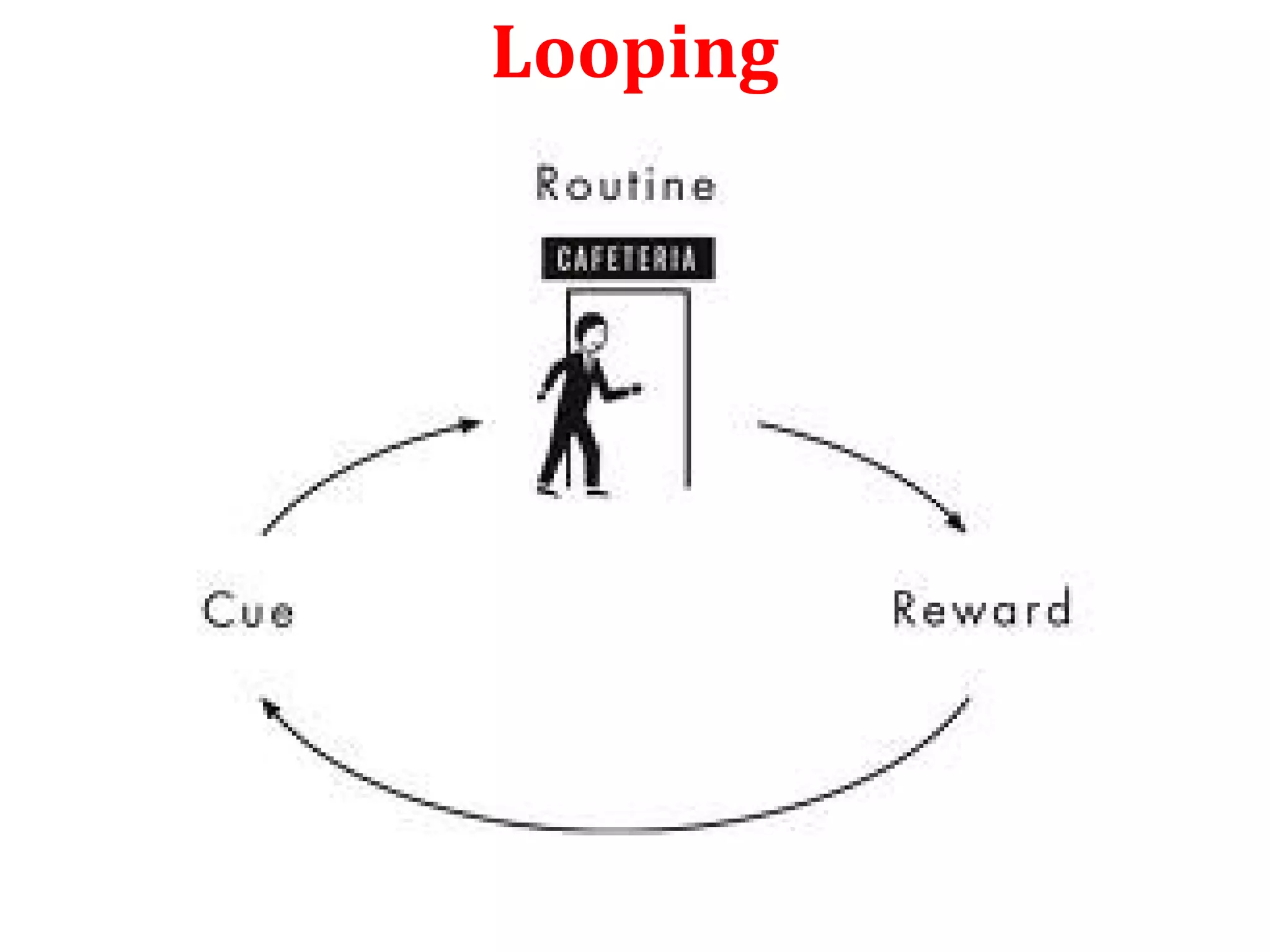
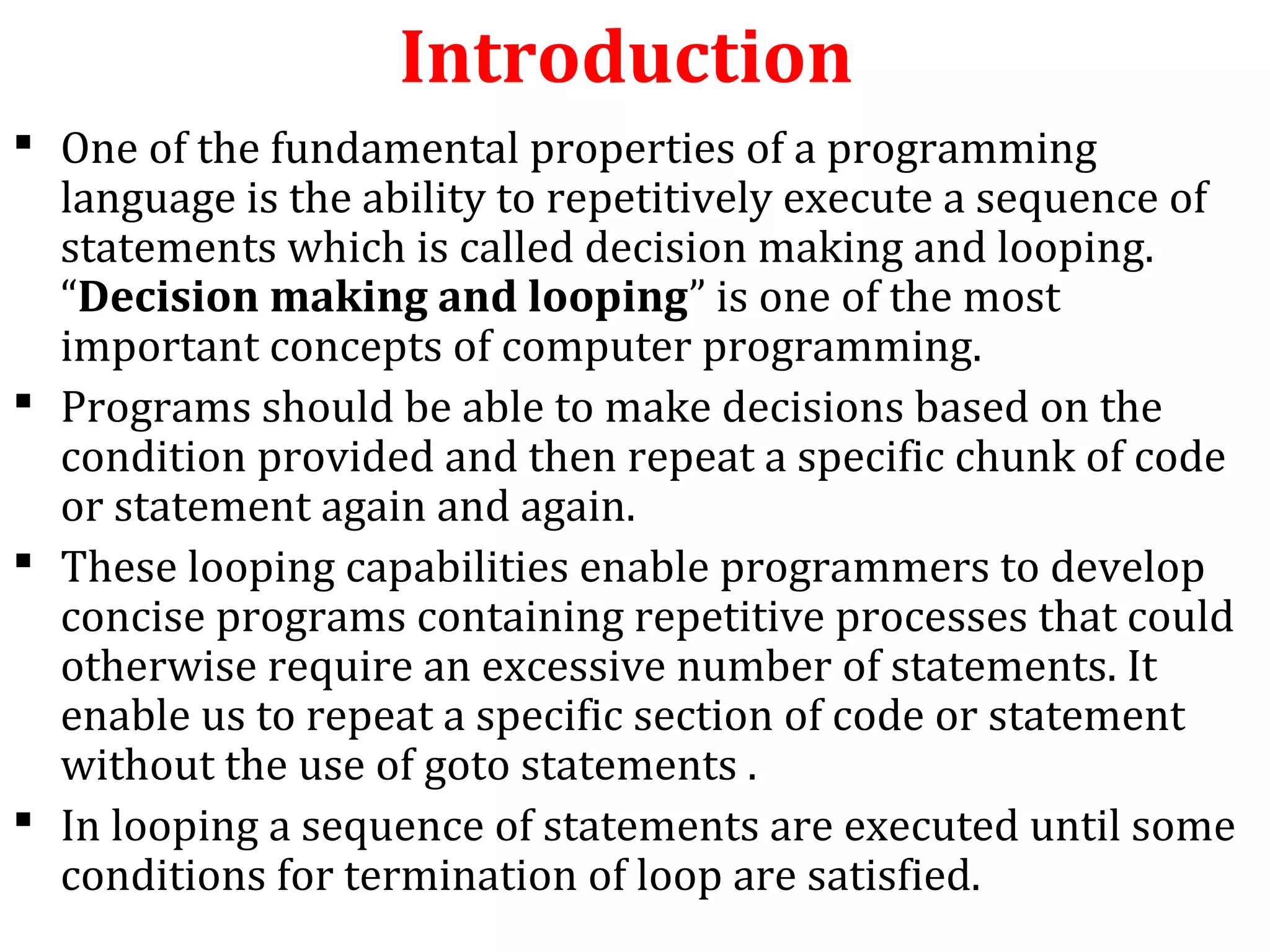
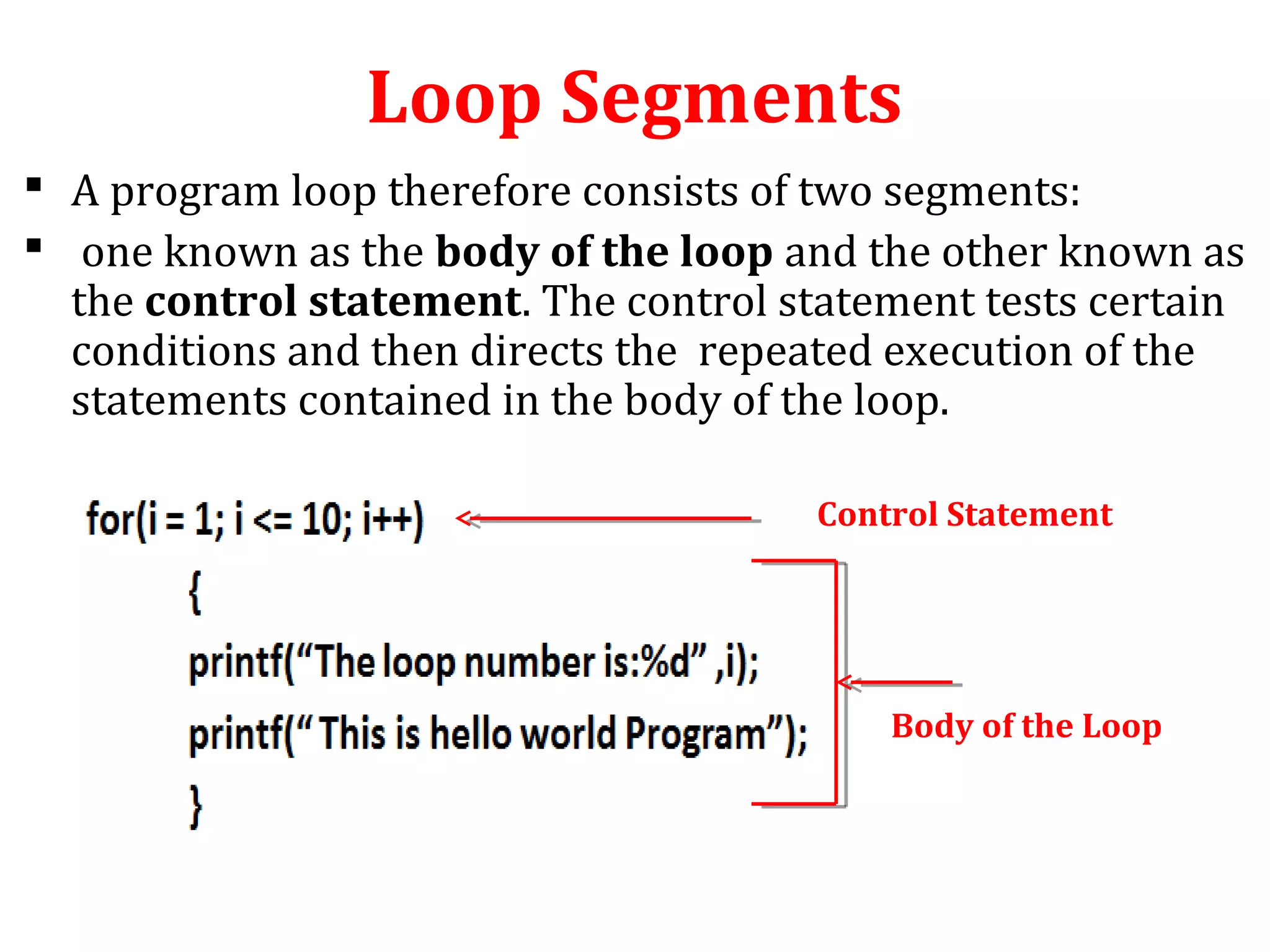
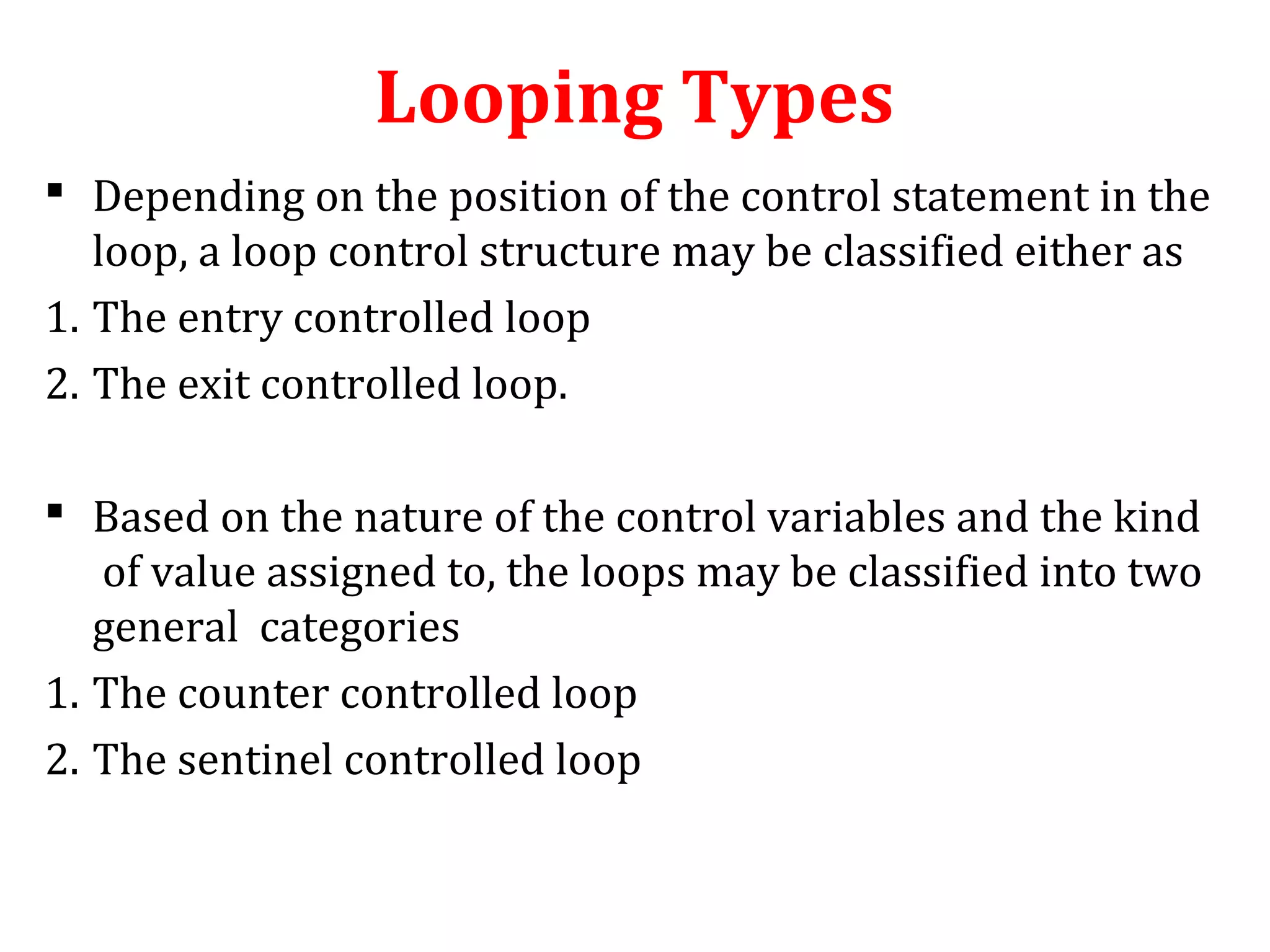
