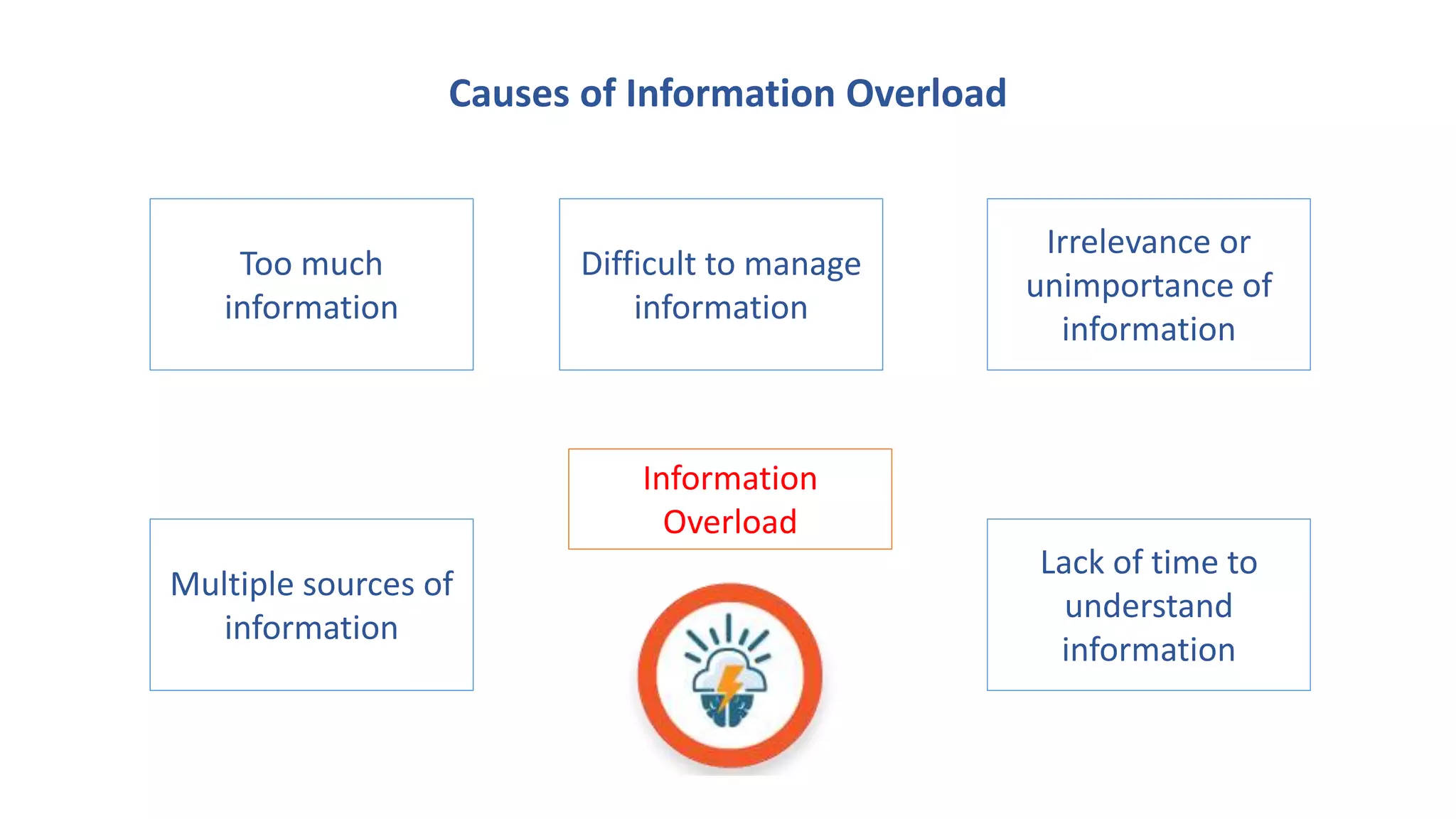
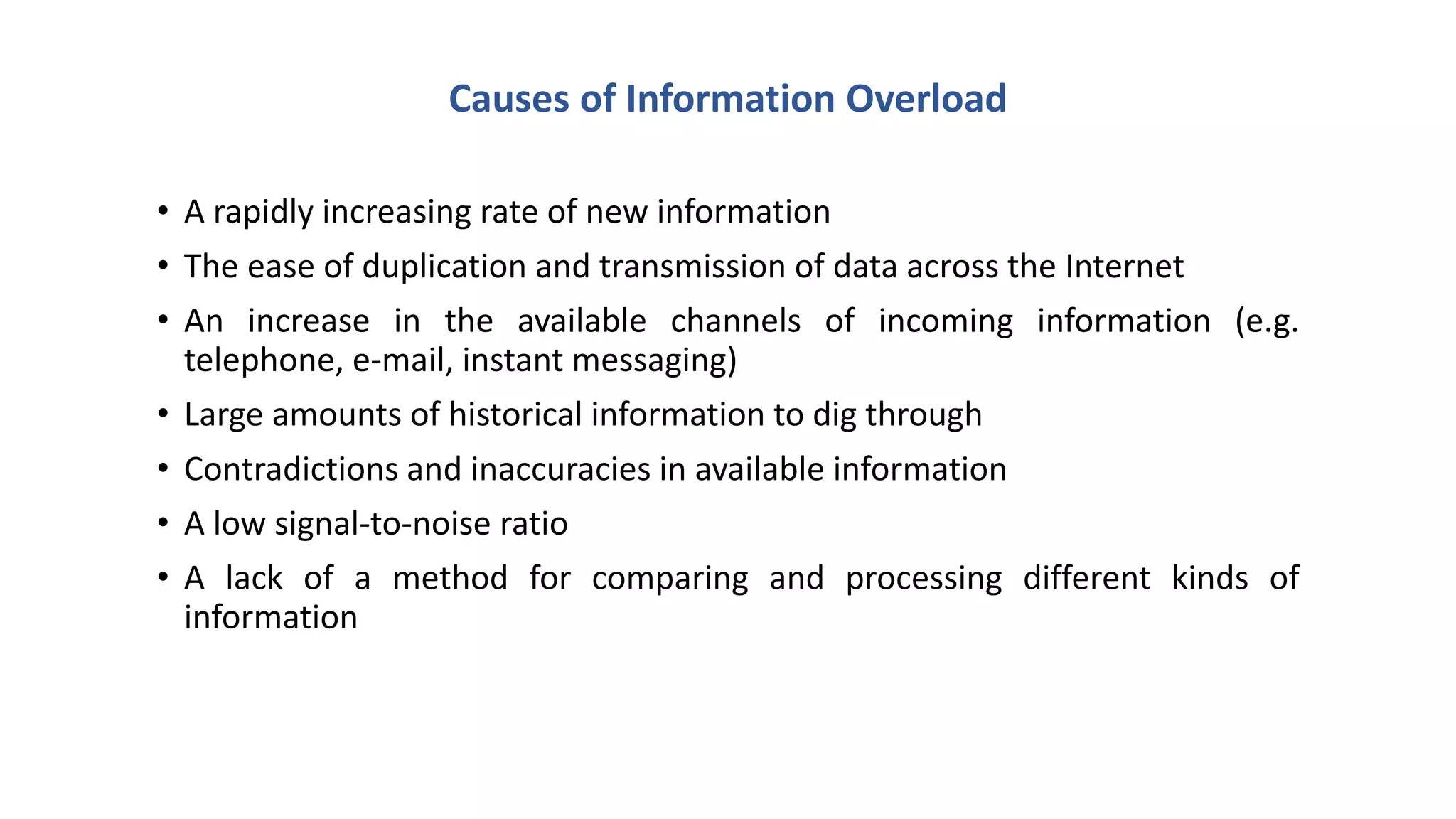
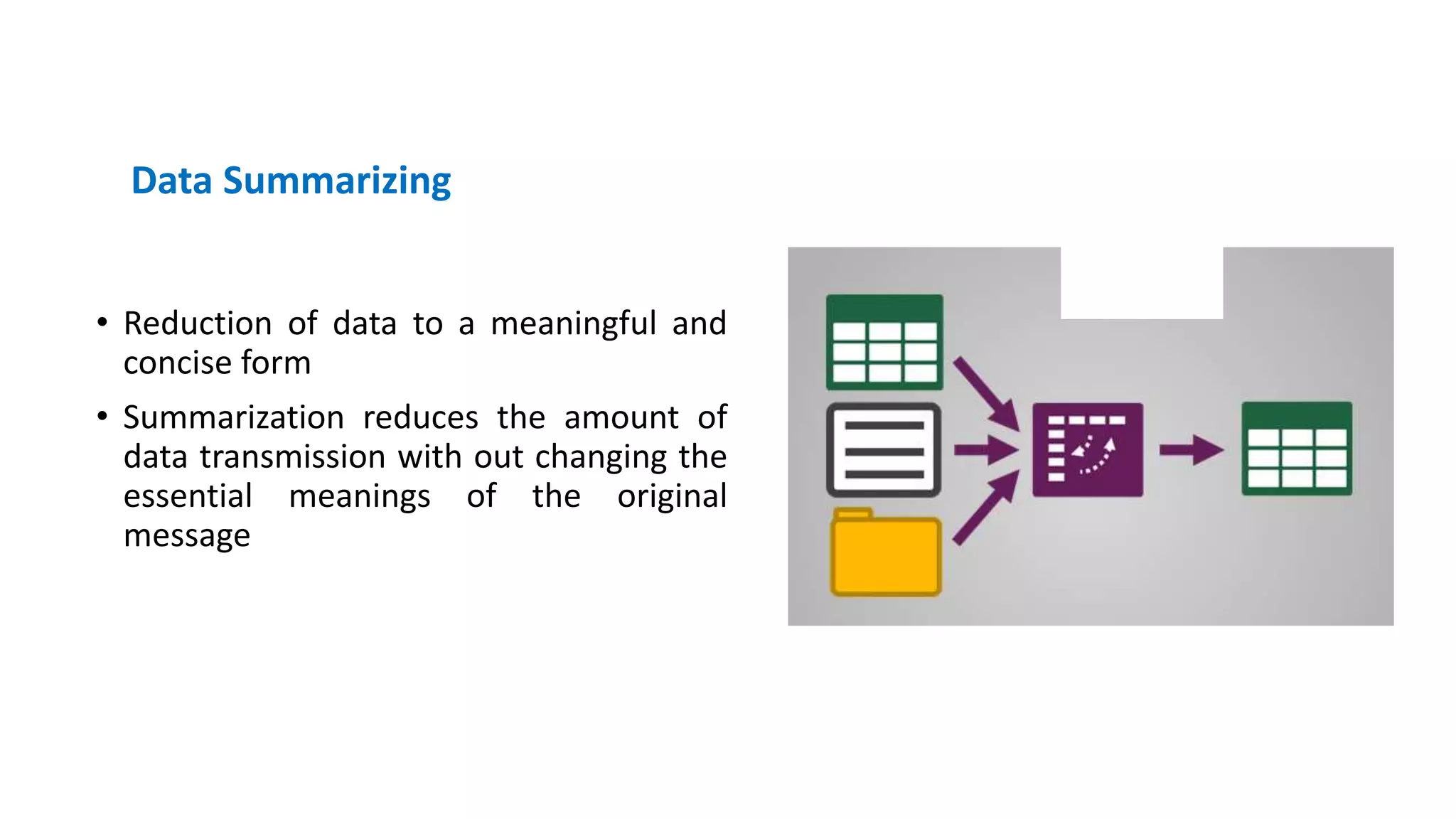
