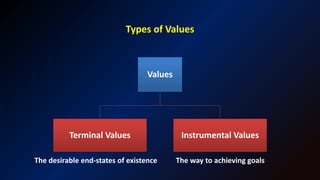
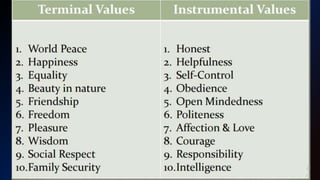
This document discusses ethics, values, morals, and the sources of values. It defines ethics as a set of rules that determine right and wrong conduct based on principles such as fairness and justice. Morals are beliefs determined by society and culture regarding right and wrong. Values are things that are important to individuals, like truth, wisdom, and love. There are terminal values, which are desirable life goals, and instrumental values, which are means of achieving goals. Sources of values include family, teachers, peers, culture and tradition. The document also discusses ethical dilemmas, which require choosing between two morally correct but conflicting options.