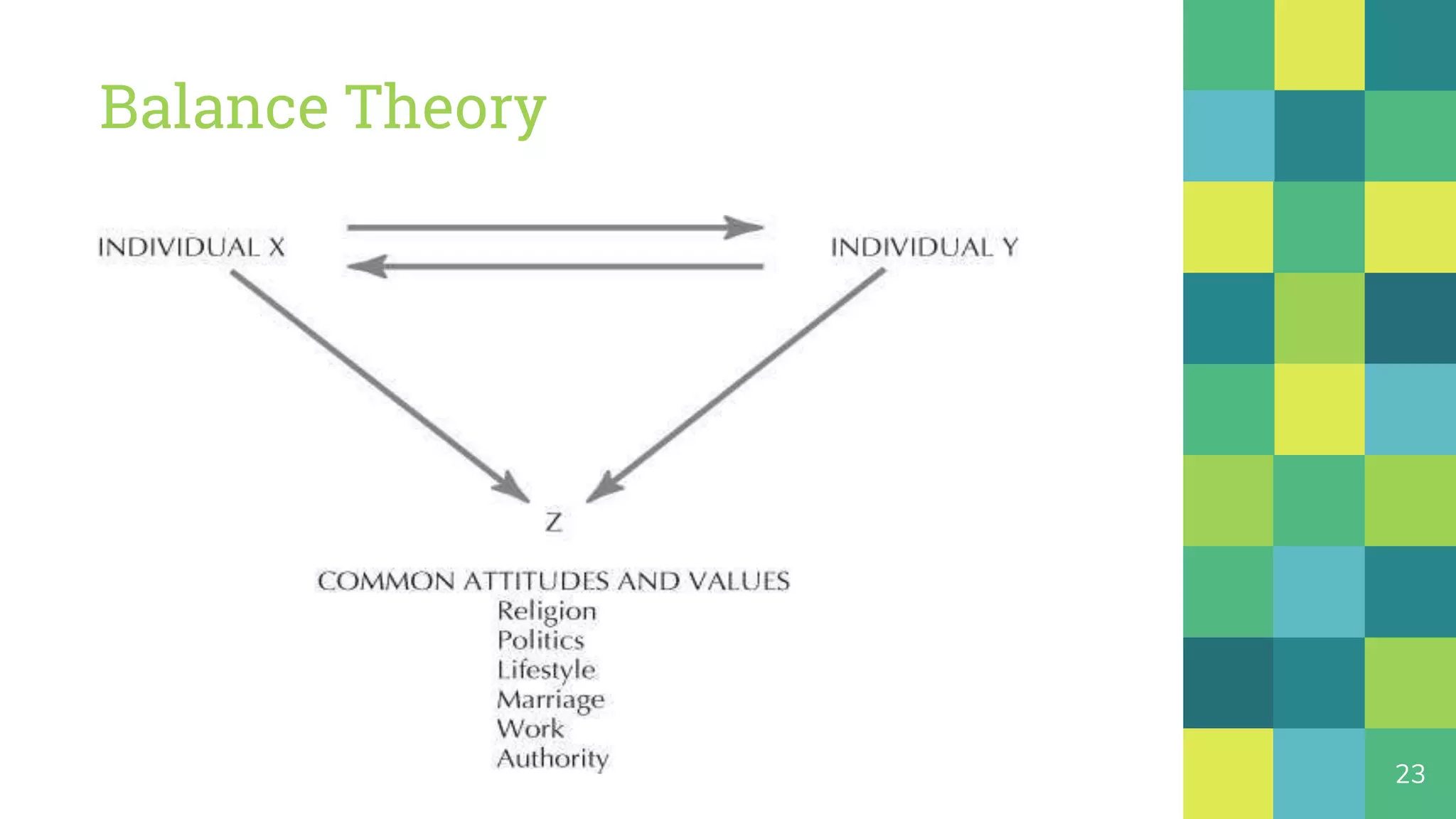
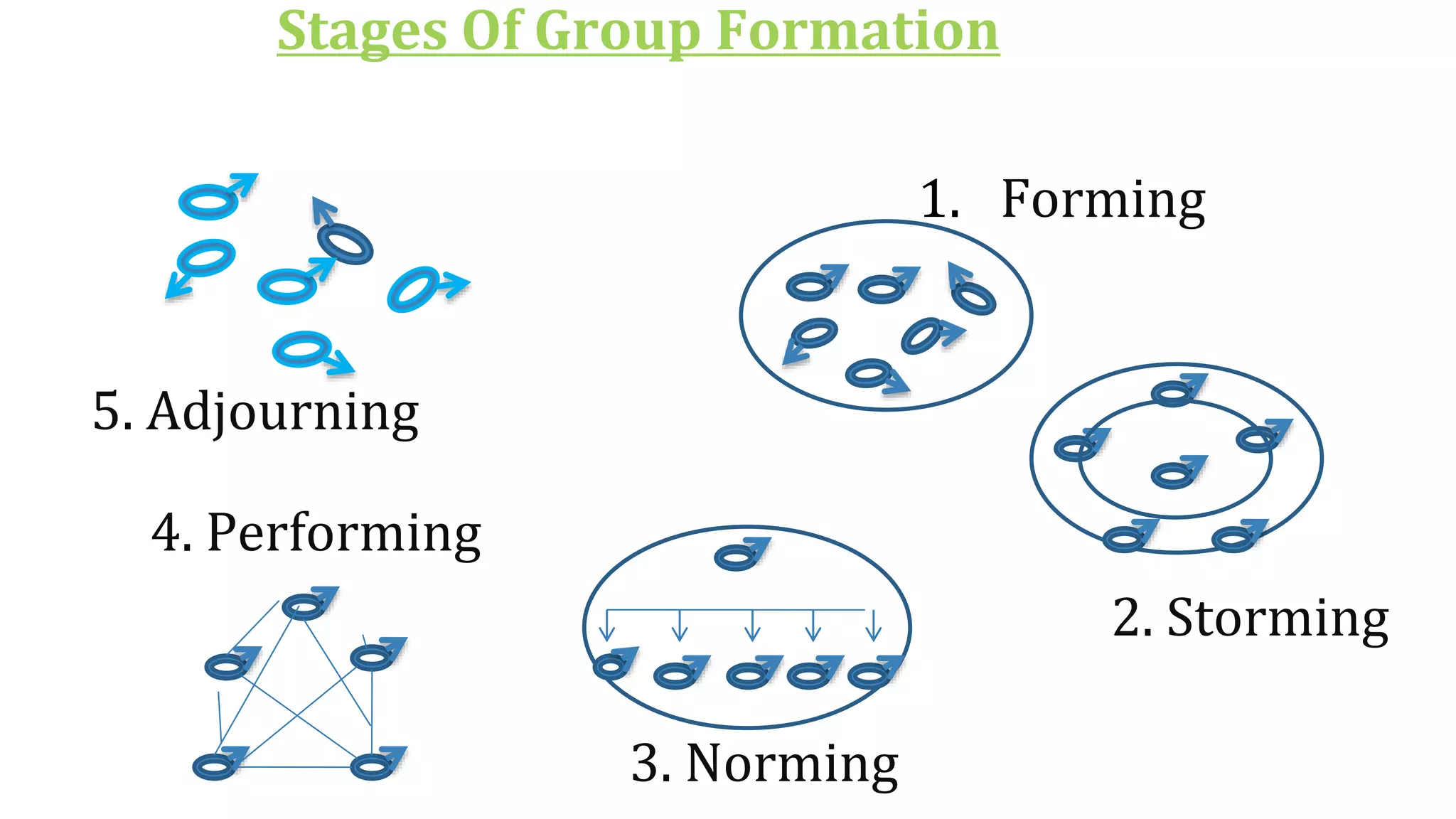
This document provides an overview of teams and groups. It discusses key topics like group dynamics, team vs group, team composition, managing team performance, importance of groups, stages of group formation, and group structure. The stages of group formation discussed are forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. Group structure is defined as including roles, norms, status, and cohesiveness. People join groups for reasons like security, status, self-esteem, power, and goal achievement.