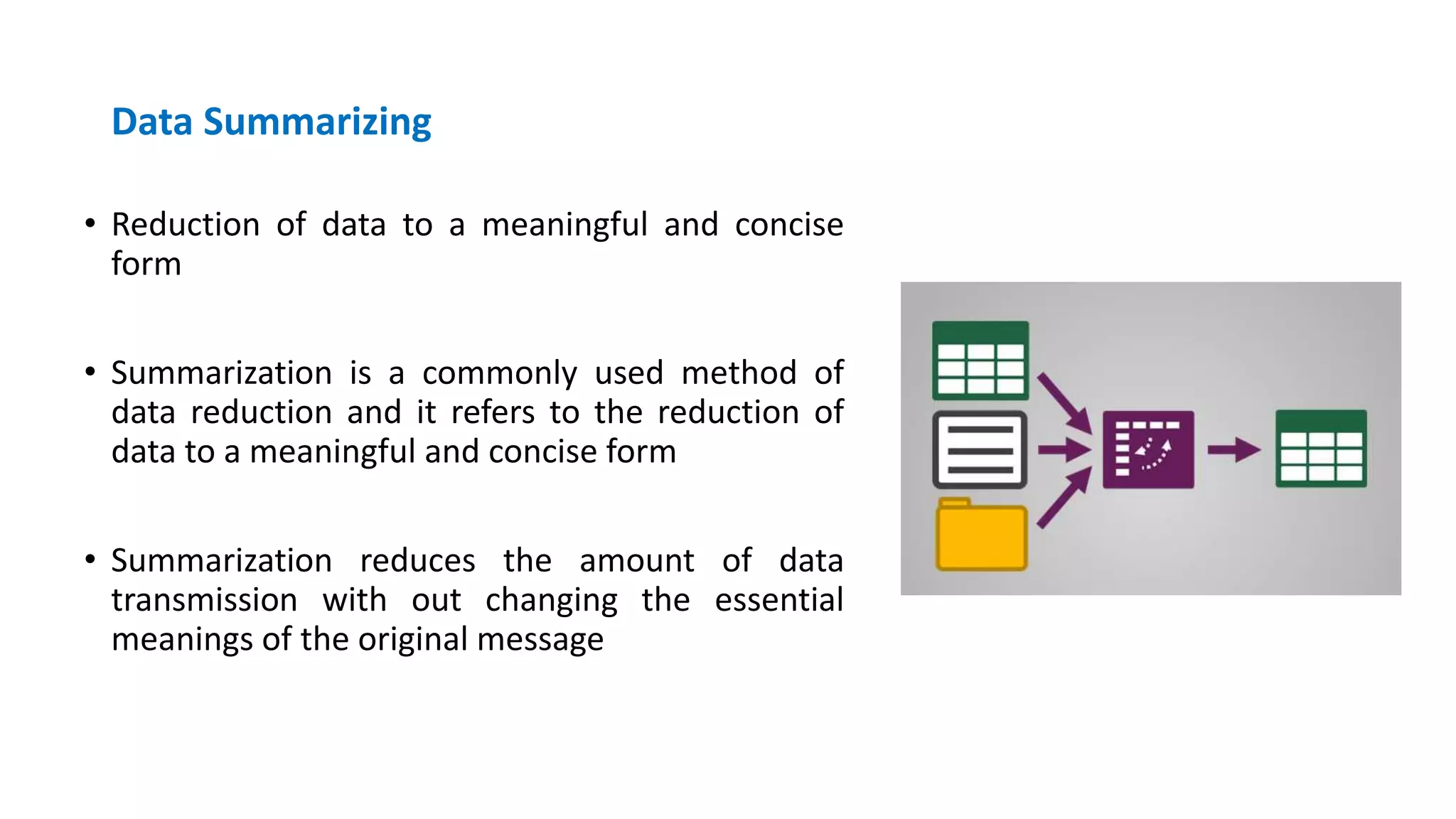
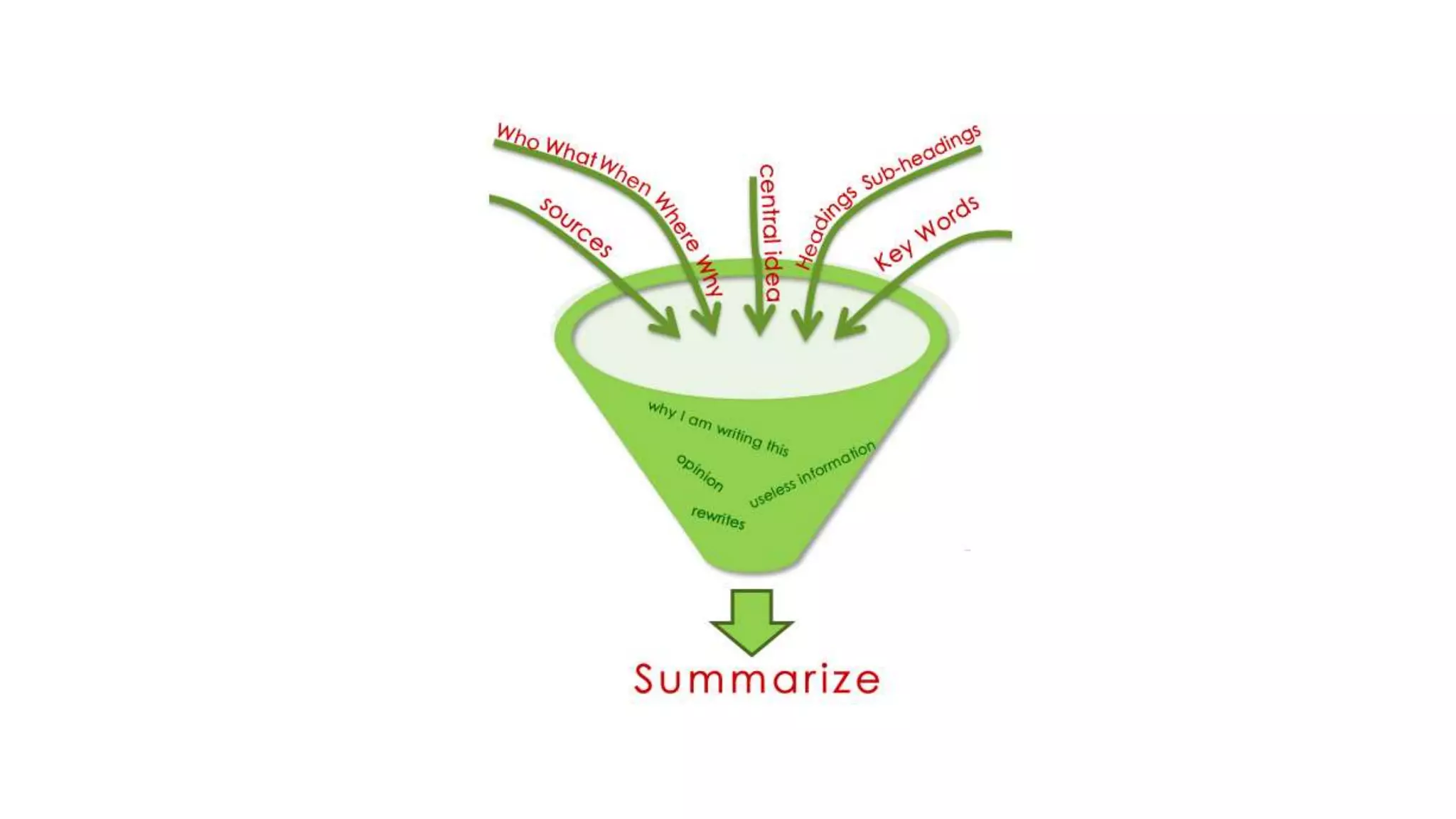
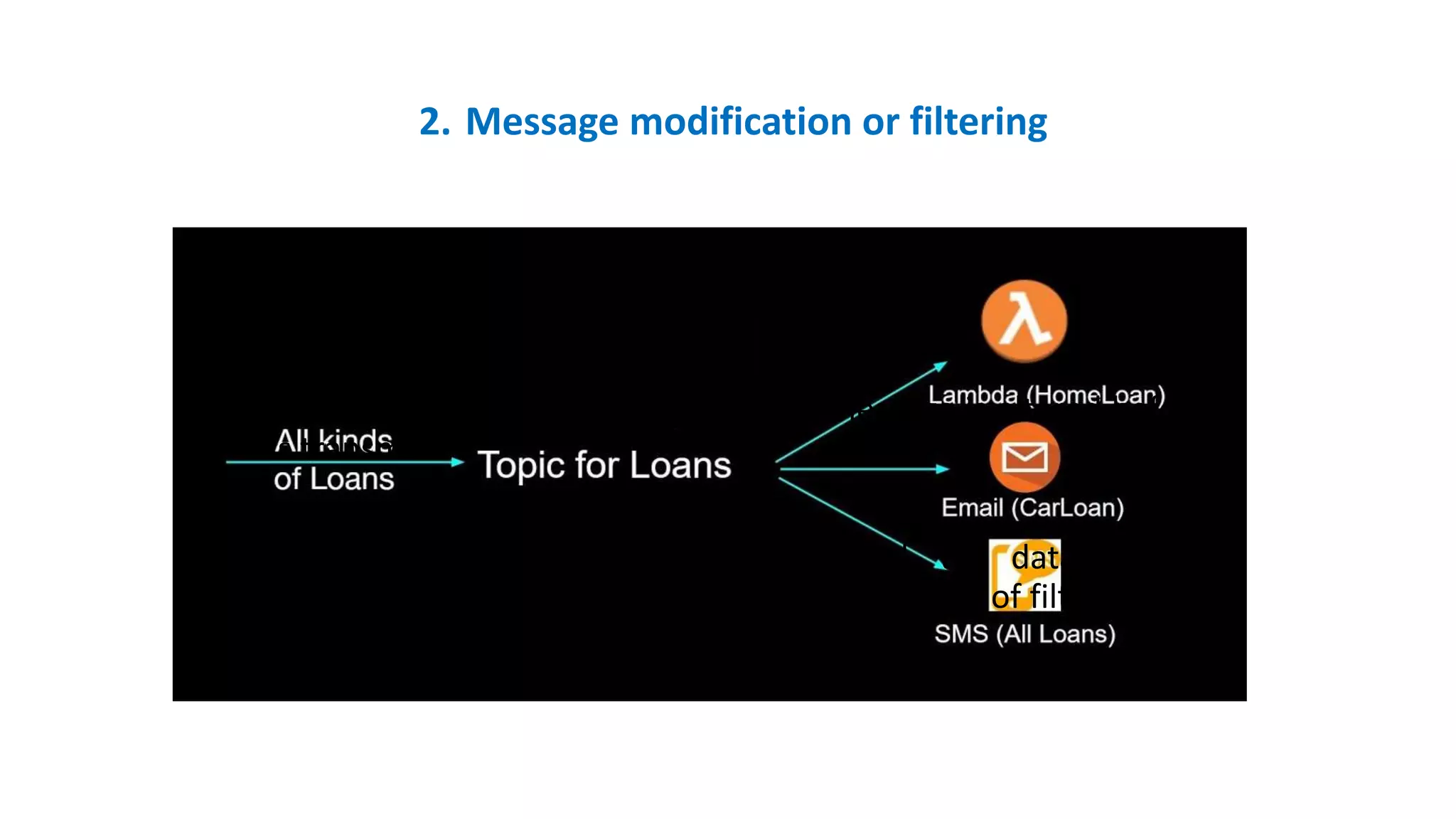
