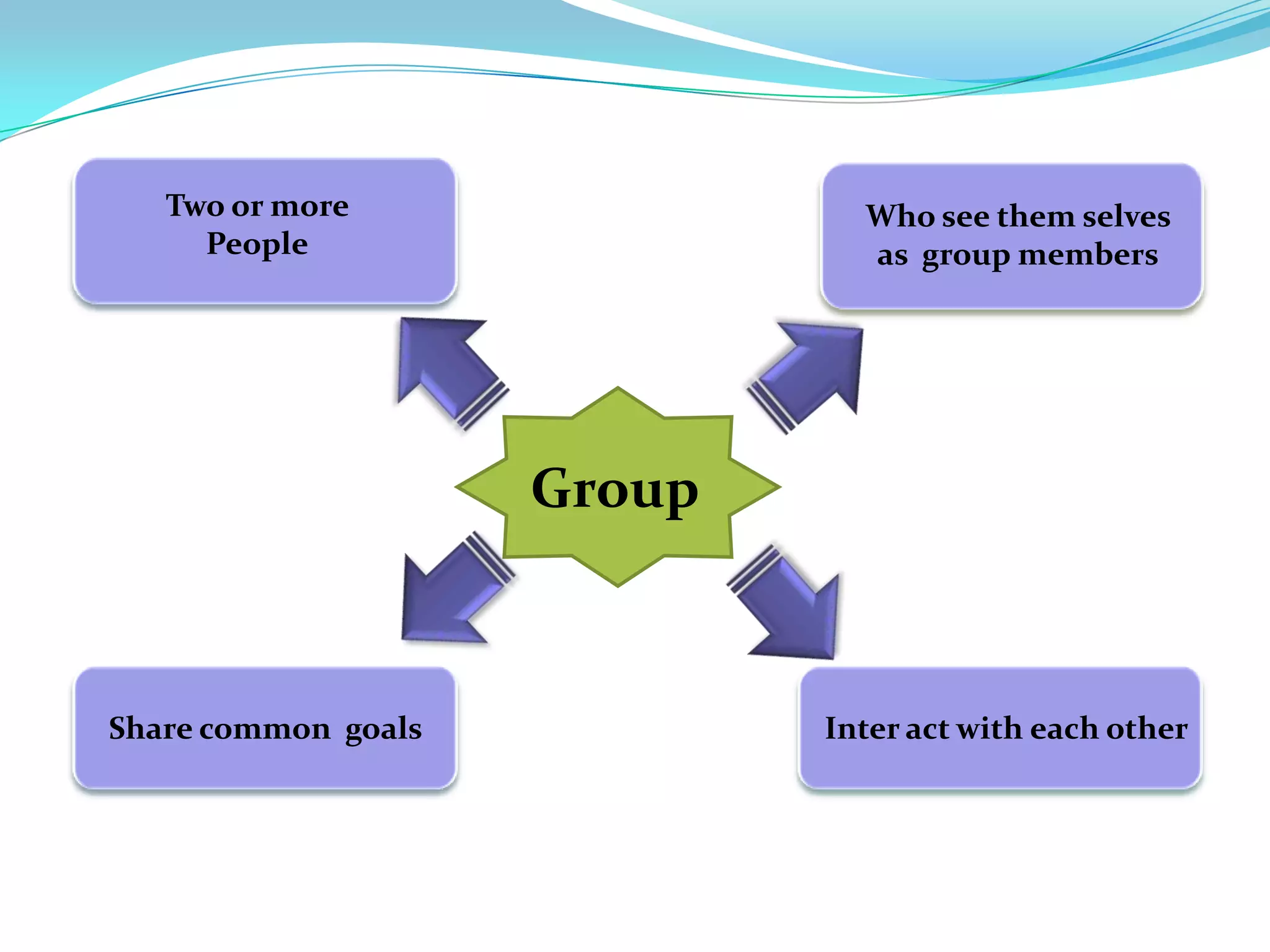
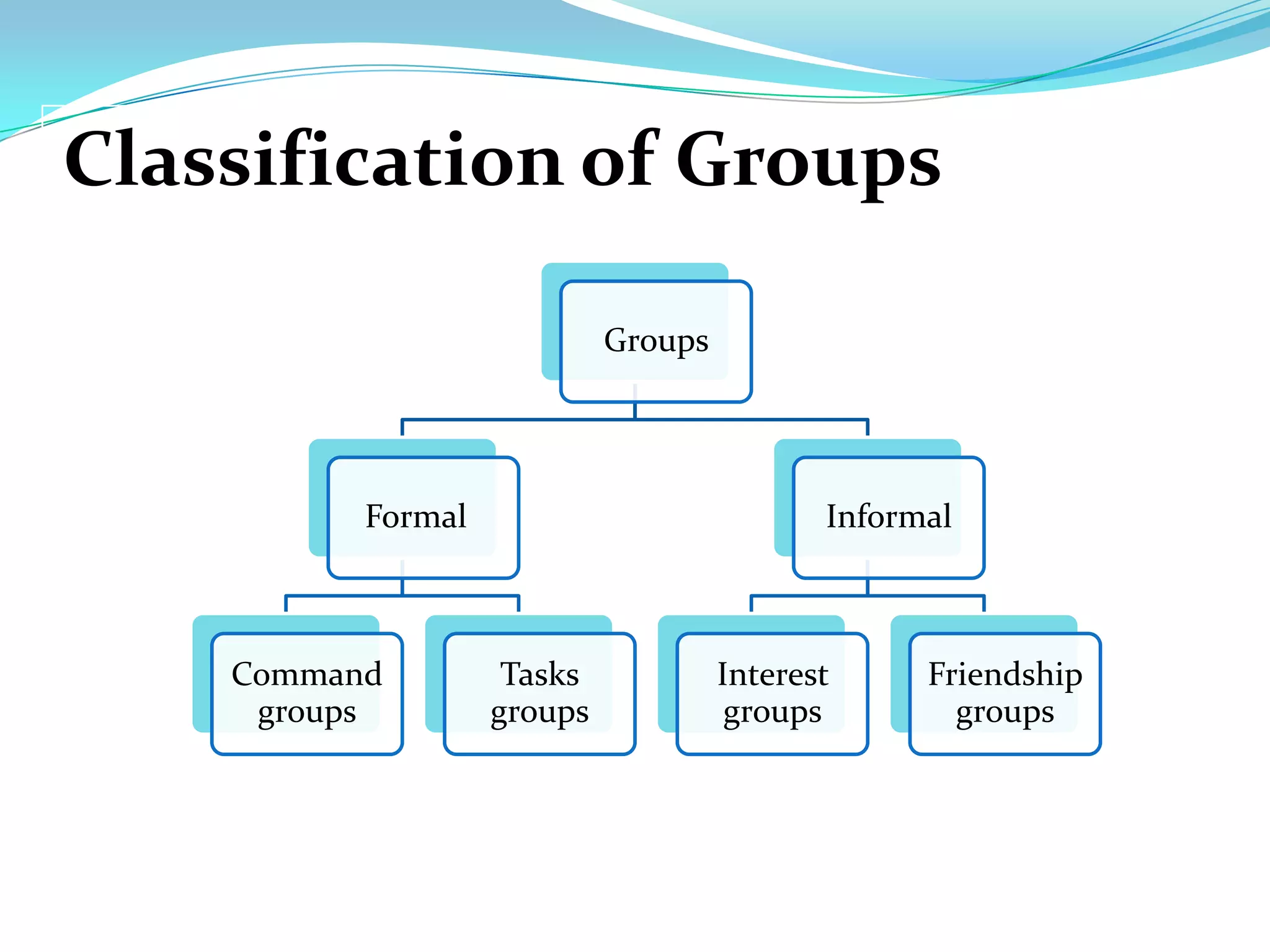
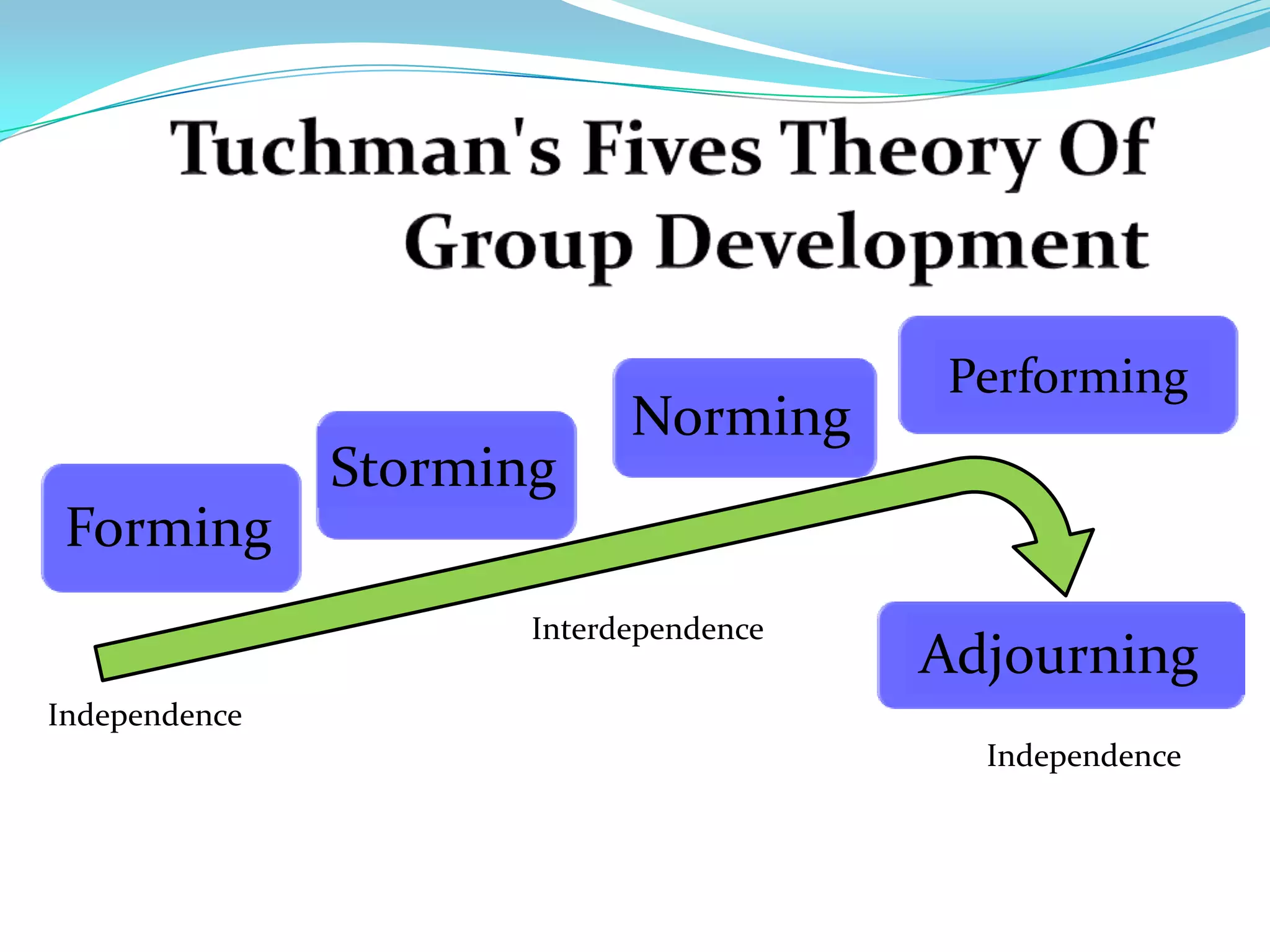
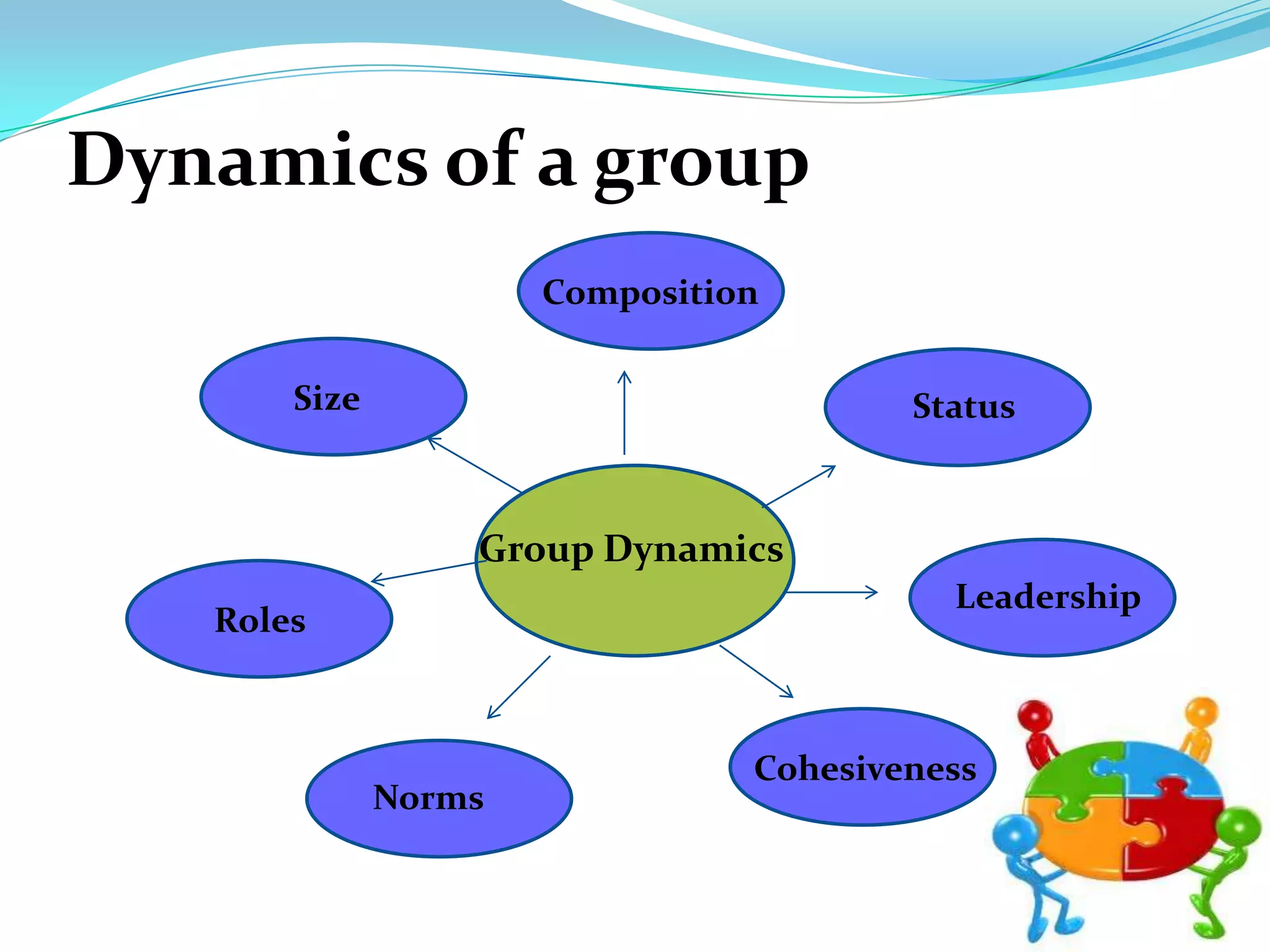
