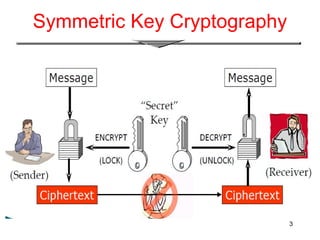
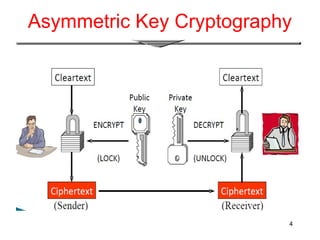
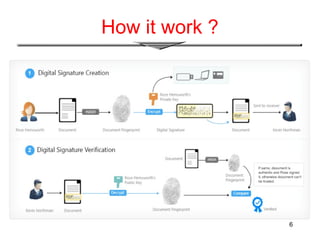
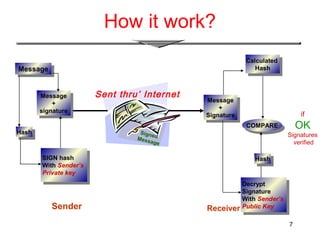
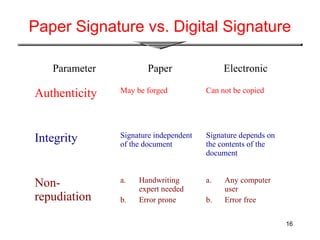
The document provides an overview of digital signatures, explaining their function as a type of asymmetric cryptography used for authentication and to maintain message integrity. It details the creation and verification processes of digital signatures, the key requirements including key pairs and certificates, and discusses their benefits such as authentication and integrity, as well as drawbacks like the need for secure key management. Applications of digital signatures include electronic mail, data storage, and electronic funds transfer.