This document defines key concepts in logic and propositions:
1) A proposition is a statement that is either true or false, such as "Dogs have six legs" or "2+3=5".
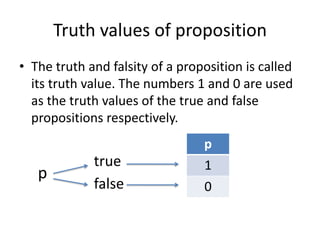
2) The truth value of a proposition is either 1 (true) or 0 (false).
3) Two propositions are equivalent if they have the same truth value. The negation of a proposition, denoted by p', is its opposite truth value.
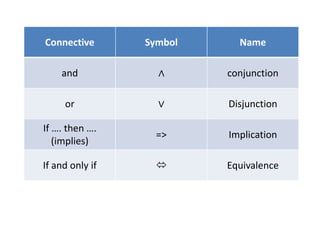
4) A compound proposition combines two or more simple propositions using logical connectives like "and", "or", or "if/then".