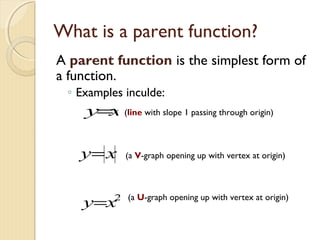
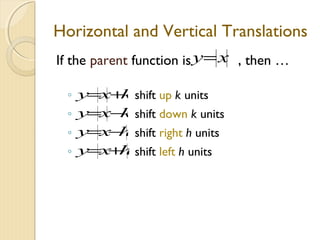
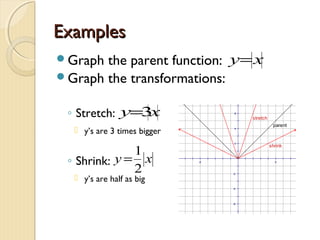
This document discusses transformations of parent functions. It defines a parent function as the simplest form of a function, such as y=x, y=x^2, etc. Transformations include horizontal and vertical shifts which move the graph left, right, up or down; stretches which multiply the y-values making the graph skinnier; shrinks which reduce the y-values making the graph fatter; and reflections which flip the graph over the x-axis. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to graph different transformations of common parent functions. The document concludes by describing the transformation y=4x-2-5 as a shrink by a factor of 4, a right shift of 2 units, and a down shift of 5