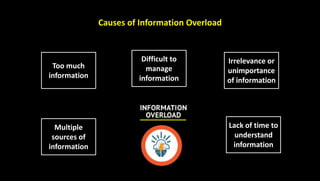
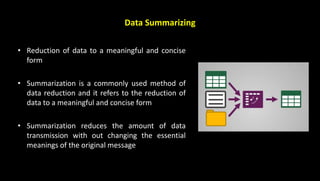
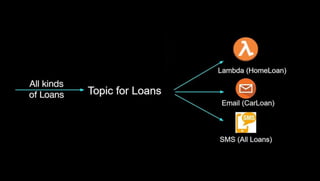
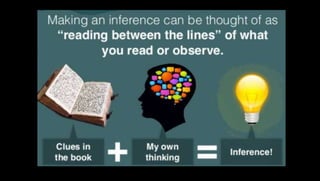
This document discusses information overload and techniques for managing it. It defines information overload as having too much information that makes understanding issues and decision-making difficult. Common causes include an increasing rate of new information and multiple sources. The document recommends summarizing, filtering, and routing only relevant messages to reduce overload. It also provides specific techniques for each, such as reducing data to concise, meaningful summaries and drawing inferences from large datasets.