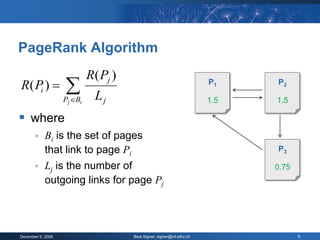
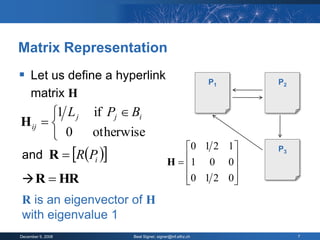
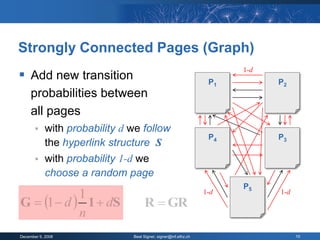
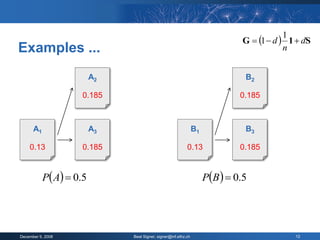
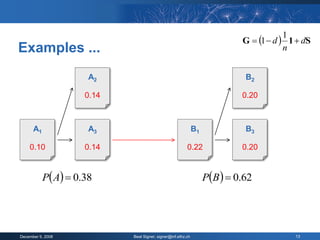
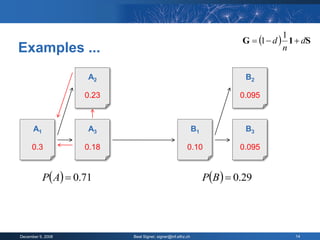
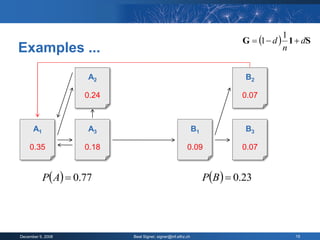
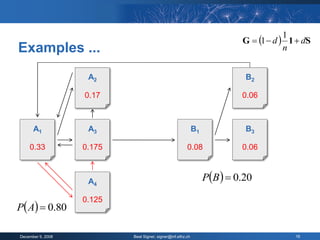
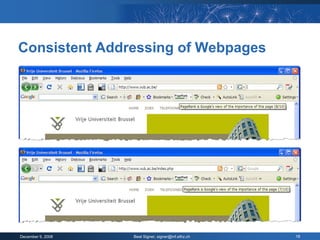
The document provides an overview of the PageRank algorithm, developed by Larry Page and Sergey Brin at Stanford University as part of a search engine project. It explains the mechanics of calculating PageRank, including how it factors in the quantity and quality of linking pages, as well as its implications for website development and SEO practices. The document also highlights the various factors that influence a page's ranking, both positive and negative, and discusses tool options for tracking PageRank and optimizing web content.