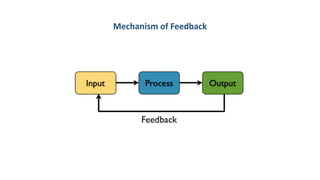
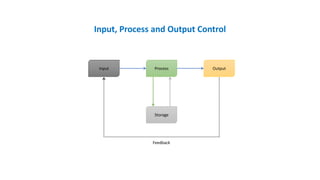
The document discusses the role of feedback in management information systems, detailing positive and negative feedback types. Positive feedback amplifies system output and can cause instability, while negative feedback reduces output, promoting system regulation and stability. It also covers input, process, and output controls, emphasizing their importance in data handling and system performance.