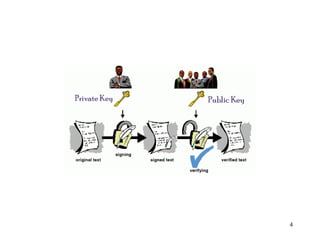
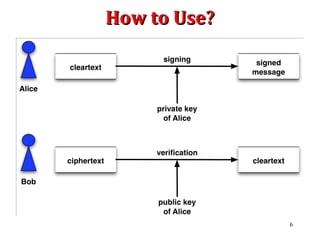
Digital signatures are encrypted electronic signatures that provide a higher level of security compared to traditional electronic signatures by binding a unique coded message to both the document and the signer. They ensure authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation, making them legally enforceable under laws like the ICT Act 2006 in Bangladesh. Conversely, electronic signatures, often just a scanned image of a signature, lack the same security measures and can be easily forged, making them less reliable.












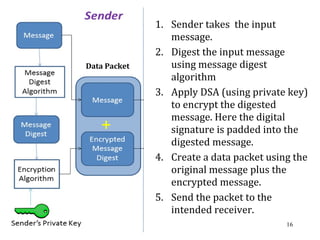
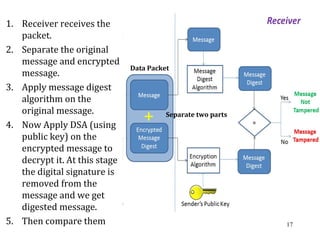


![DSA: How Signature isDSA: How Signature is
Generated by the Sender ?Generated by the Sender ?
Let N be the bit length of q. And let min(N, outlen) denote the
minimum of the positive integers N and outlen. Outlen is the bit
length of the hash function output block.
The signature of a message m consists of the pair of numbers r
and s that is computed according to the following equations:
r = (gk
mod p) mod q
z= H(m) [z = the leftmost min(N, outlen) bits of Hash(m)]
s = (k-1
(H(m) + xr) ) mod q.
When computing s, the string z obtained from Hash(m) is
converted to an integer.
(r , s) is considered to be the signature of the sender.
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalsignature-150609035740-lva1-app6892/85/Digital-signature-21-320.jpg)



![DSA: How Signature isDSA: How Signature is
Verified by the Receiver ?Verified by the Receiver ?
2. If the two conditions in step 1 are satisfied, the verifier
computes the following:
w = (s')–1
mod q.
z = H(m' )
u1 = (z * w) mod q = (H(m' ) * w) mod q
u2 = (r' * w) mod q.
v = [ ( (gu1
* yu2
) mod p) mod q ]
The string z obtained from Hash(m') is converted to an integer
2. If v = r', then the signature considered to be verified.
If m' = m, r' = r, and s'= s then v = r‘.
3. If v ≠ r', then the message or the signature may have been
modified. The signature is considered invalid. 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalsignature-150609035740-lva1-app6892/85/Digital-signature-25-320.jpg)

![ExampleExample
Receiver Side:
1. Let bob received the message and signatures as m', r', and s‘.
Then Bob verifies the signature by computing:
w = (s')–1
mod q.
z = H(m' )
u1 = (z * w) mod q = (H(m' ) * w) mod q
u2 = (r' * w) mod q.
v = [ ( (gu1
* yu2
) mod p) mod q ]
2. If v = r', then the signature and message considered to be
authenticated.
3. If v ≠ r', The signature and message is considered invalid.
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalsignature-150609035740-lva1-app6892/85/Digital-signature-27-320.jpg)

