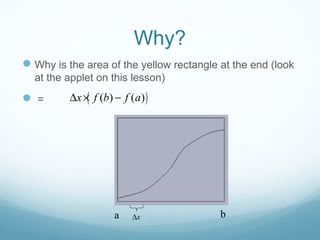
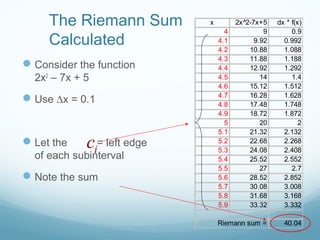
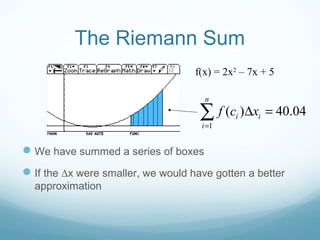
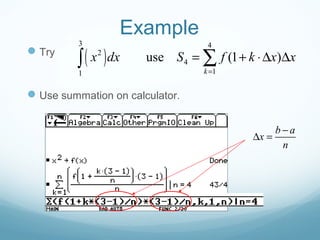
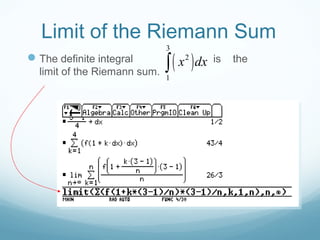
This document discusses Riemann sums and the definite integral. It explains that the definite integral is defined as the limit of Riemann sums as the size of the subintervals approaches zero. It provides examples of calculating Riemann sums and shows how the definite integral can be approximated by Riemann sums. The document also outlines some key properties of the definite integral, such as how to integrate sums and how the integral relates to calculating the area under a curve.



![Riemann Sum
1. Partition the interval [a,b] into n subintervals
a = x0 < x1 … < xn-1< xn = b
1. Call this partition P
2. The kth
subinterval is ∆xk = xk-1 – xk
3. Largest ∆xk is called the norm, called ||P||
— Choose an arbitrary value from each
subinterval, call it
ic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/riemannsumsdefiniteintegrals-160418033021/85/Riemann-sumsdefiniteintegrals-5-320.jpg)

![The Definite Integral
The definite integral is the limit of the Riemann sum
We say that f is integrable when
the number I can be approximated as accurate as needed by
making ||P|| sufficiently small
f must exist on [a,b] and the Riemann sum must exist
( )0
1
lim( )
b
a P
n
i i
k
f f c xI x dx
→
=
= ∆= ∫ ∑](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/riemannsumsdefiniteintegrals-160418033021/85/Riemann-sumsdefiniteintegrals-9-320.jpg)
![If f is defined on the closed interval [a, b] and the limit of
a Riemann sum of f exists, then we say f is integrable on [a, b]
and we denote the limit by
∫∑ =∆
=
→∆
b
a
n
i
ii
x
dxxfxcf )()(lim
1
0
The limit is called the definite integral of f from a to b. The
number a is the lower limit of integration, and the number b
is the upper limit of integration.
Definition of the Definite
Integral](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/riemannsumsdefiniteintegrals-160418033021/85/Riemann-sumsdefiniteintegrals-10-320.jpg)

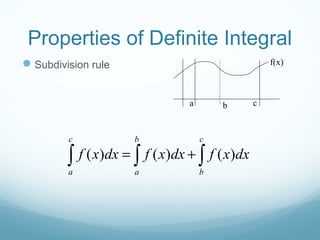
![Properties of Definite Integral
Integral of a sum = sum of integrals
Factor out a constant
Dominance
( ) ( ) [ , ]
( ) ( )
b b
a a
f x g x on a b
f x dx g x dx
≤
≤∫ ∫](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/riemannsumsdefiniteintegrals-160418033021/85/Riemann-sumsdefiniteintegrals-14-320.jpg)
![Area As An Integral
The area under
the curve on the
interval [a,b]
a c
f(x)
( )
b
a
A f x dx= ∫
A](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/riemannsumsdefiniteintegrals-160418033021/85/Riemann-sumsdefiniteintegrals-16-320.jpg)