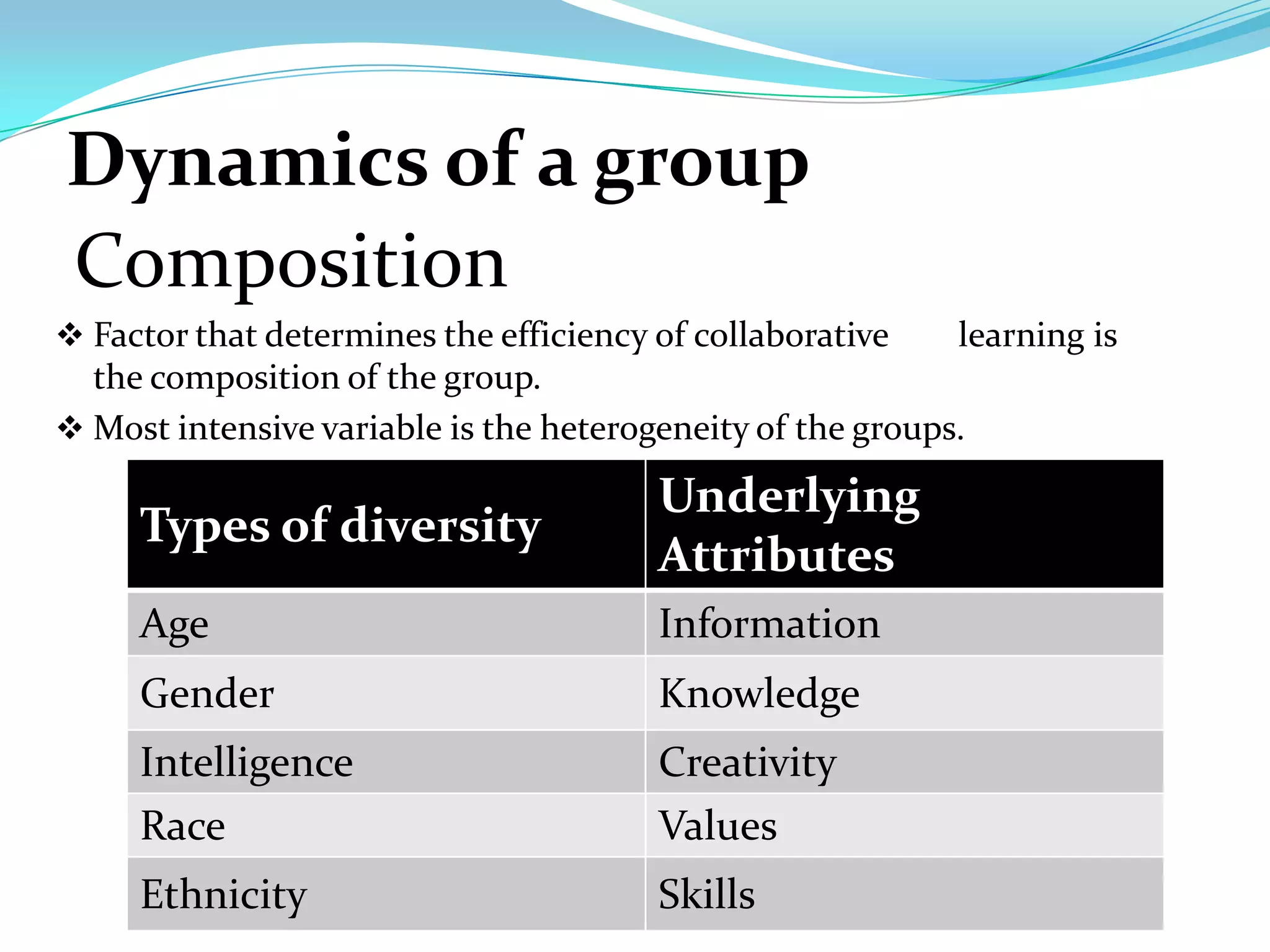
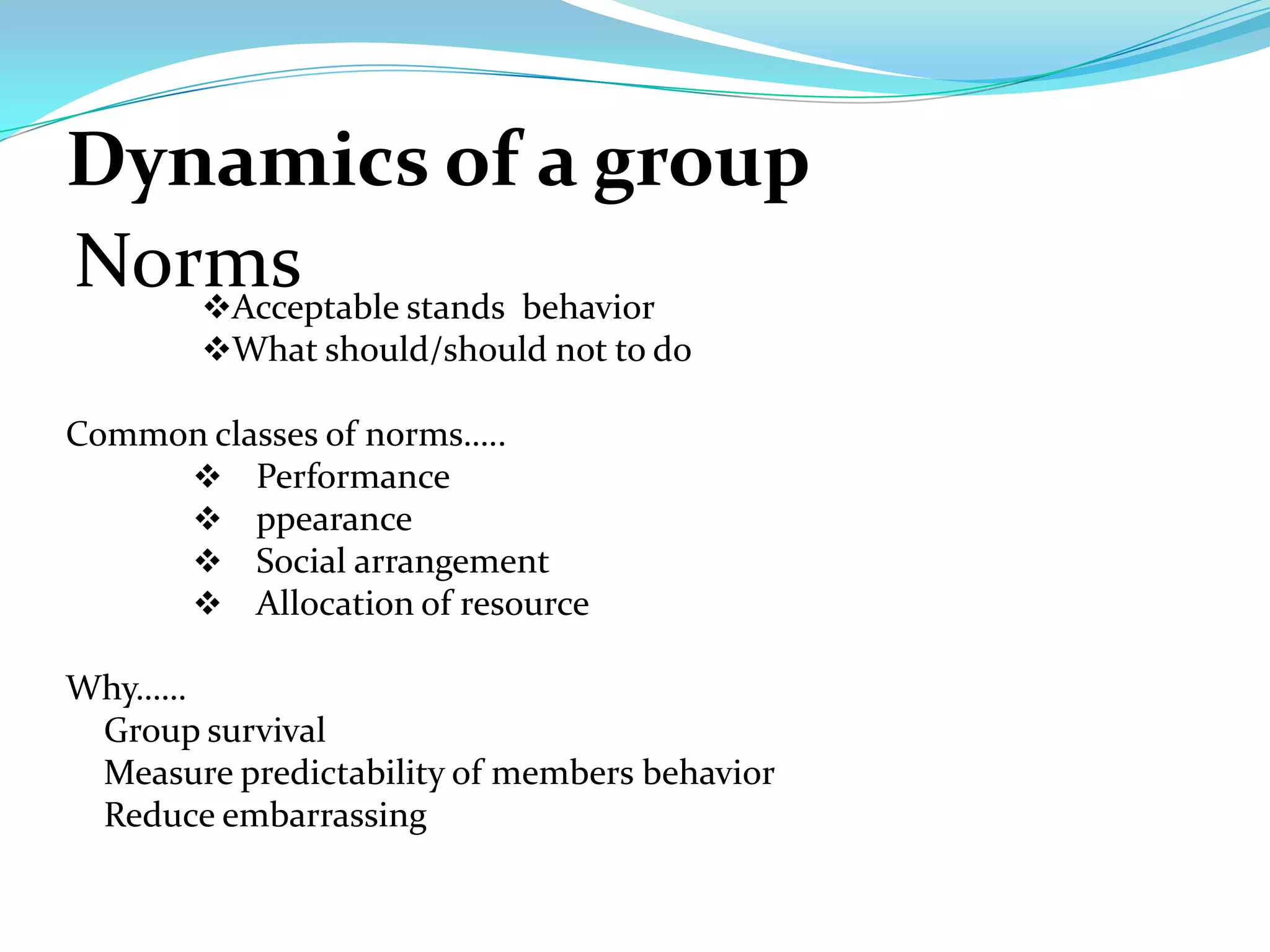
Group dynamics and behavior play an important role in organizations. A group is defined as two or more people who share a common identity and behave accordingly. There are formal groups structured by the organization and informal groups formed by employee interests and friendships. Groups go through stages of forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. Key group dynamics include composition, size, roles, norms, leadership, and cohesiveness. Both internal group factors and external organizational conditions influence group behavior. Effective group decision making can generate more complete information but can also be time consuming and increase pressure to conform.