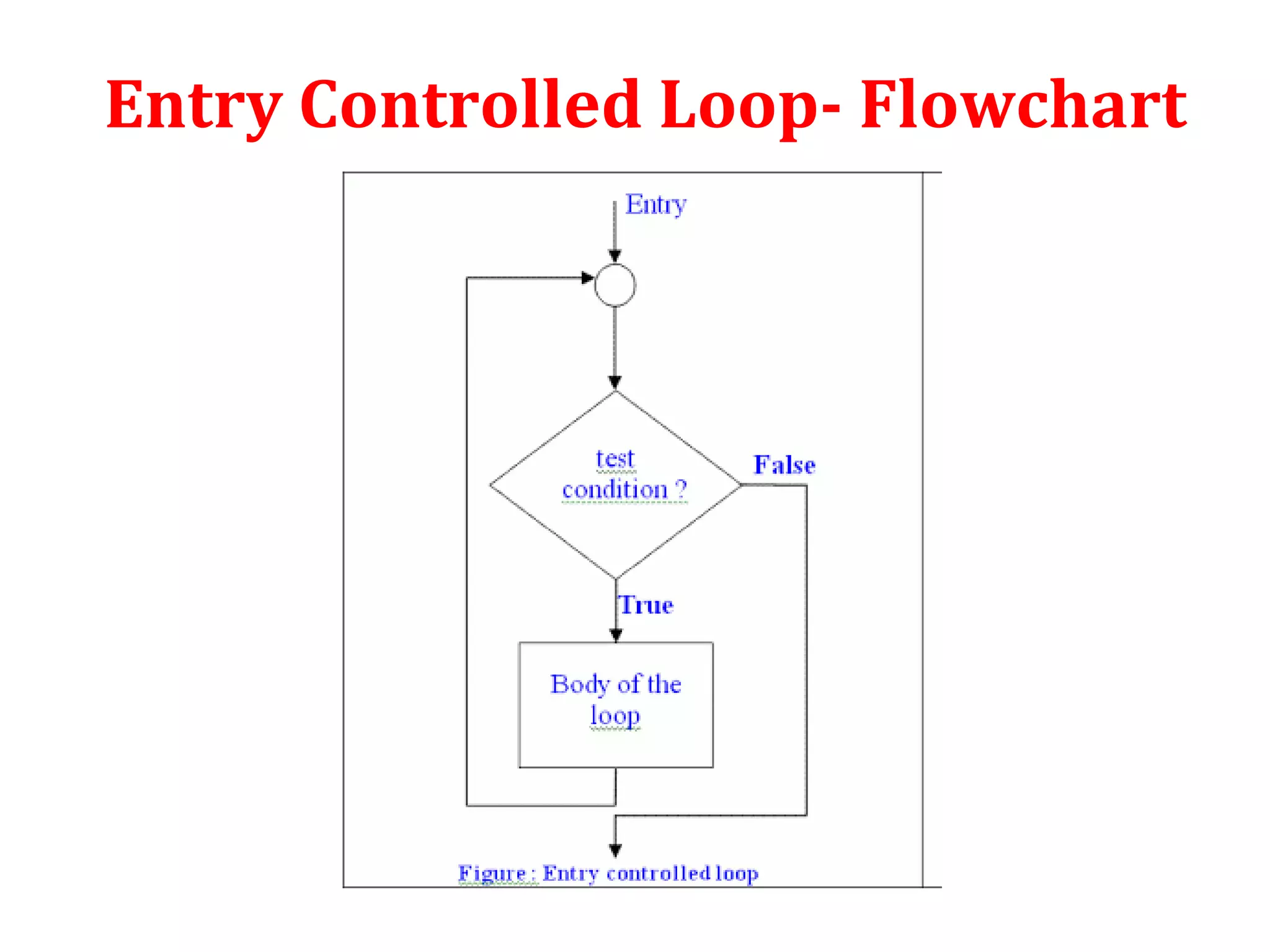
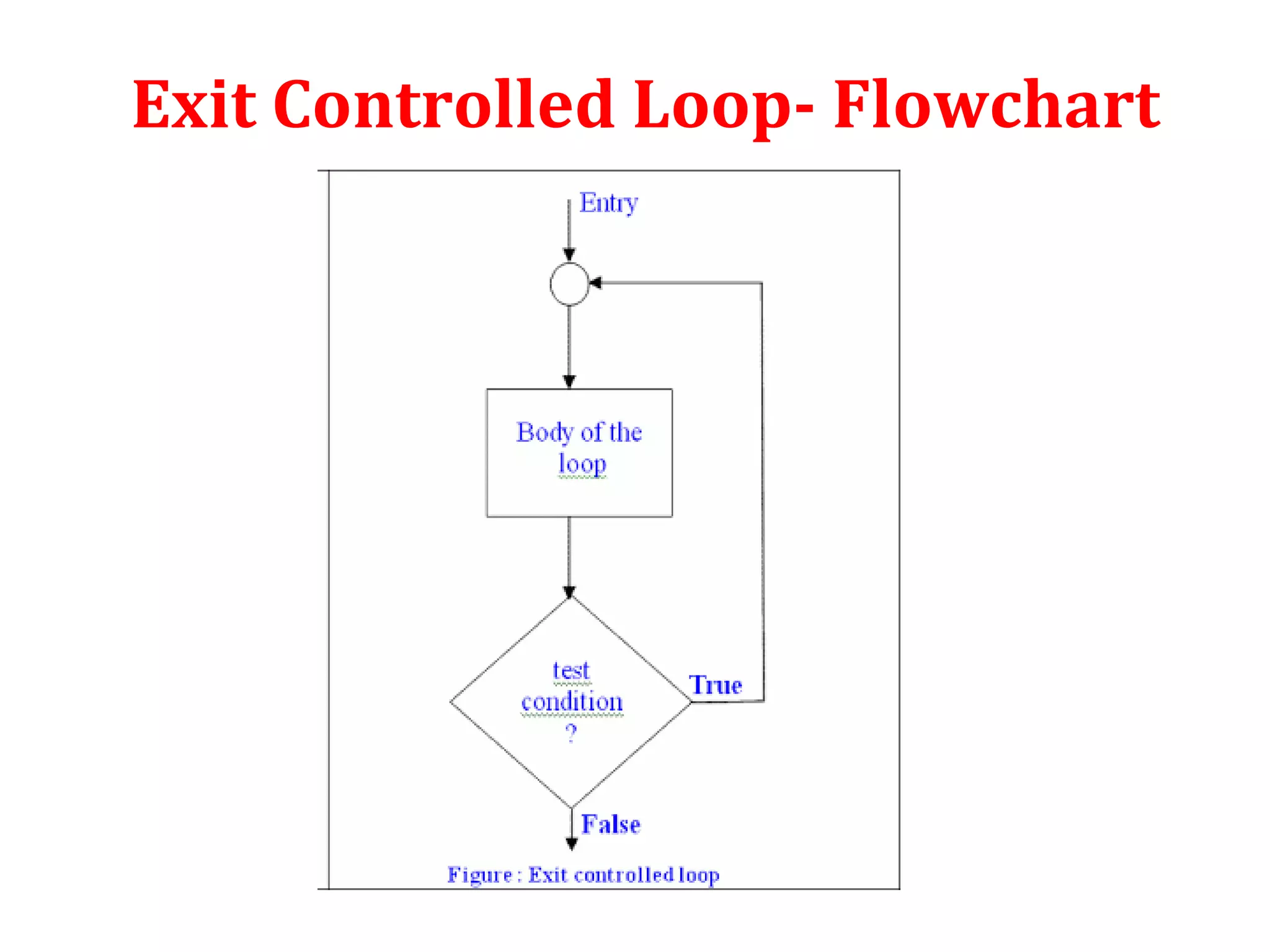
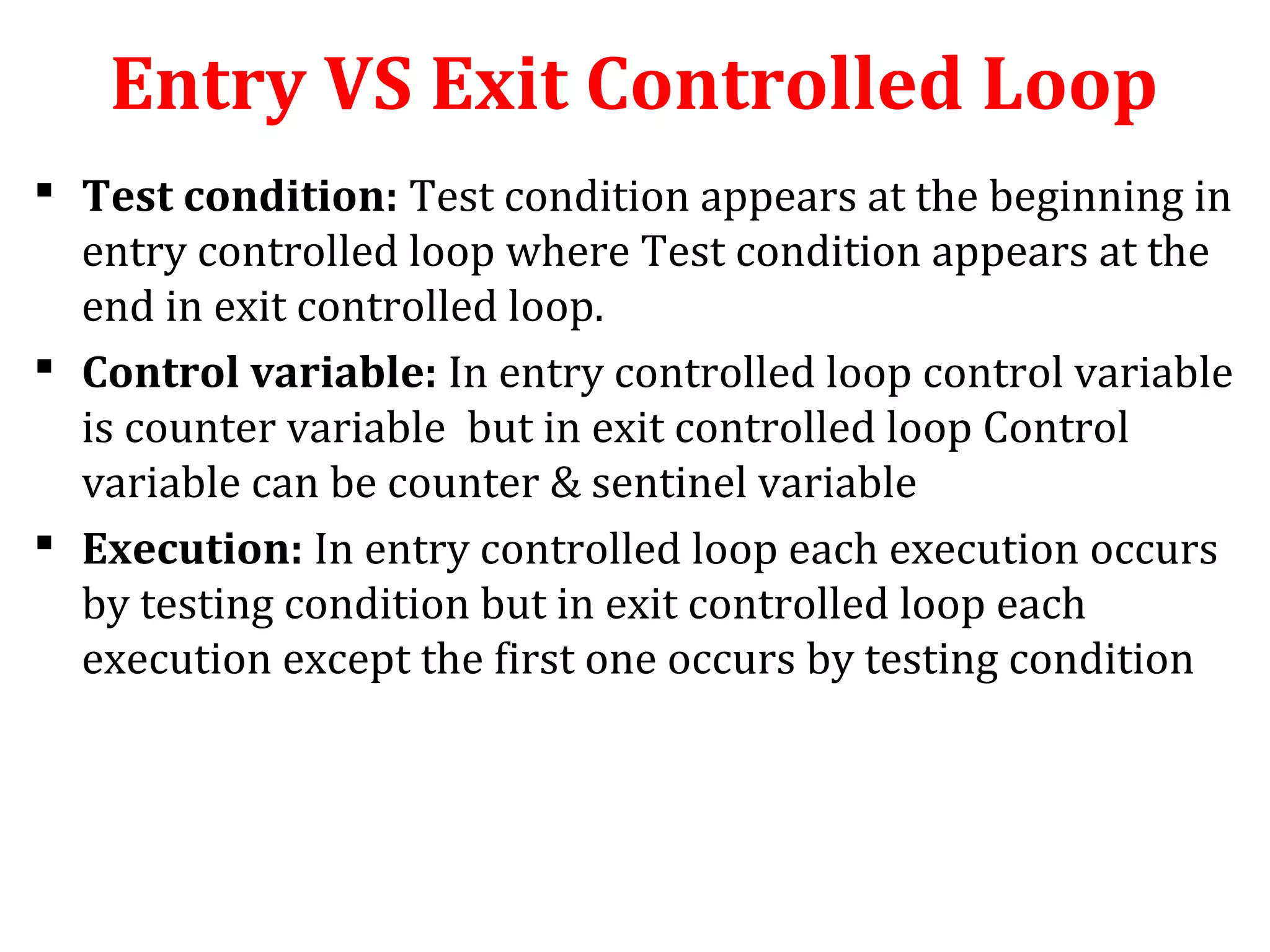
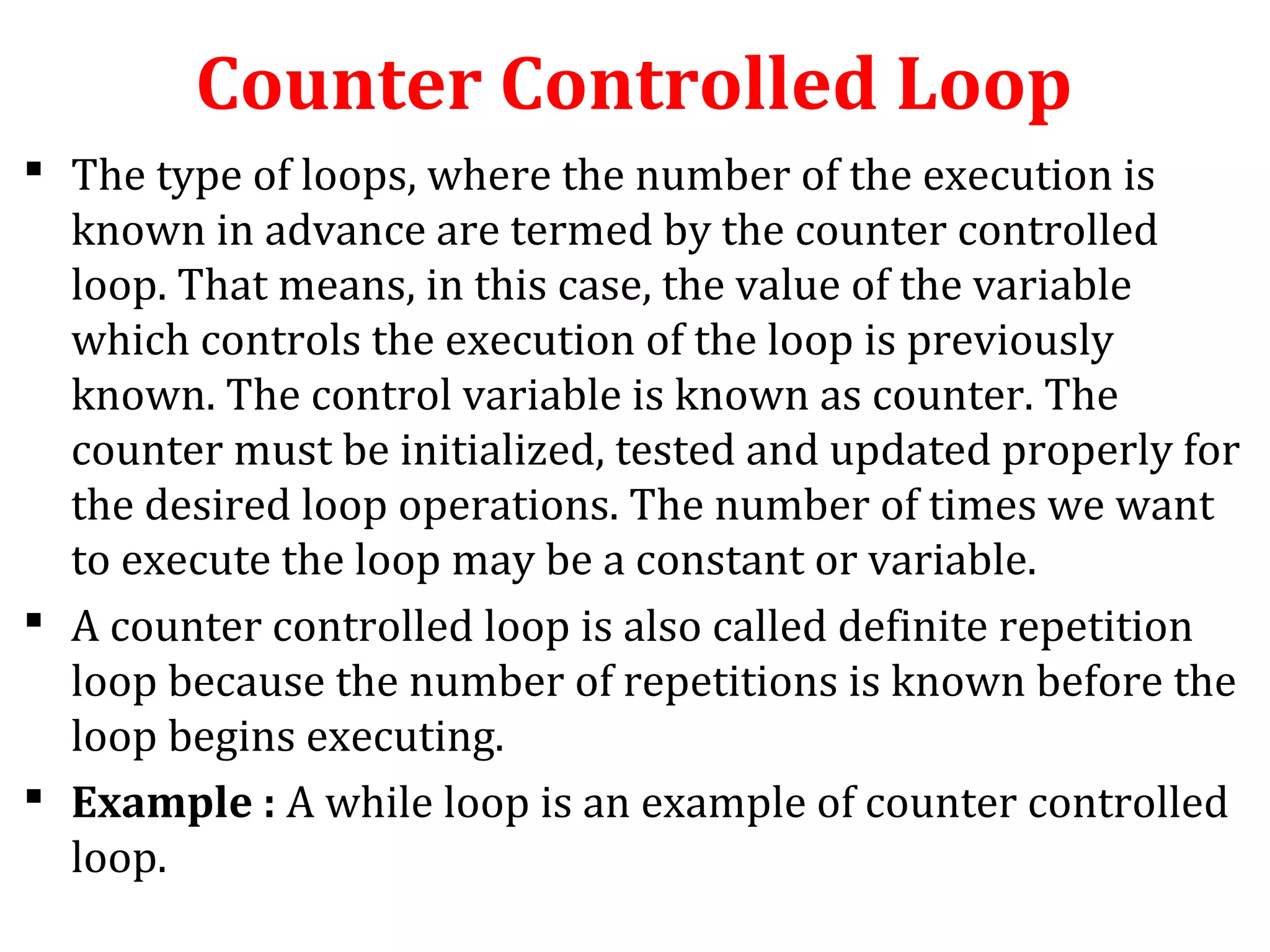