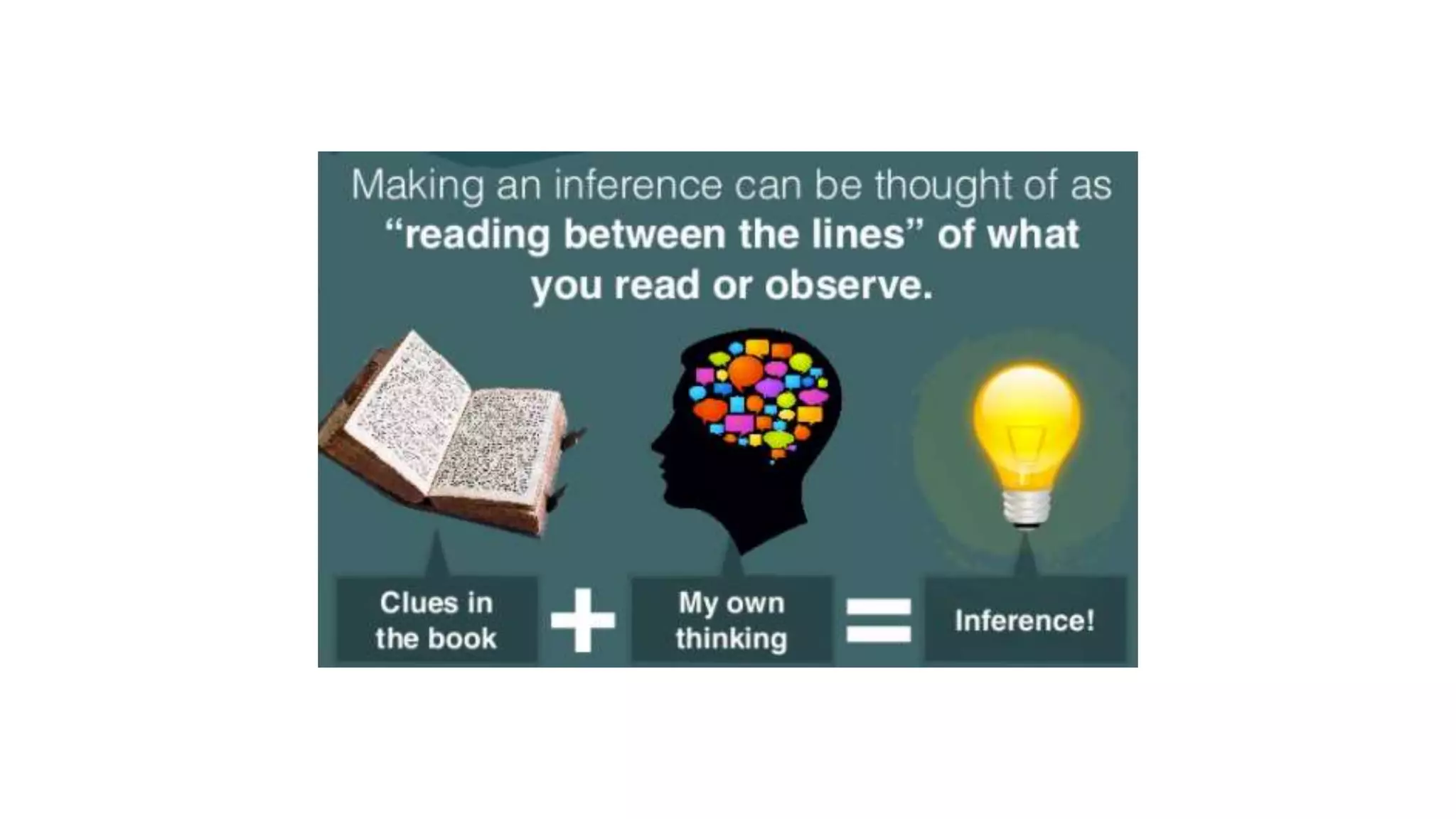
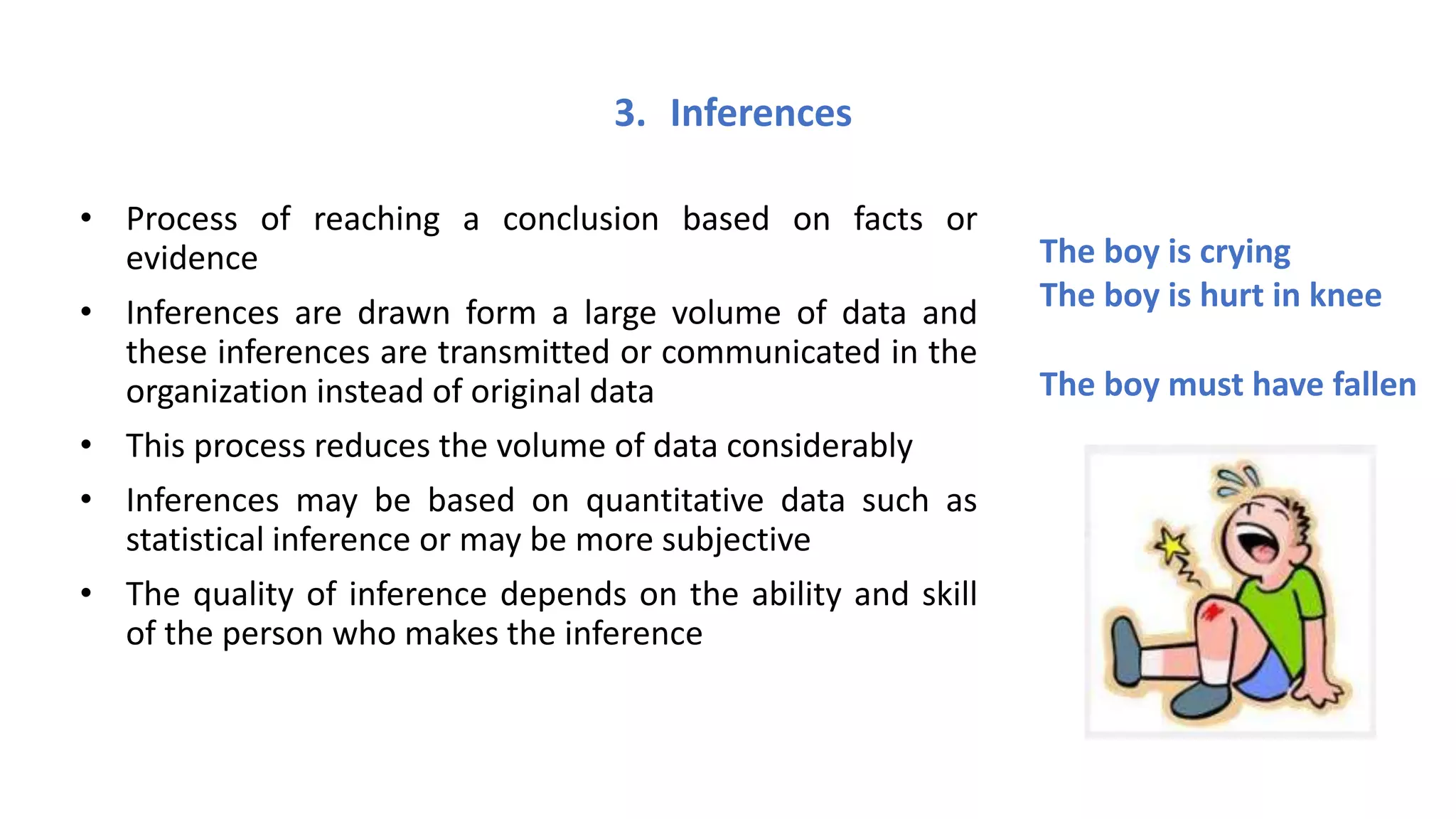
The document discusses the quality and value of information in management information systems, emphasizing that effective decision-making relies on dimensions such as utility, satisfaction, error, and bias. It also covers the concept of information overload, which occurs when the volume of input exceeds processing capacity, leading to negative consequences like stress and delayed decision-making. Finally, it suggests strategies to manage information overload, including focusing on essential sources, summarizing data, filtering messages, drawing inferences, and routing information effectively.