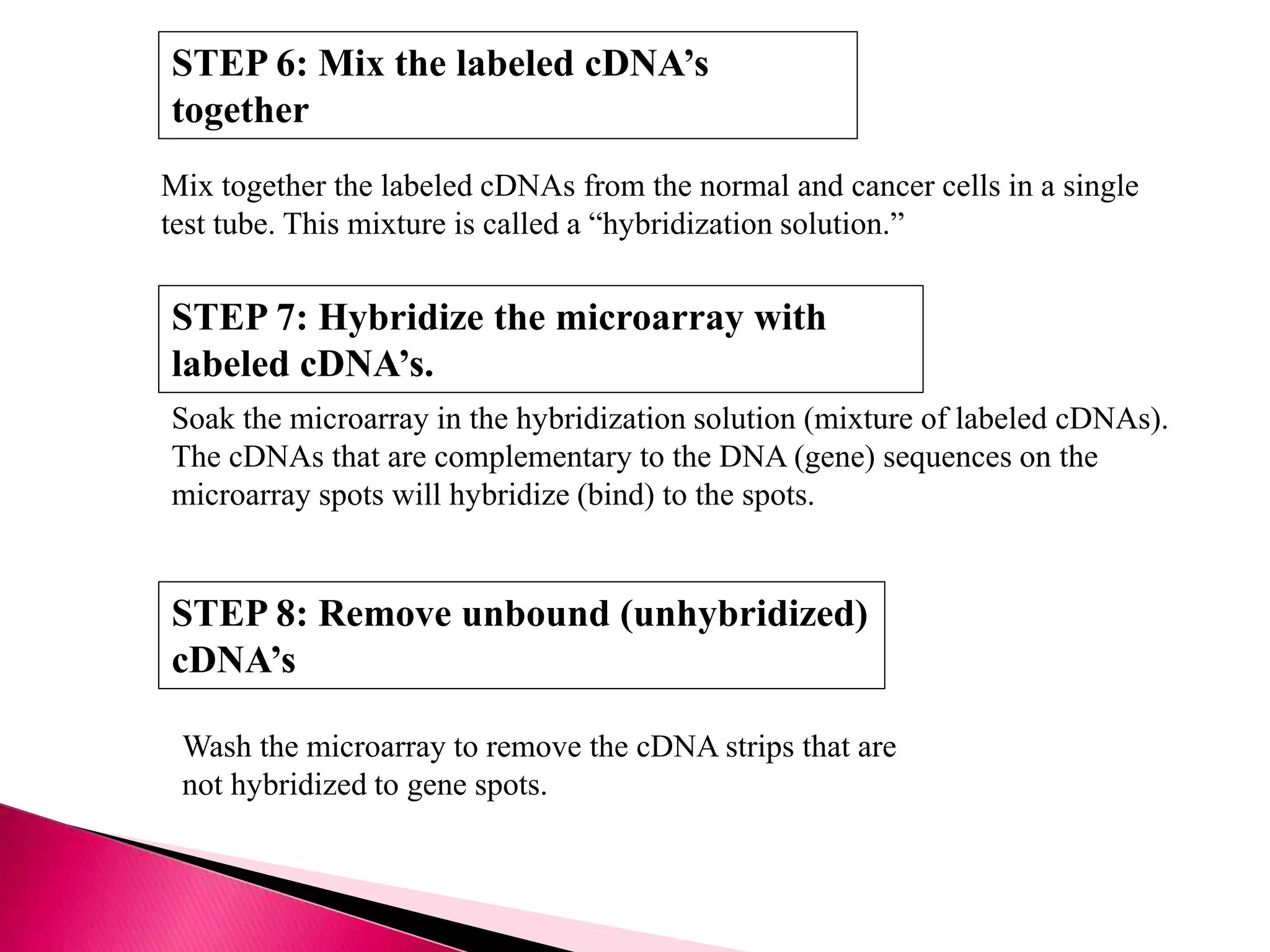
DNA microarrays contain multiple DNA sequences spotted on a small surface, allowing simultaneous monitoring of thousands of gene expressions. They are valuable tools in research requiring identification or quantitation of specific DNA sequences. In medicine, microarrays can determine gene transcriptional programs for cell functions, compare programs to aid disease diagnosis and classification, and identify new therapeutic targets. Cancer analysis through microarrays involves isolating mRNA from normal and cancerous cells, synthesizing cDNA, labeling with dyes, hybridizing to a microarray, and scanning to identify differently expressed genes involved in cancer.