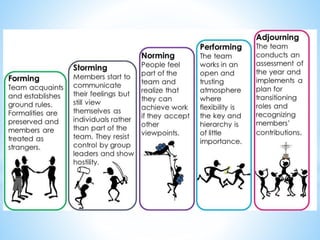
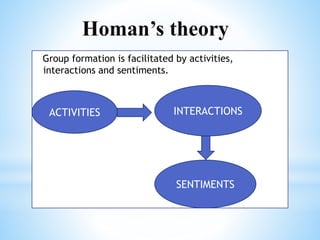
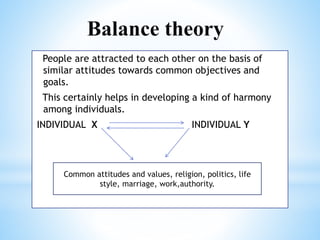
The document discusses the meaning and features of groups and teams, emphasizing their formation, differences, and development stages. It outlines various types of groups such as formal, informal, command groups, and committees, along with theories of group formation like propinquity and exchange theory. The text also highlights what makes a team effective, including clear objectives, roles, communication, leadership, and mutual cooperation.