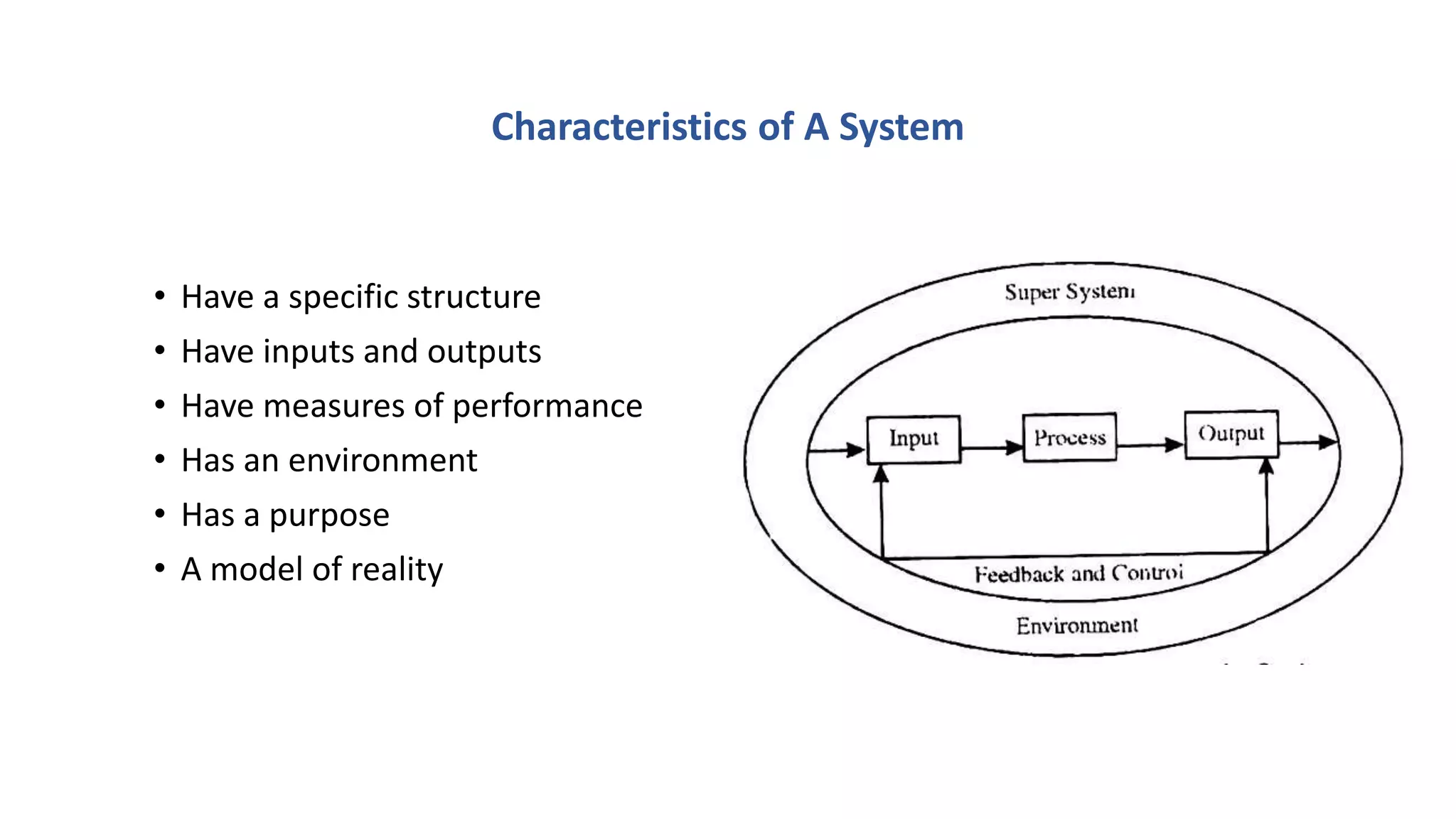
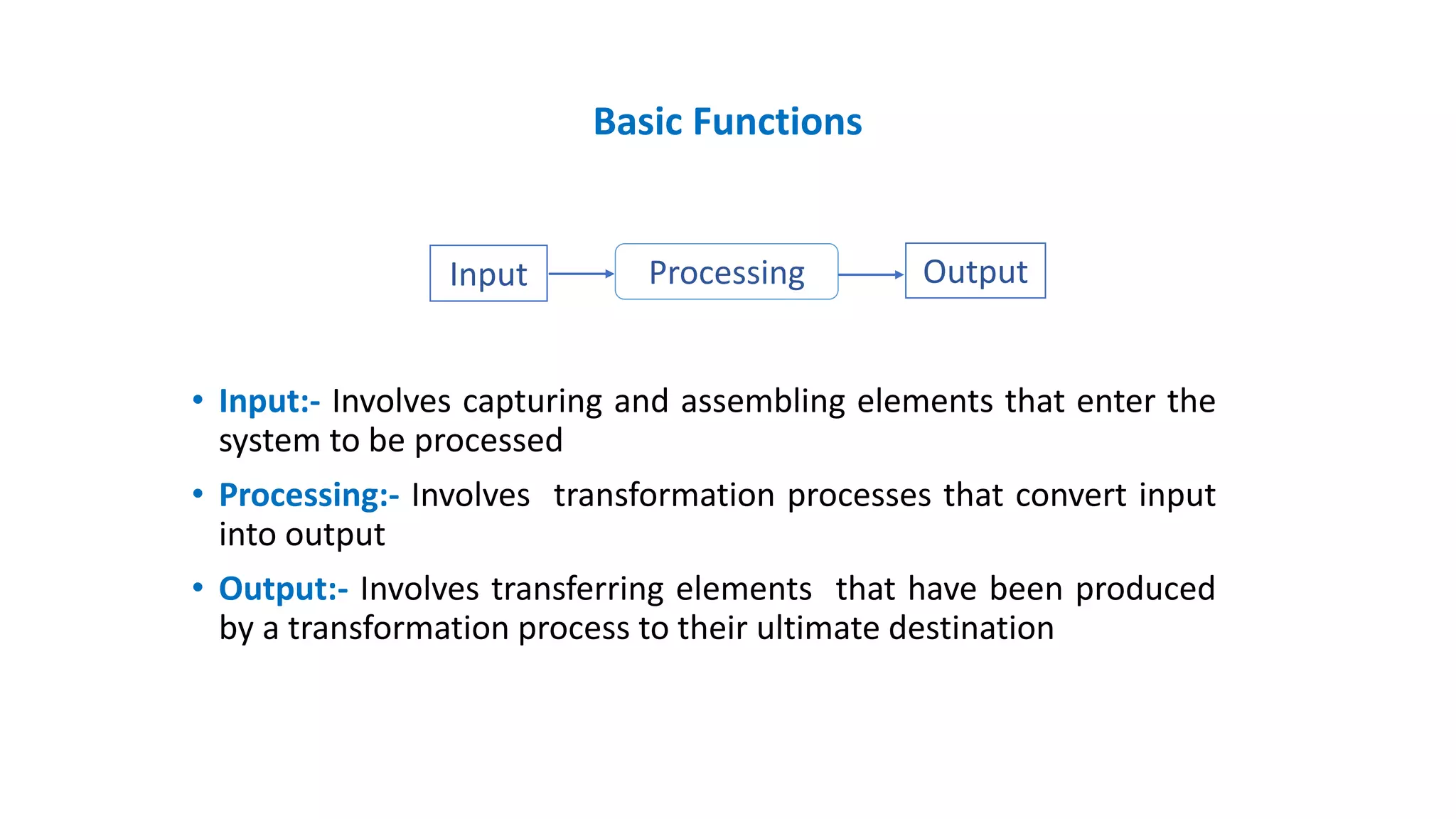
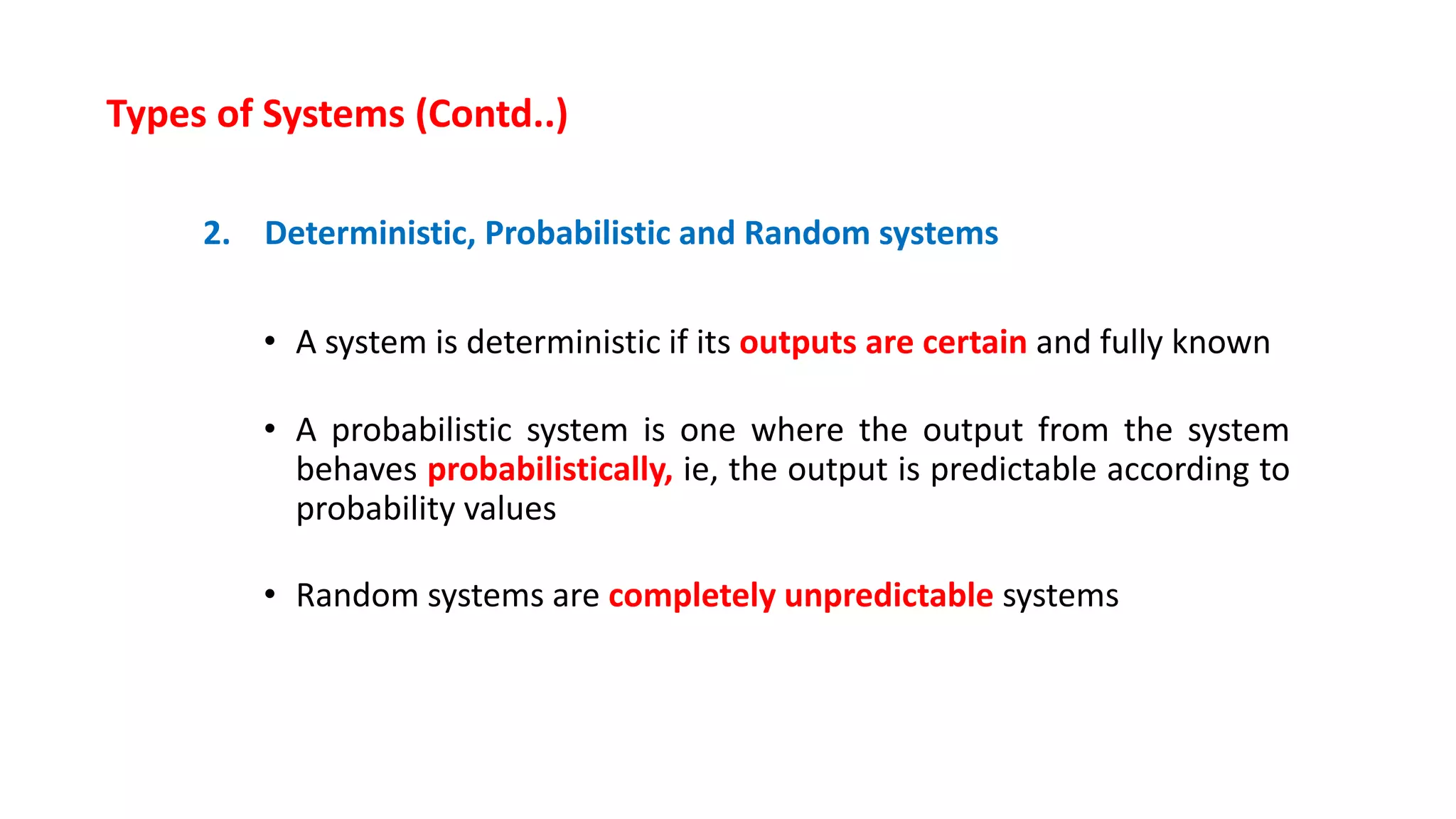
This document discusses systems concepts in management information systems. It defines a system as an orderly grouping of interdependent components working together according to a plan to achieve a specific objective. A system has inputs, processes, outputs, and feedback/control mechanisms. It also has boundaries and interacts with its environment. The document describes different types of systems including closed/open, deterministic/probabilistic, human/machine, adaptive/non-adaptive, simple/complex, and abstract/concrete systems. It provides examples of systems like an educational institution and a manufacturing plant.