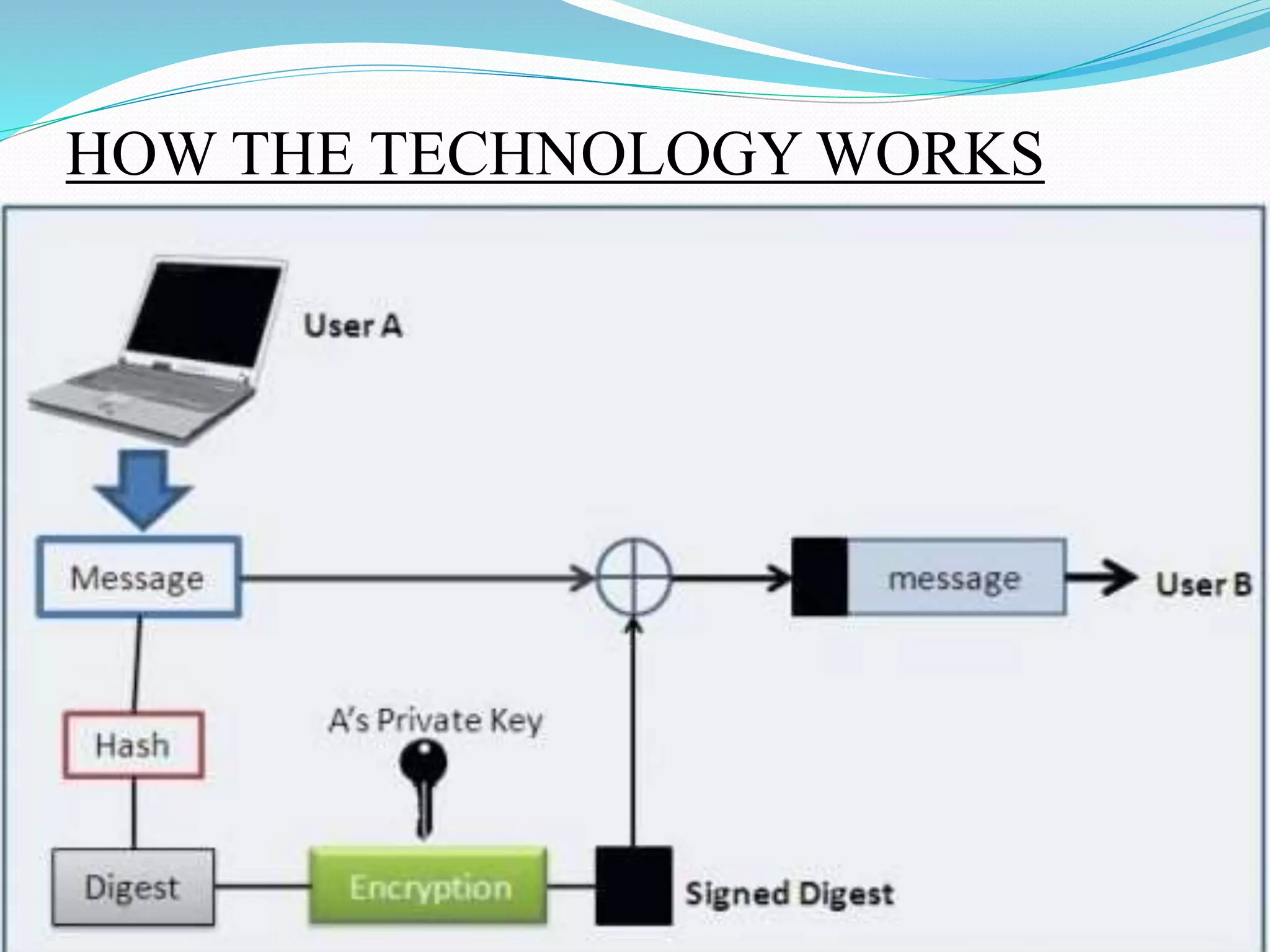
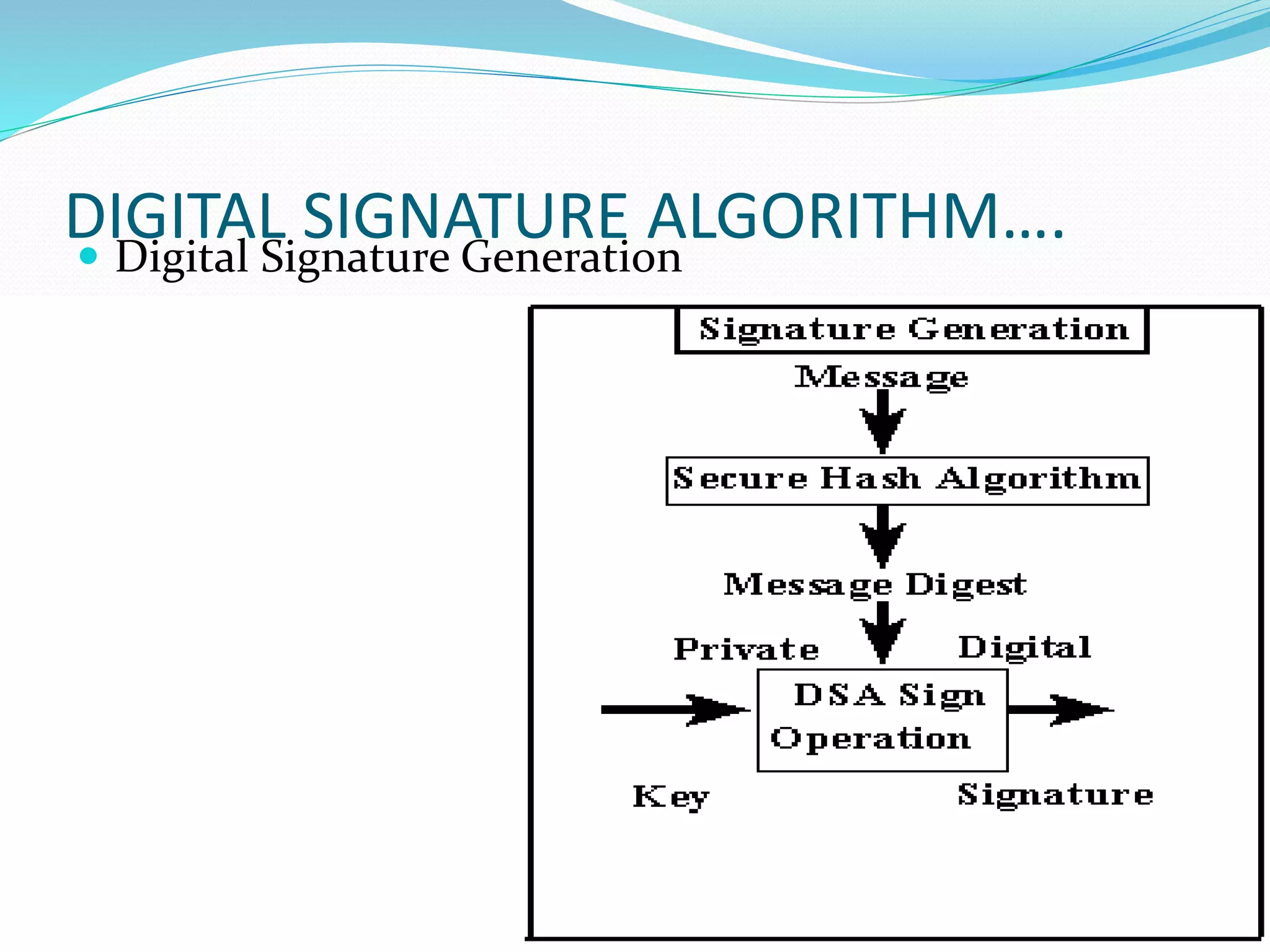
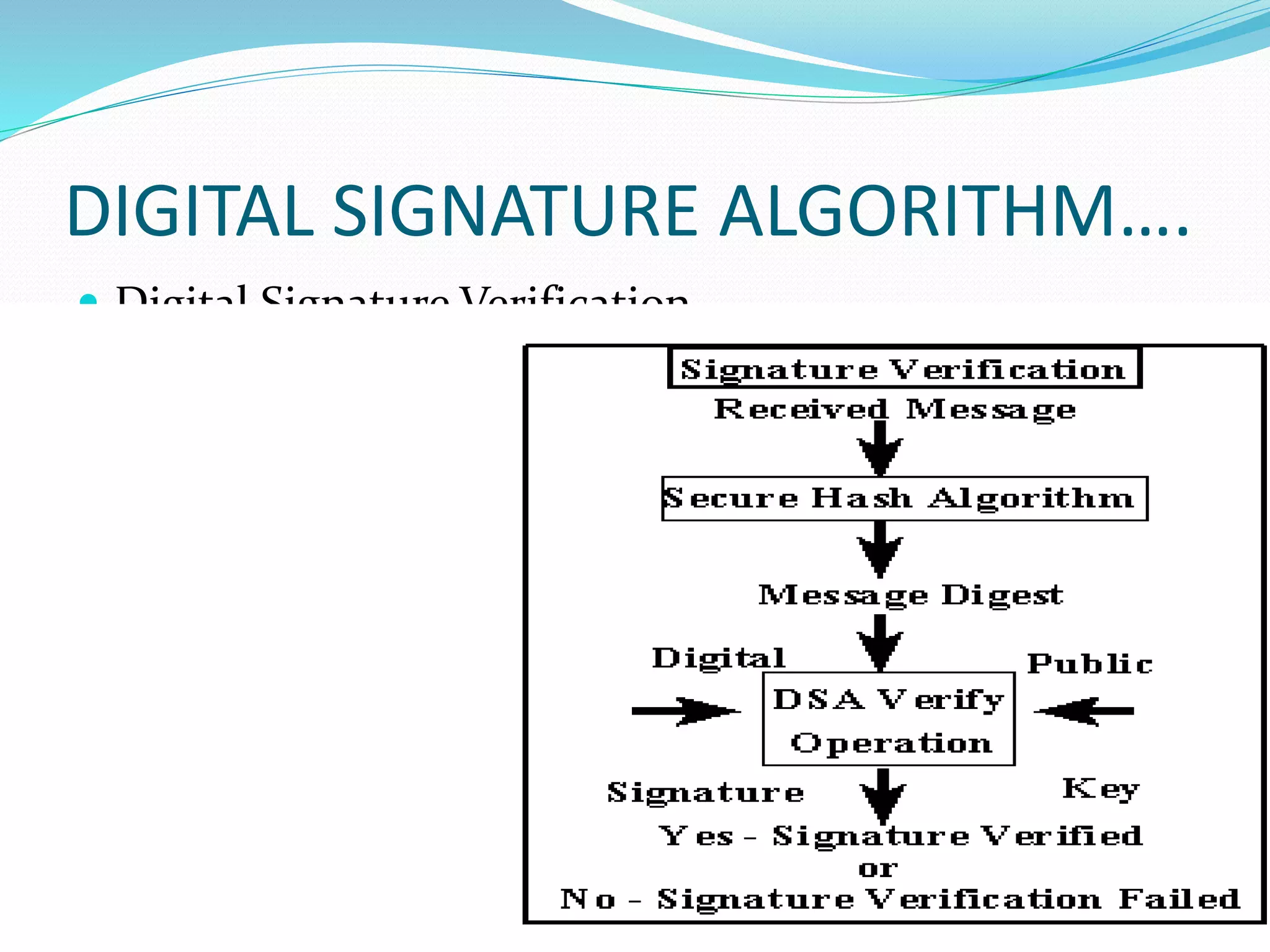
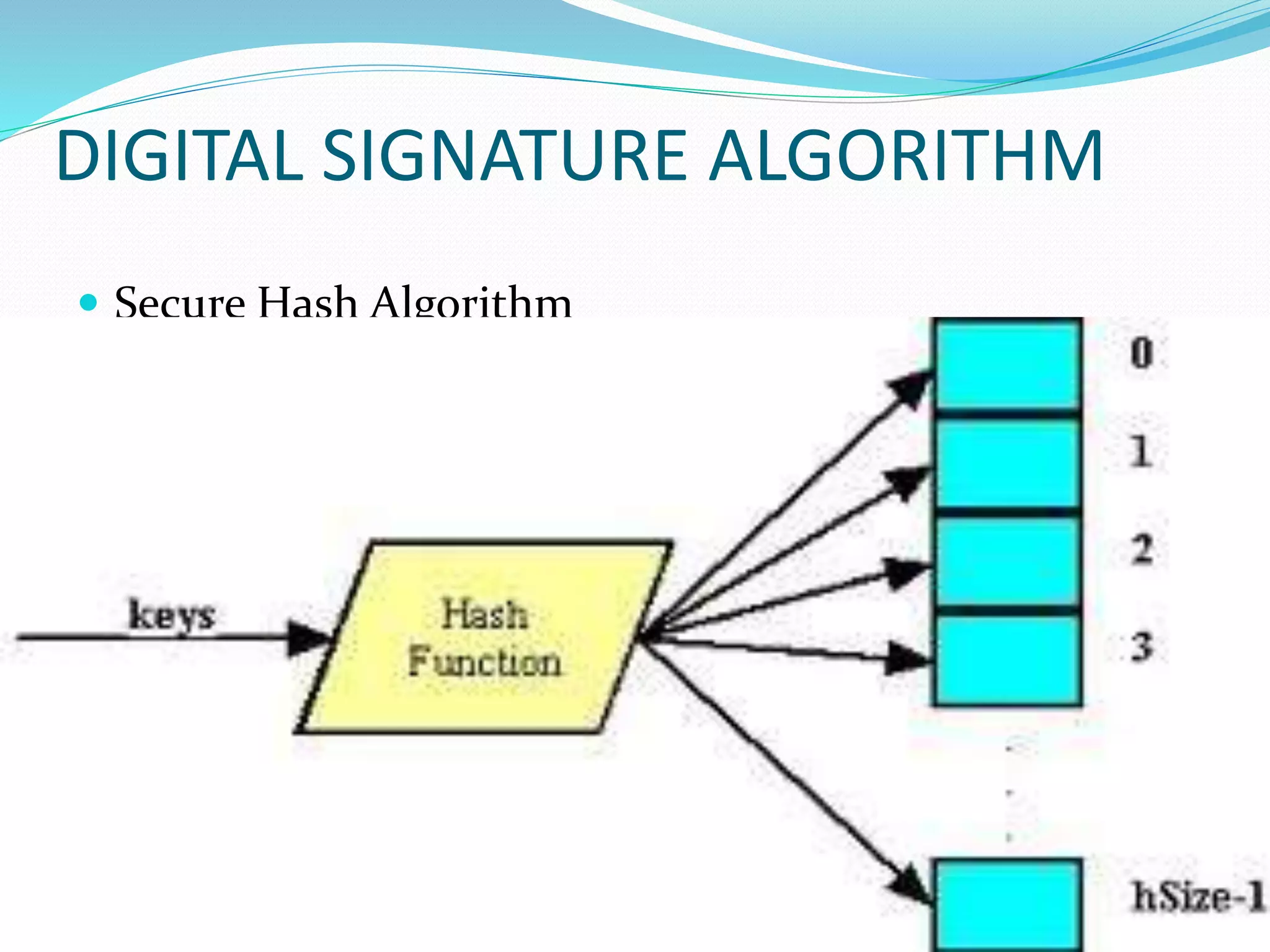
The document discusses the concept of digital signatures, detailing their history, functionality, and the technological requirements for their implementation. It highlights the importance of digital signatures in providing authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation for electronic documents, especially in e-commerce and e-governance. Additionally, it addresses challenges, applications, and potential drawbacks associated with digital signatures.