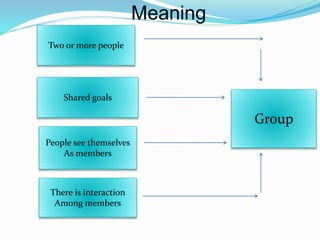
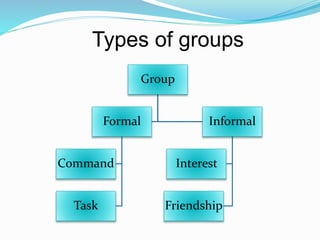
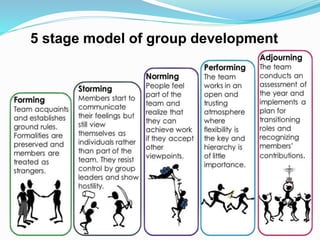
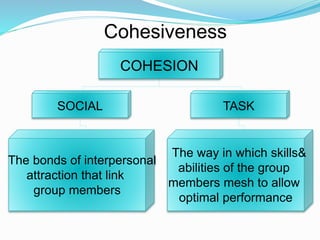
Groups form when two or more people come together around shared goals. Groups can be either formal, with established rules and hierarchies, or informal, consisting of personal relationships. People join groups for reasons like security, affiliation, power to achieve goals, self-esteem, and status. Effective groups develop norms, roles, cohesion, and ways to make decisions together. Studying group behavior provides insights into how relationships form and how to organize, lead, and develop groups.