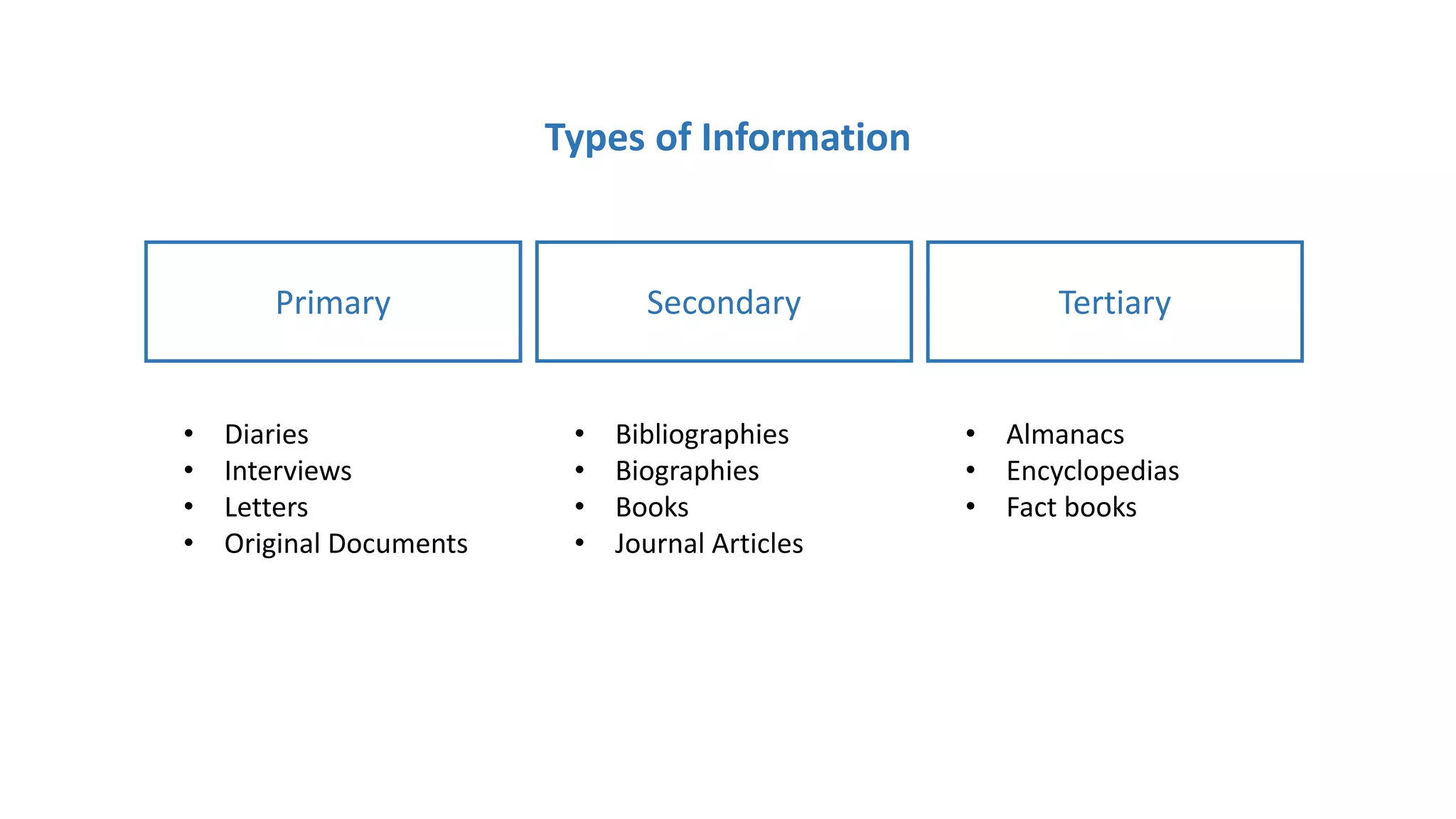
The document outlines the concept of information, its generation processes, and its role in decision-making. It discusses various types and forms of information, emphasizing the importance of distinguishing between primary, secondary, and tertiary information. Additionally, it details the steps in the information generation and communication process, including data origination, input, processing, storing, and retrieval.