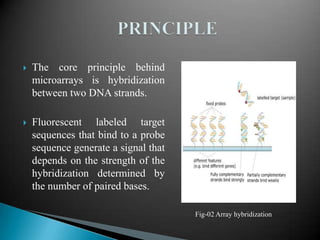
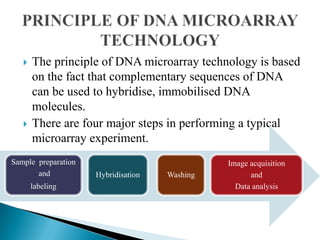
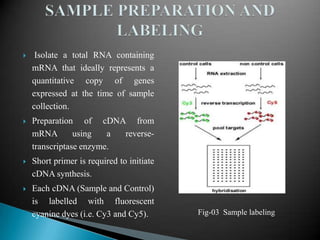
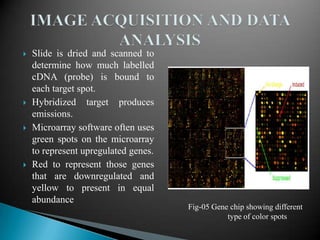
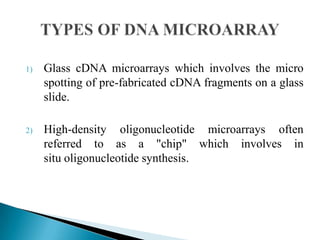
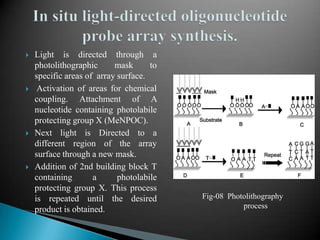
Microarray technology allows researchers to analyze the expression levels of thousands of genes simultaneously using DNA probes attached to a solid surface. There are two main types of microarrays: glass cDNA microarrays which involve spotting pre-fabricated cDNA fragments on glass slides; and high-density oligonucleotide arrays which involve the in situ synthesis of oligonucleotides on a chip. The key steps in a microarray experiment are sample preparation and labeling, hybridization of labeled cDNA to the probes, washing, and image analysis to quantify gene expression levels. Microarrays have numerous applications including gene expression profiling, comparative genomics, disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and toxicology research.