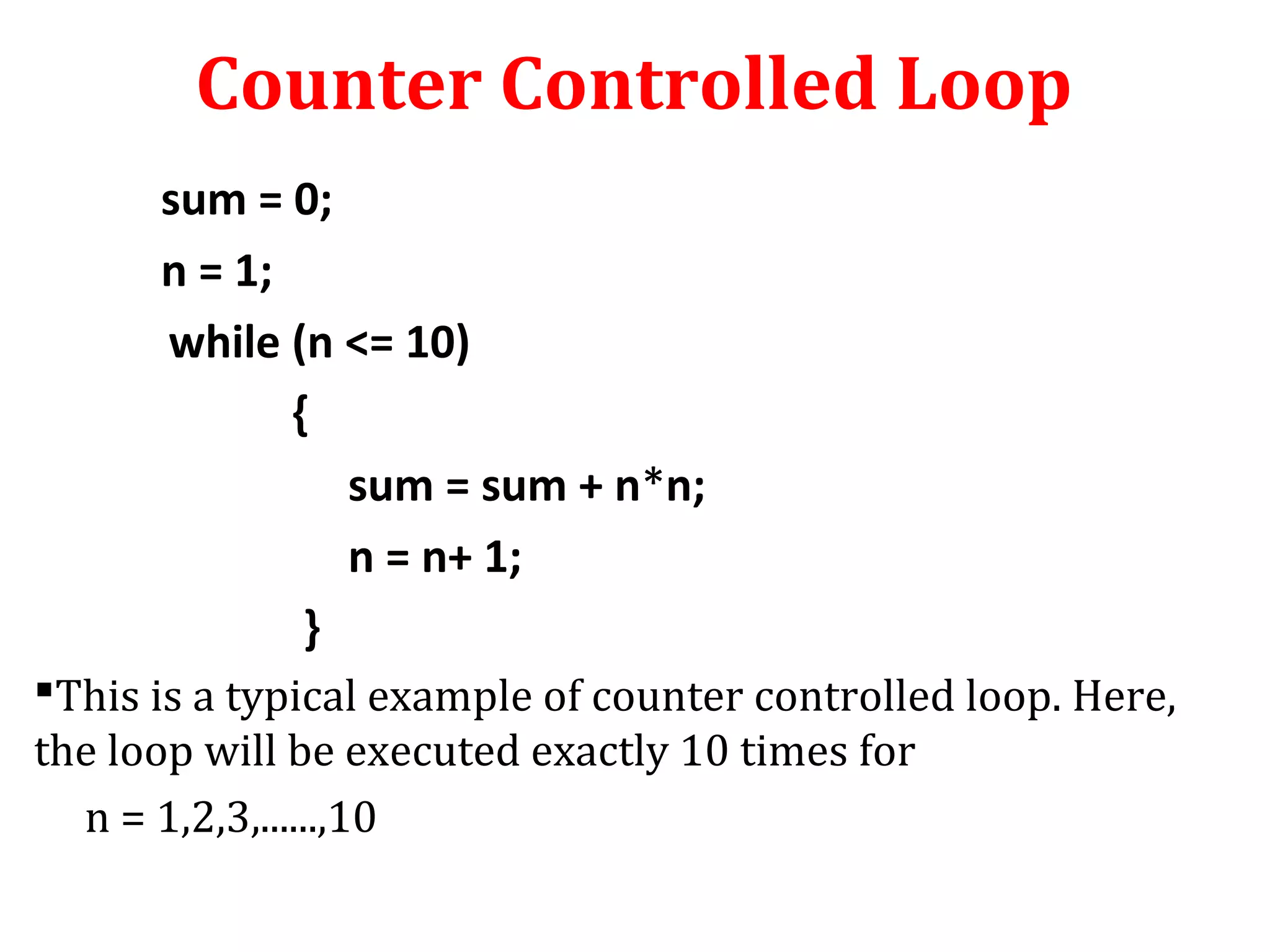
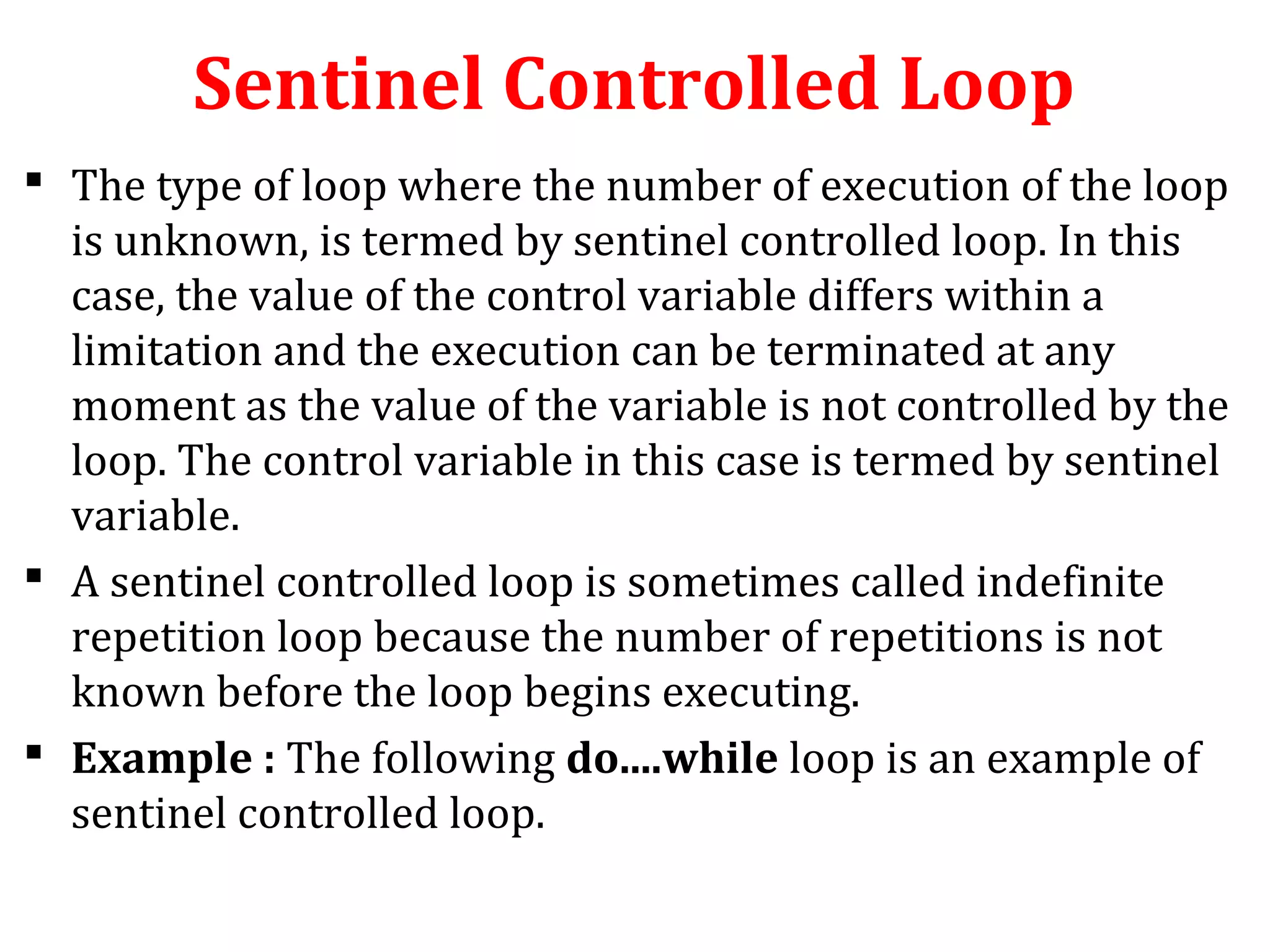
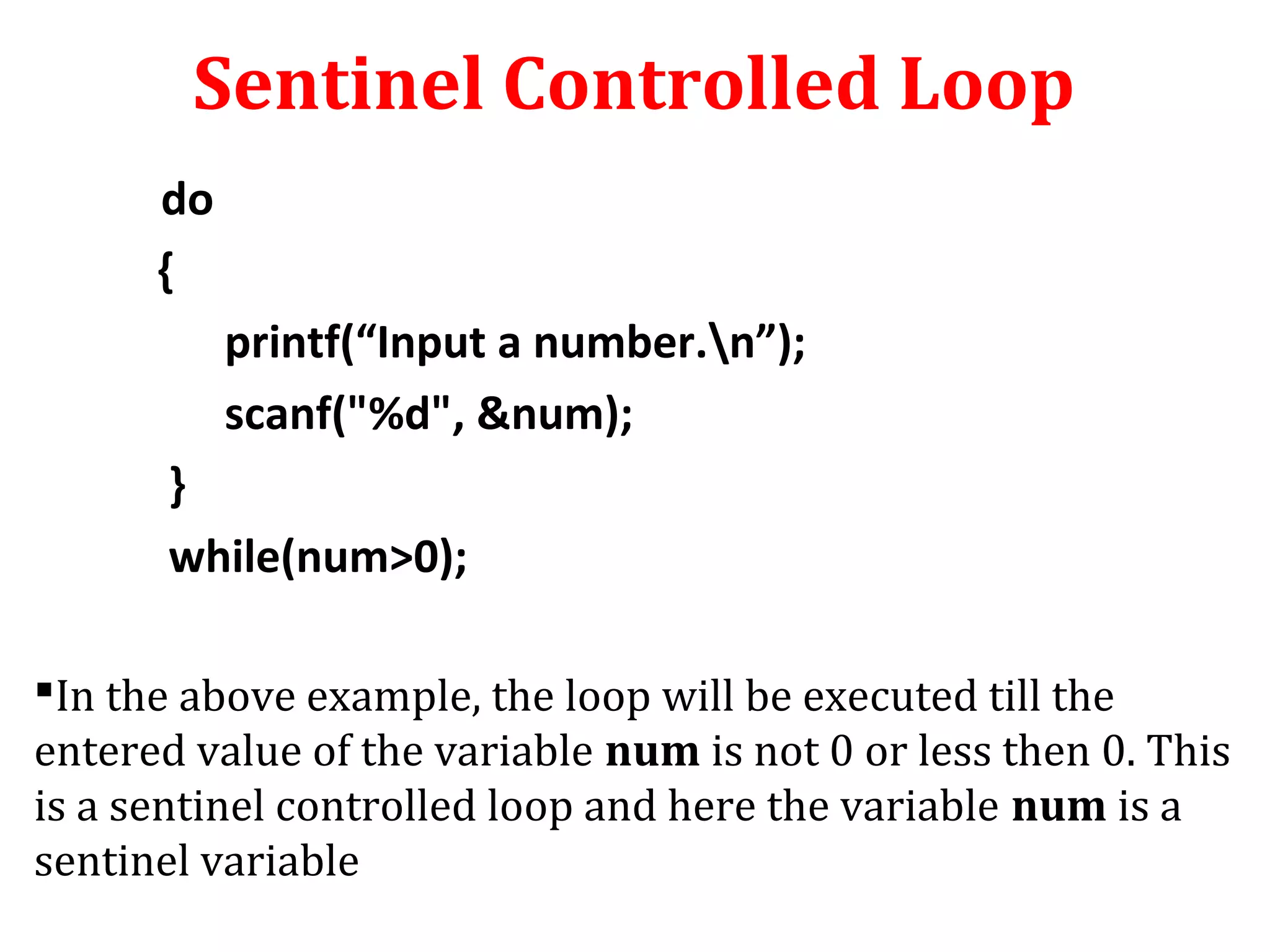
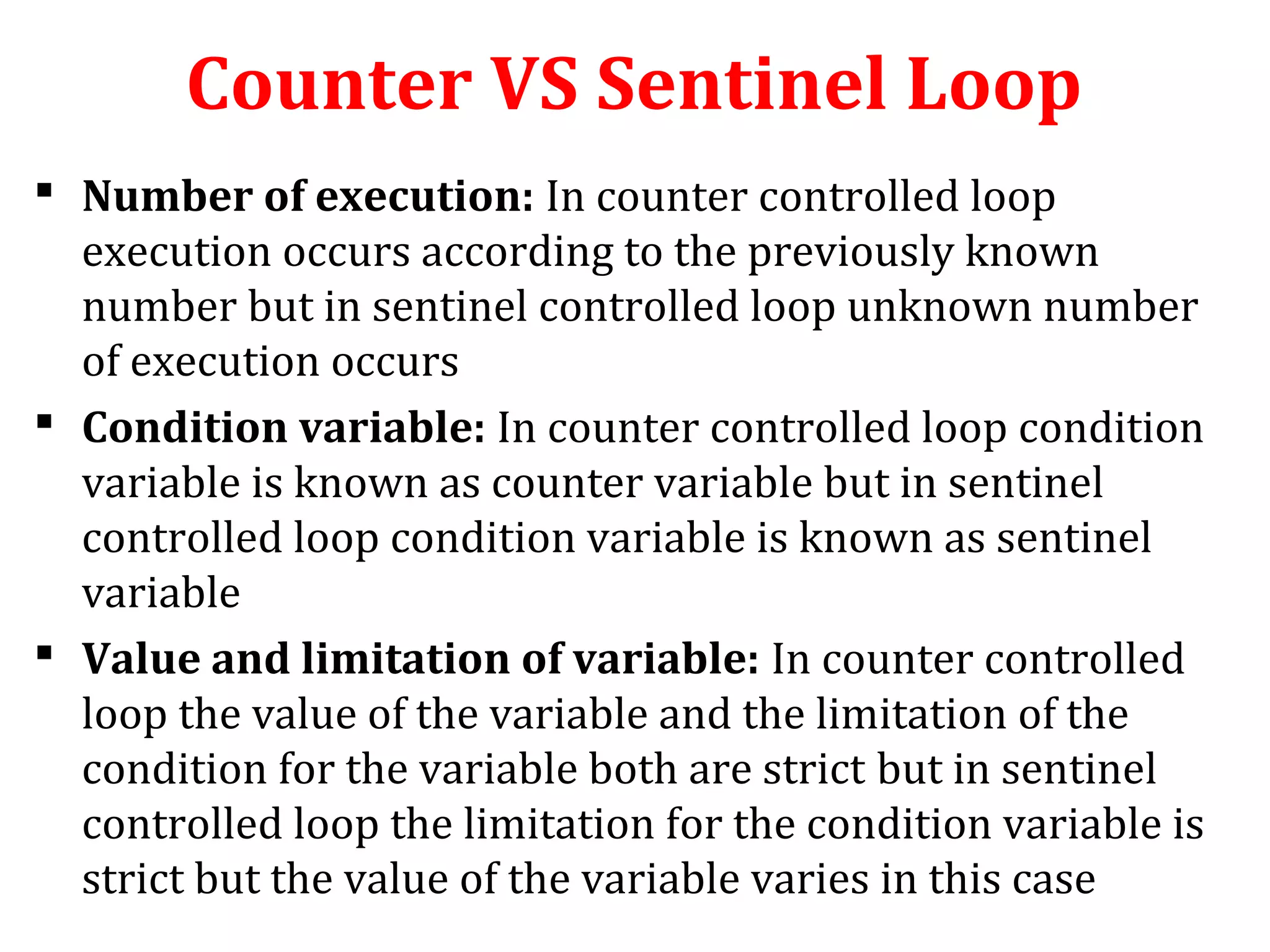
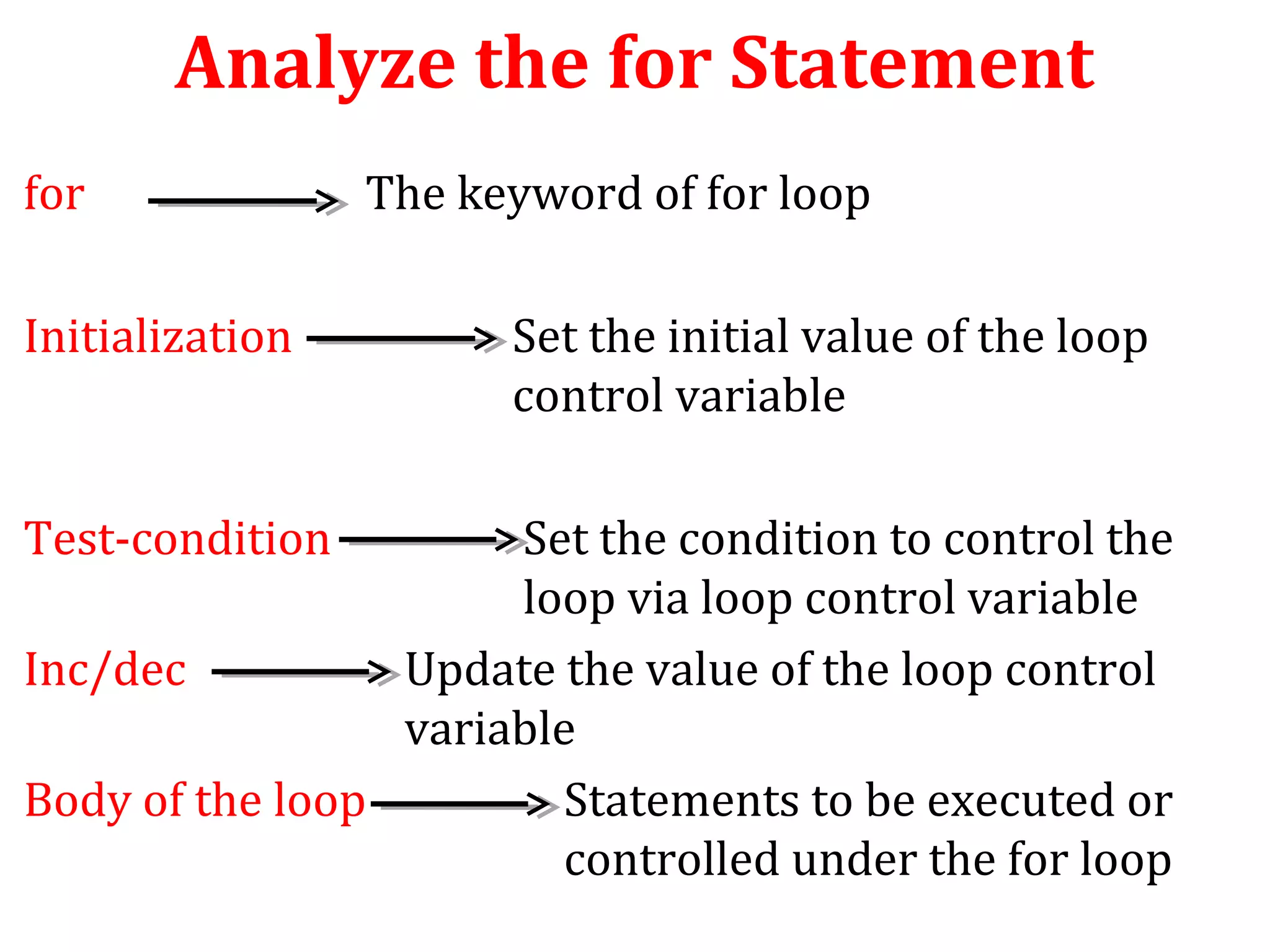
