Embed presentation
Downloaded 100 times



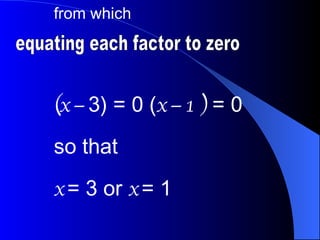



This document discusses four methods for solving quadratic equations: factorization, completing the square, using a formula, and using graphs. It provides an example of solving the equation 2x^2 - 10x + 12 + x^2 + 6x = -9 by factorizing into (x - 3)(x - 1) = 0, finding that the solutions are x = 3 or x = 1.





