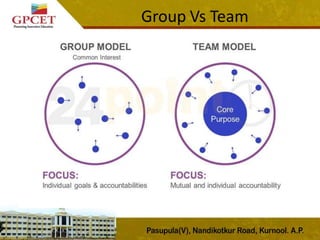
1) The document discusses group behavior and defines a group as two or more interacting and interdependent individuals who come together to achieve particular objectives.
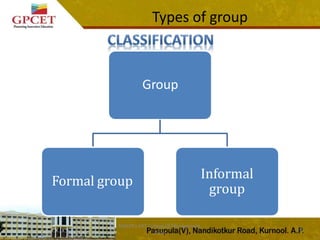
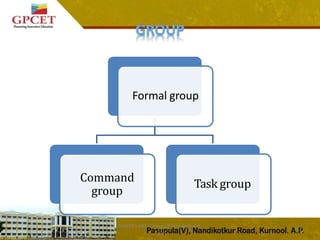
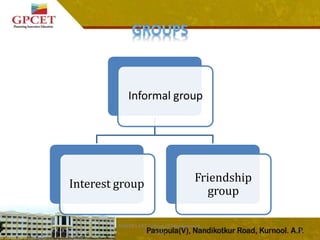
2) It describes the different types of groups including formal groups like command groups and task groups, and informal groups like interest groups and friendship groups.
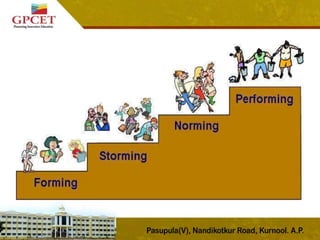
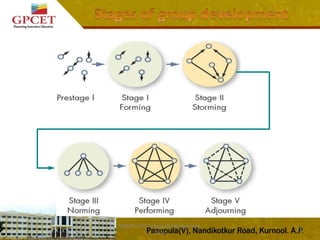
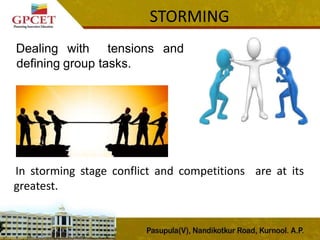
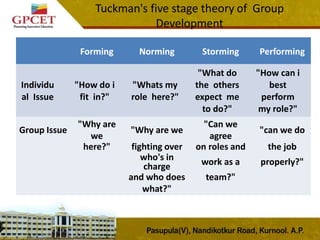
3) Tuckman's stages of group development are explained, including forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning stages. The document provides details on the characteristics and outcomes of each stage.