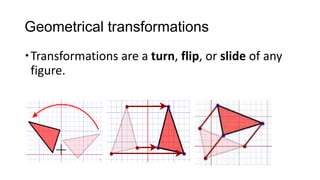
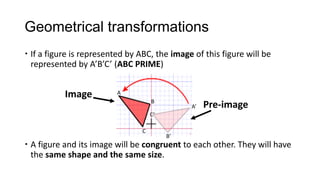
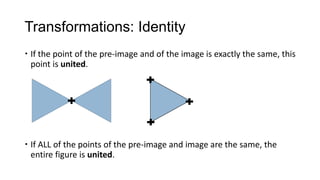
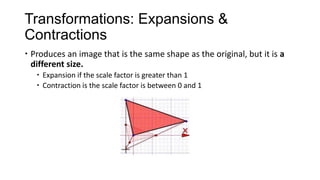
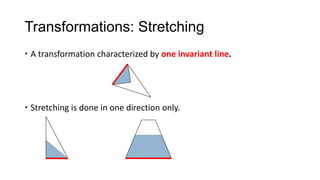
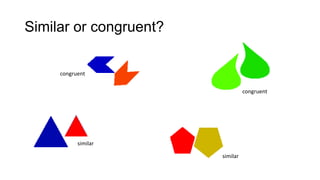
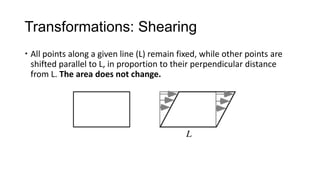
1) Geometrical transformations include turns, flips, or slides of figures that result in a congruent image.
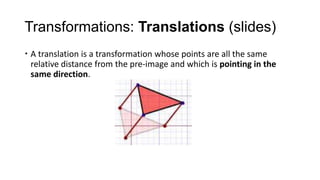
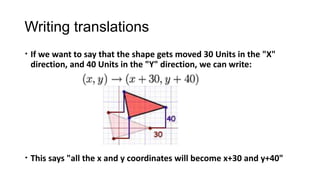
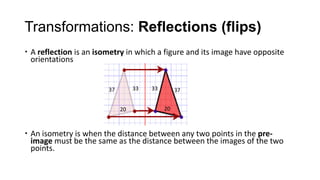
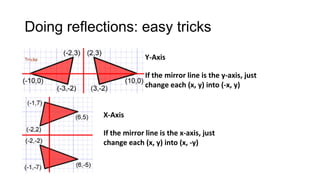
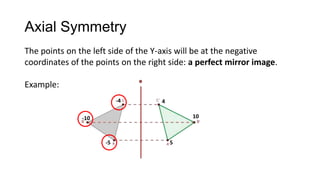
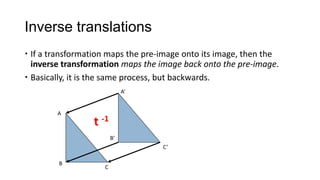
2) Translations (slides) move every point of a figure by the same displacement vector, resulting in a figure pointing in the same direction. Reflections (flips) produce an image with the opposite orientation across a mirror line.
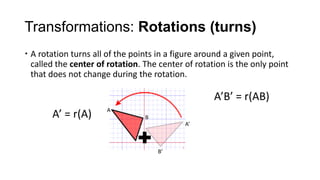
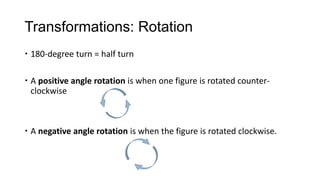
3) Rotations turn all points of a figure around a central point, with the center of rotation unchanged. A 180-degree rotation is a half turn.