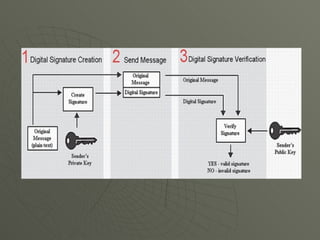
This document provides an overview of digital signatures, including how they work and their legal aspects. It discusses how encryption scrambles messages and digital signatures verify authorship and document integrity. Digital signatures use public/private key pairs, where the private key is unique to the signer. To create a digital signature, a hash of the message and private key is computed. Verification involves recomputing the hash with the public key and signature to validate authenticity. Digital signatures provide evidence of authorship, represent a legal ceremony of approval, and make documents more efficient to process.