1) 2-D geometric transformations allow manipulation of objects in 2-D space by changing their position, size, and orientation.
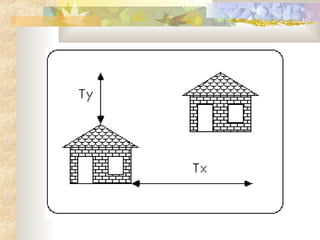
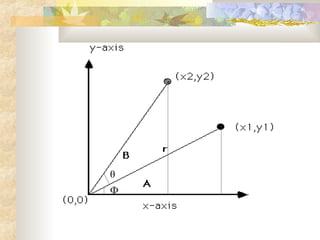
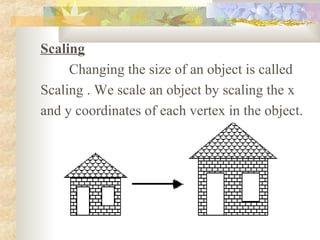
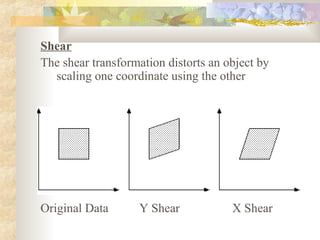
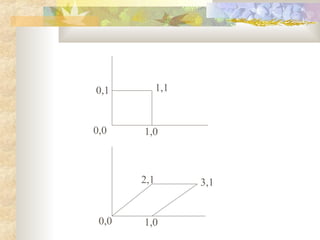
2) The basic geometric transformations are translation, rotation, scaling, reflection, and shear. Translation moves an object by shifting its coordinates. Rotation turns an object around a fixed point. Scaling enlarges or shrinks an object. Reflection produces a mirror image. Shear distorts an object.
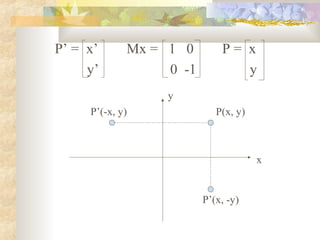
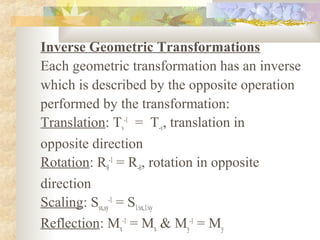
3) Each transformation can be described by a matrix equation. The inverse of a transformation performs the opposite operation to return the object to its original state.