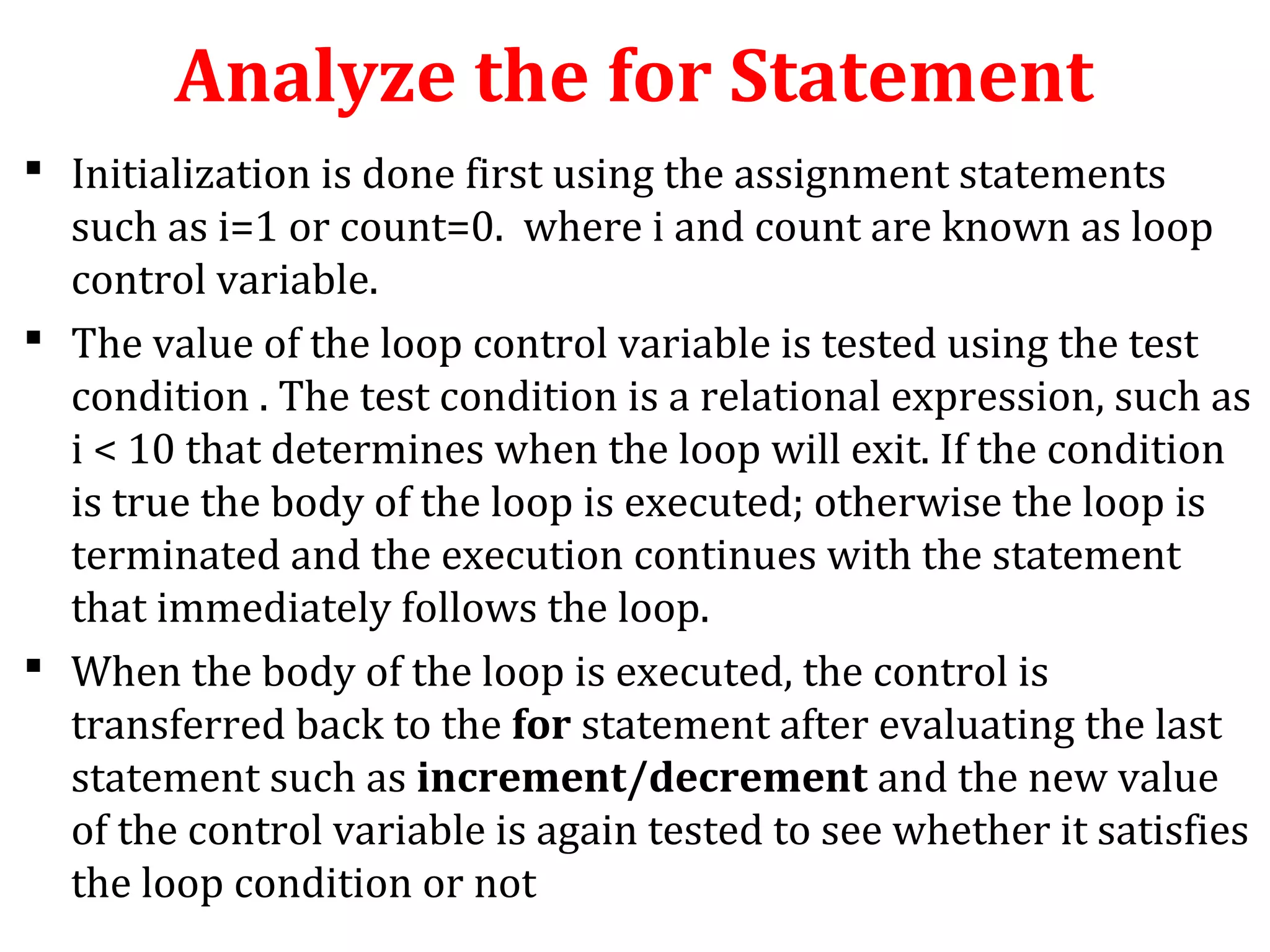
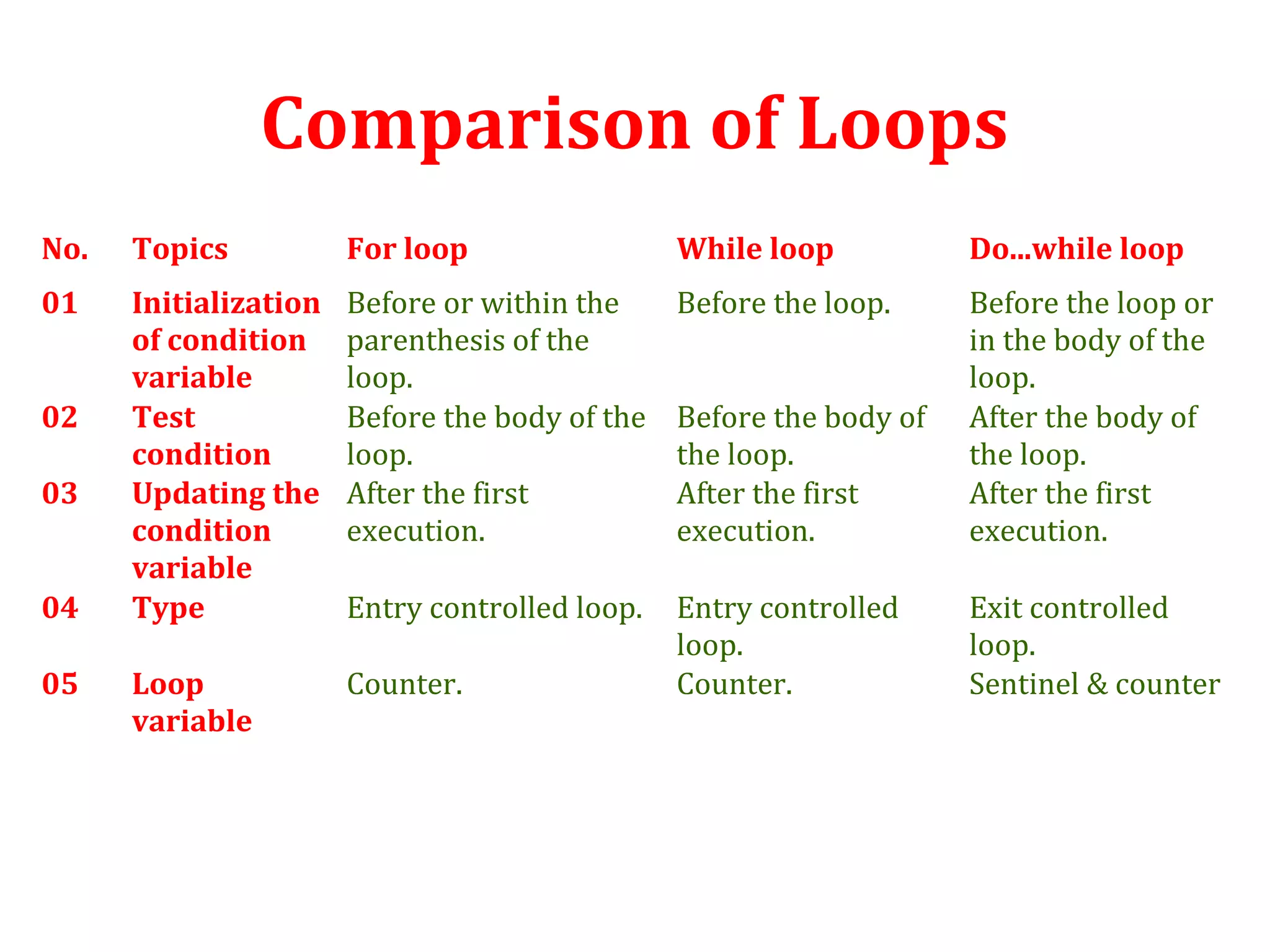
The document discusses different types of loops in programming languages. It defines looping as repetitively executing a sequence of statements, which is an important concept that allows programs to repeat tasks. There are two main types of loops - entry controlled loops where the test condition is checked before the loop body executes, and exit controlled loops where the test is checked after execution. Common loops in C include the for, while, and do-while loops. The for loop is entry controlled and uses a counter variable, while the while and do-while can use counters or sentinel values and are entry and exit controlled respectively. Selecting the right loop depends on pre-test or post-test needs as well as whether the number of repetitions is known.