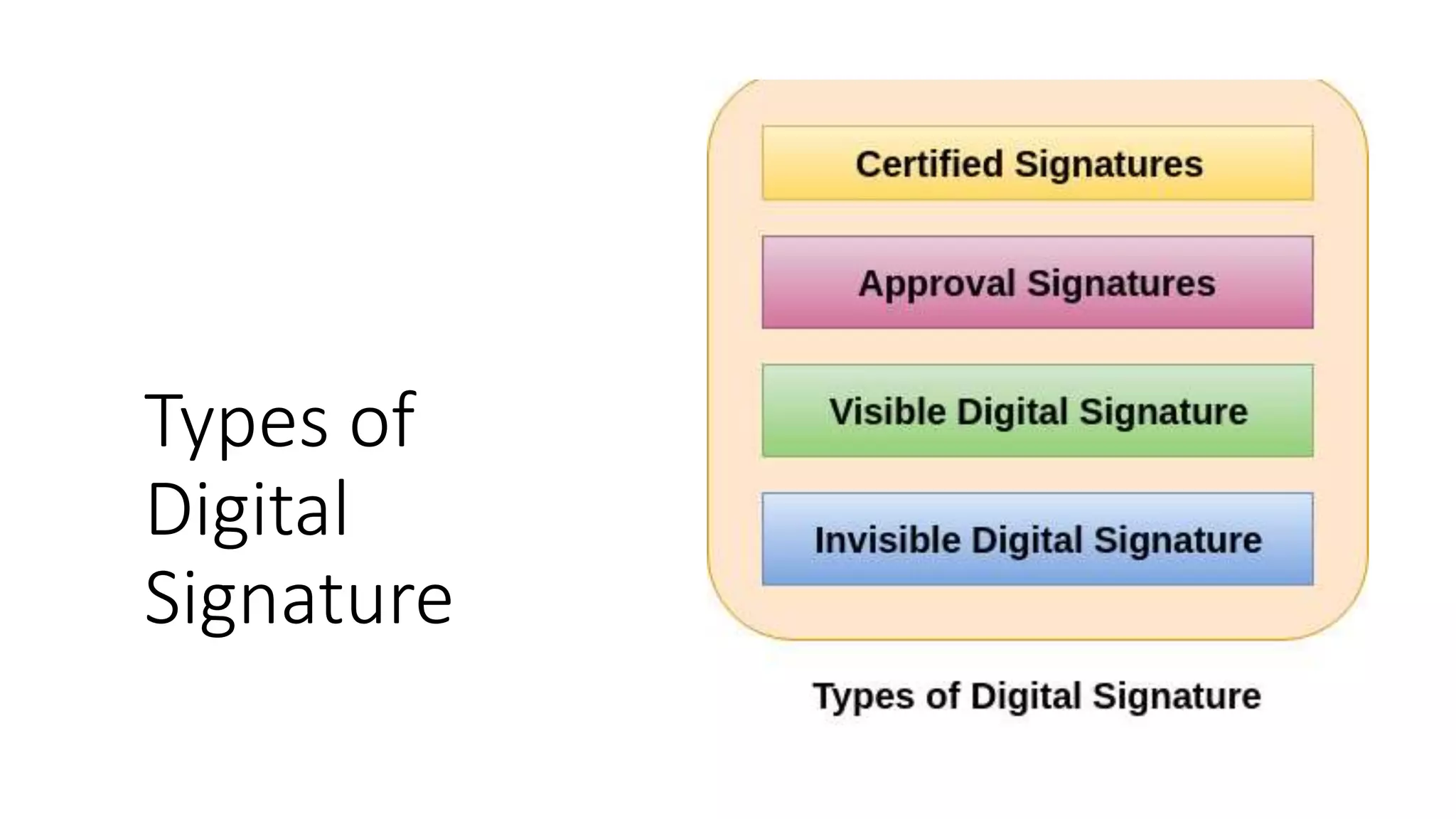
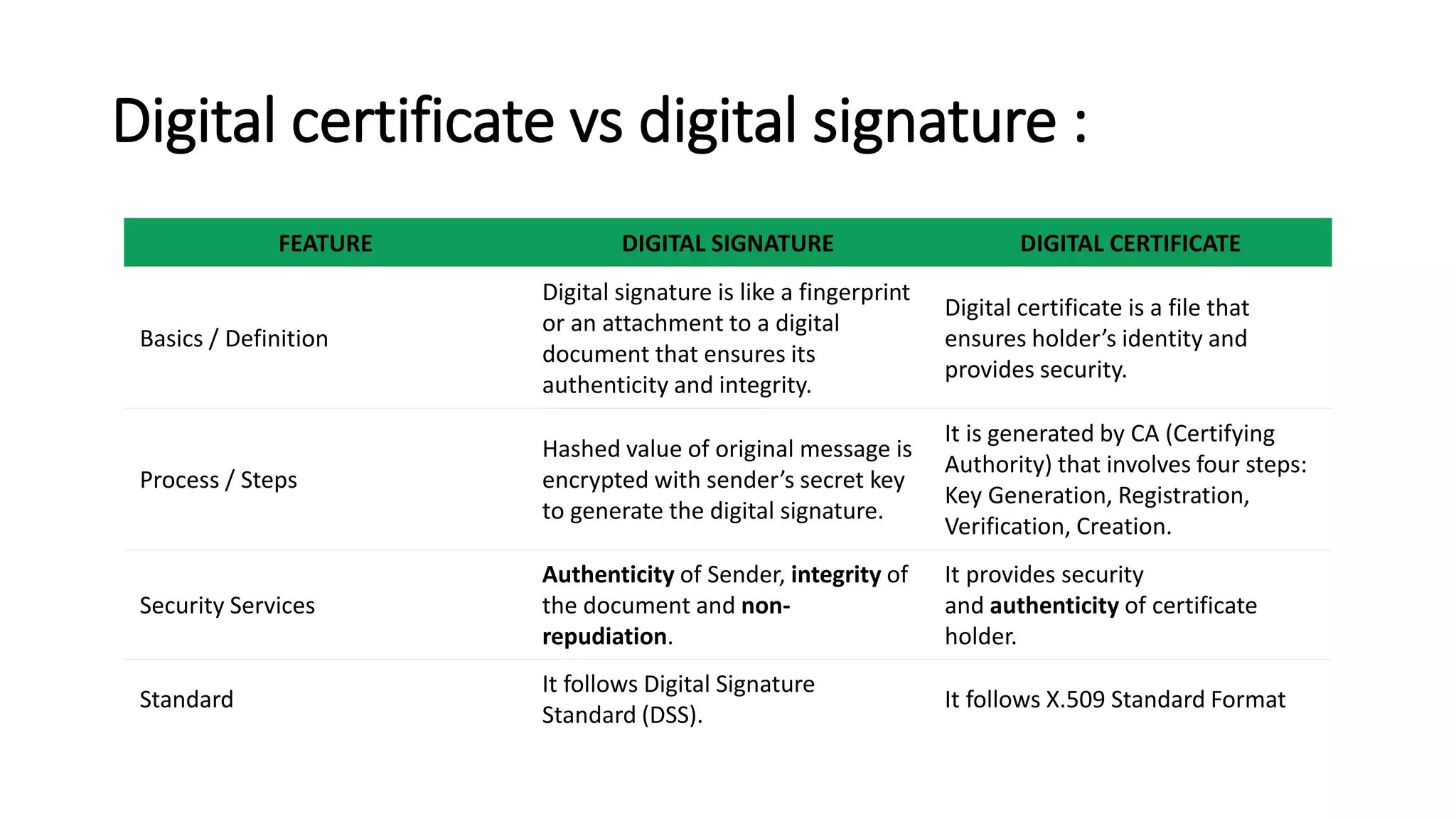
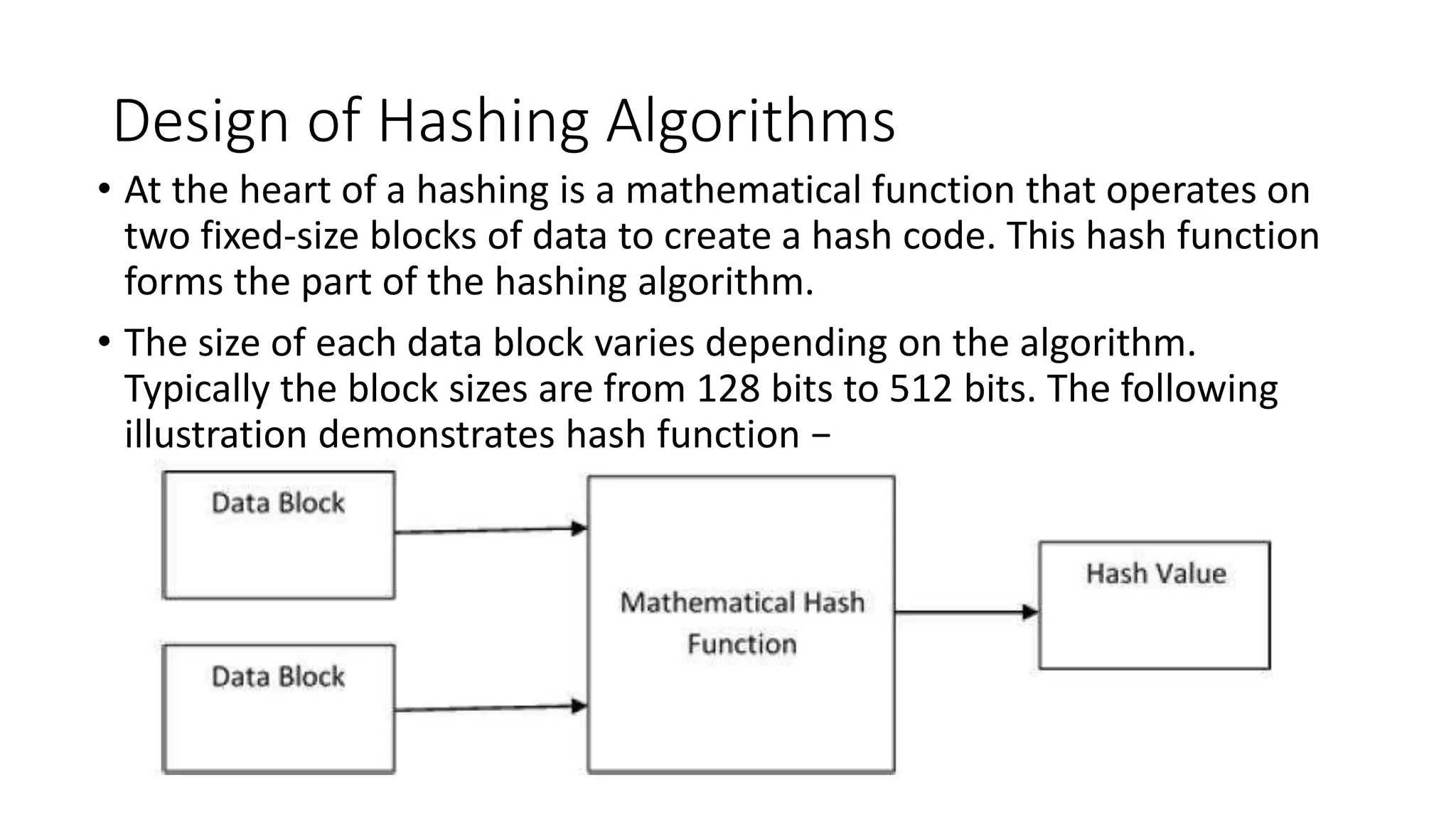
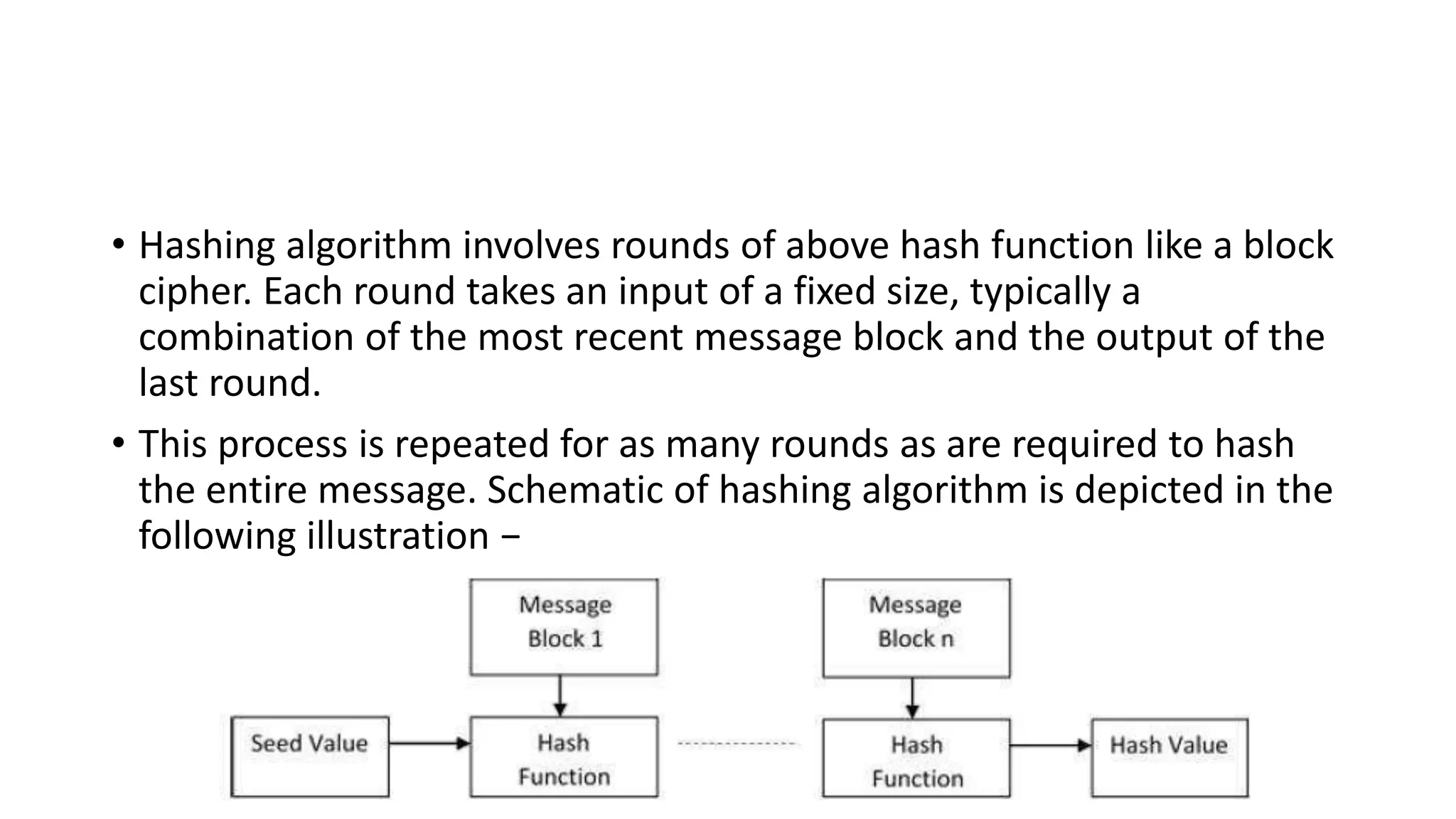
Digital signatures rely on encryption and authentication to verify the identity of a sender and ensure a document has not been altered. They use a mathematical technique that validates authenticity, integrity, and allows verification of author, date, and time. Digital signatures offer more security than traditional signatures by solving problems of tampering and impersonation. They are important for authentication, non-repudiation, and ensuring integrity of communications. Key generation and signing algorithms are used to create digital signatures, while verification algorithms are used to validate signatures.