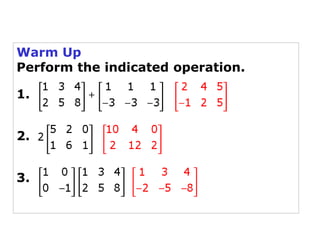
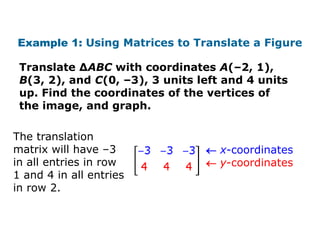
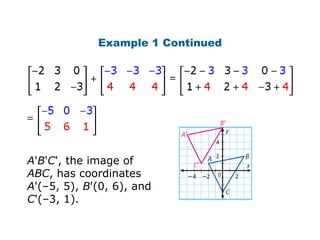
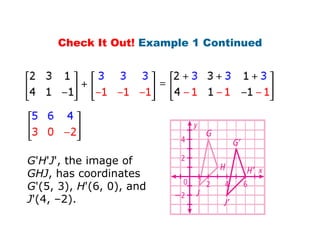
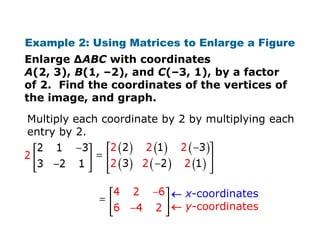
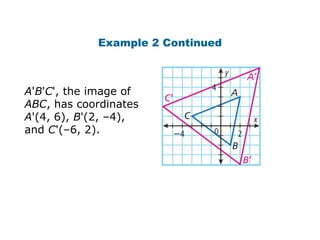
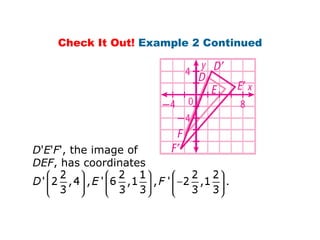
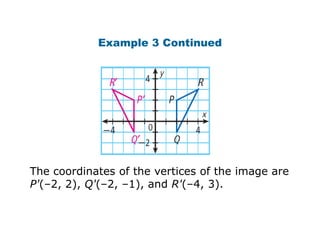
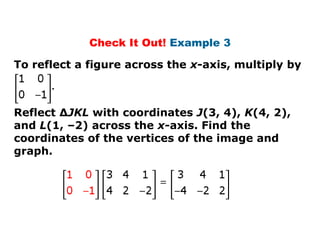
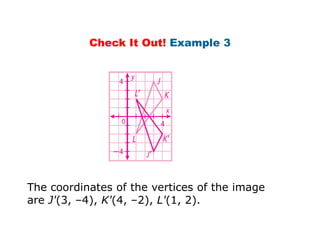
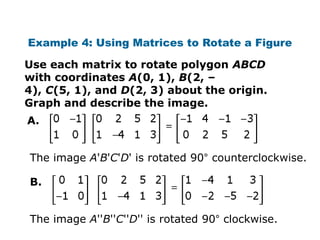
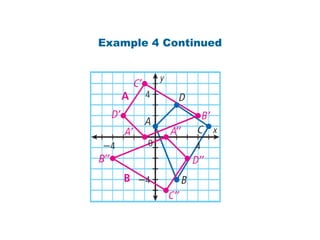
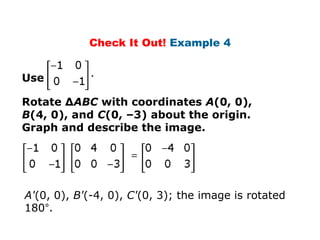
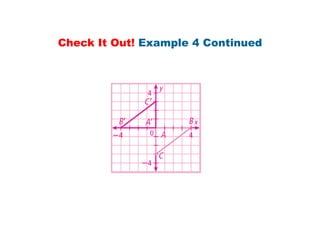
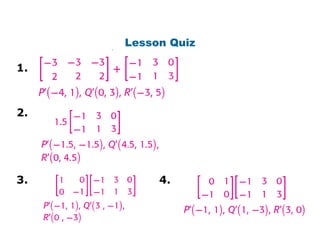
Using matrices to transform geometric figures, including translations, dilations, reflections, and rotations. Translations use a matrix with the distances of movement in each row. Dilations multiply coordinates by a scalar factor. Reflections across an axis involve changing the sign of coordinates on one side of the axis. Rotation matrices involve trigonometric functions to rotate the figure a specified number of degrees clockwise or counterclockwise. Examples show setting up and performing each type of transformation on sample polygons.