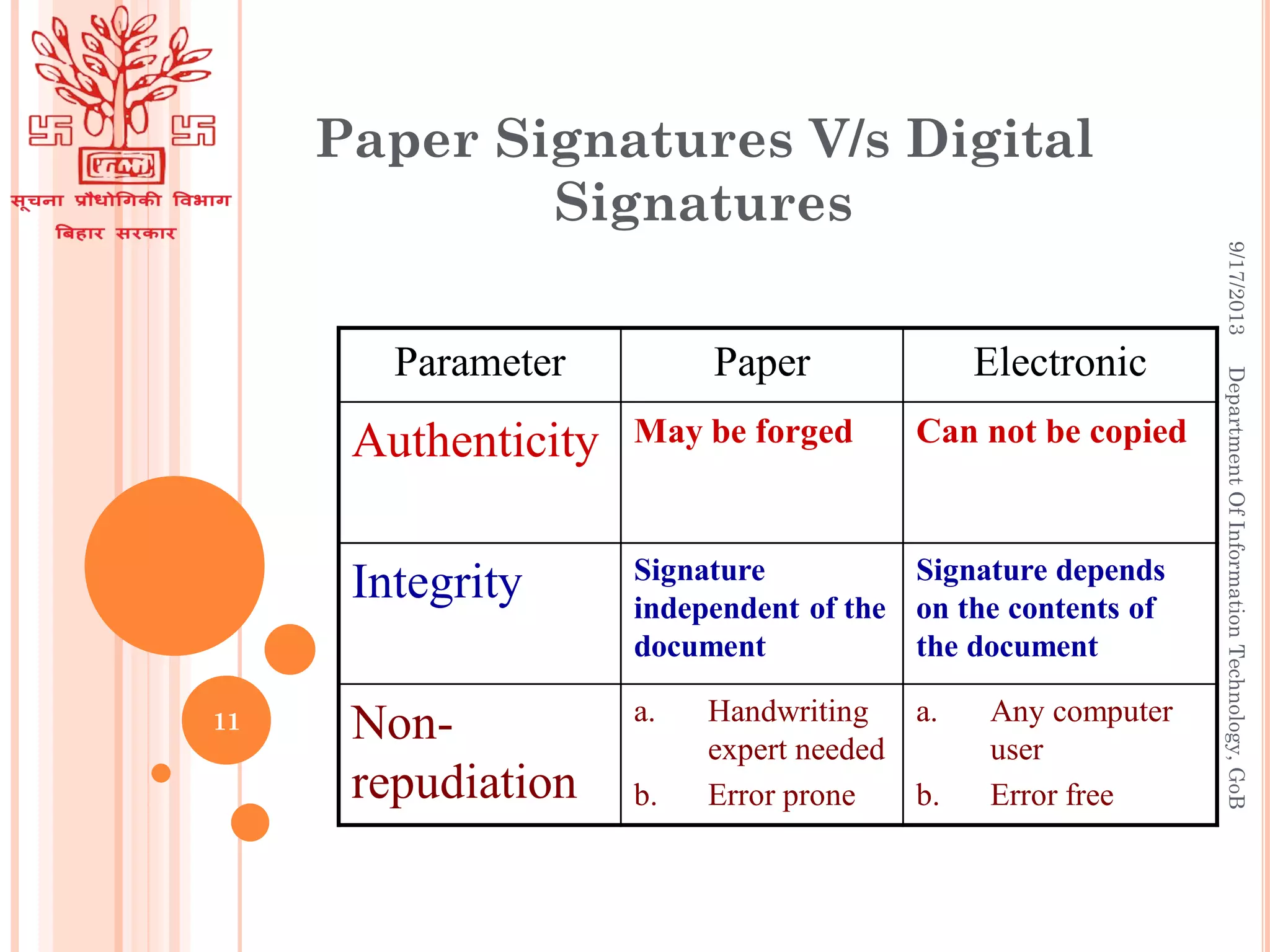
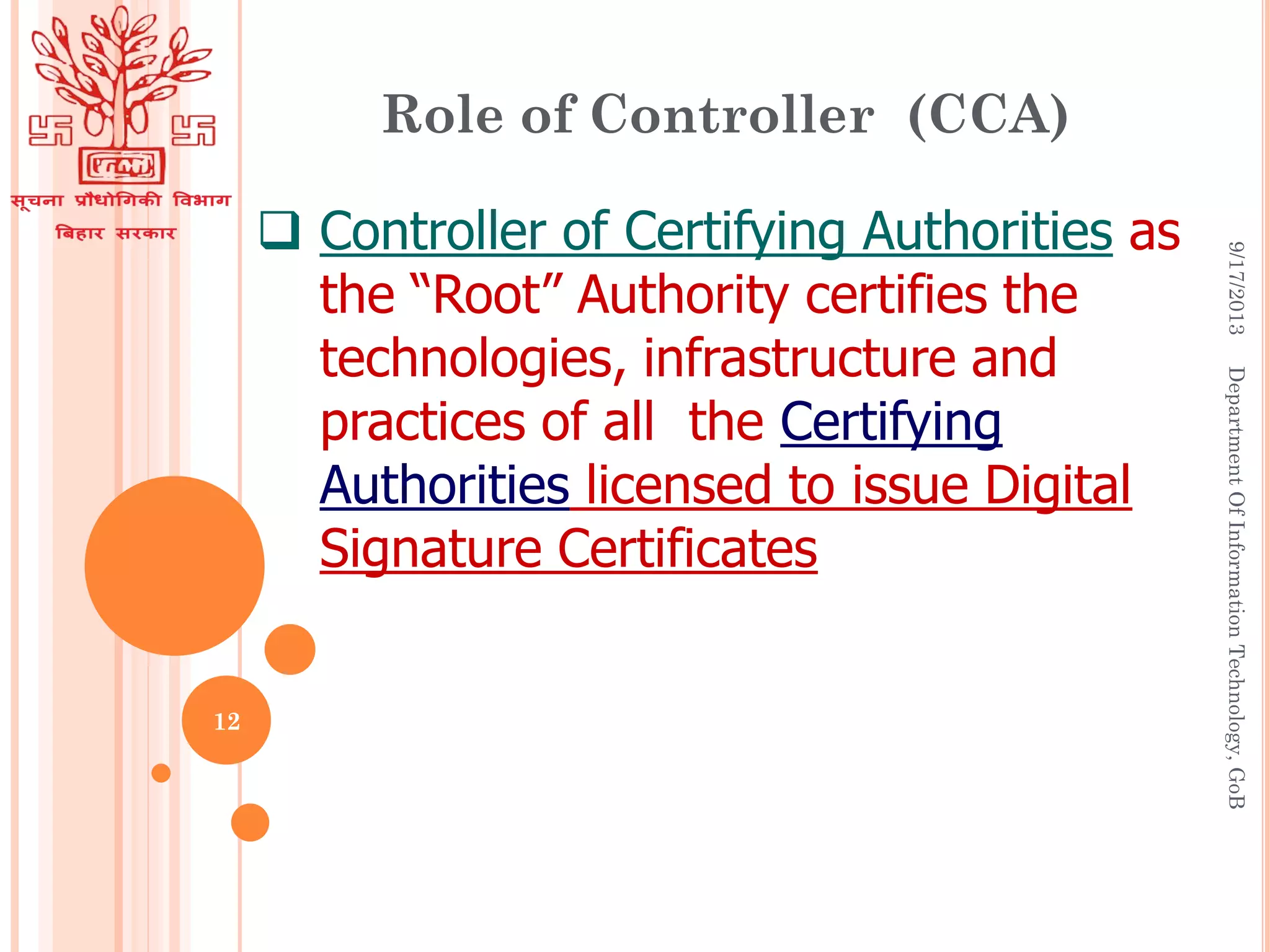
Digital signatures provide authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation for electronic documents and allow for secure e-governance and e-commerce using the internet. A digital signature is created using a private key to sign a message, and the signature can be verified using the corresponding public key. Digital signatures employ asymmetric cryptography and consist of key generation, signing, and verification algorithms. Hardware tokens like smart cards and USB tokens securely store private keys to generate digital signatures on documents. The Controller of Certifying Authorities licenses and regulates certification authorities in India to issue digital signature certificates.


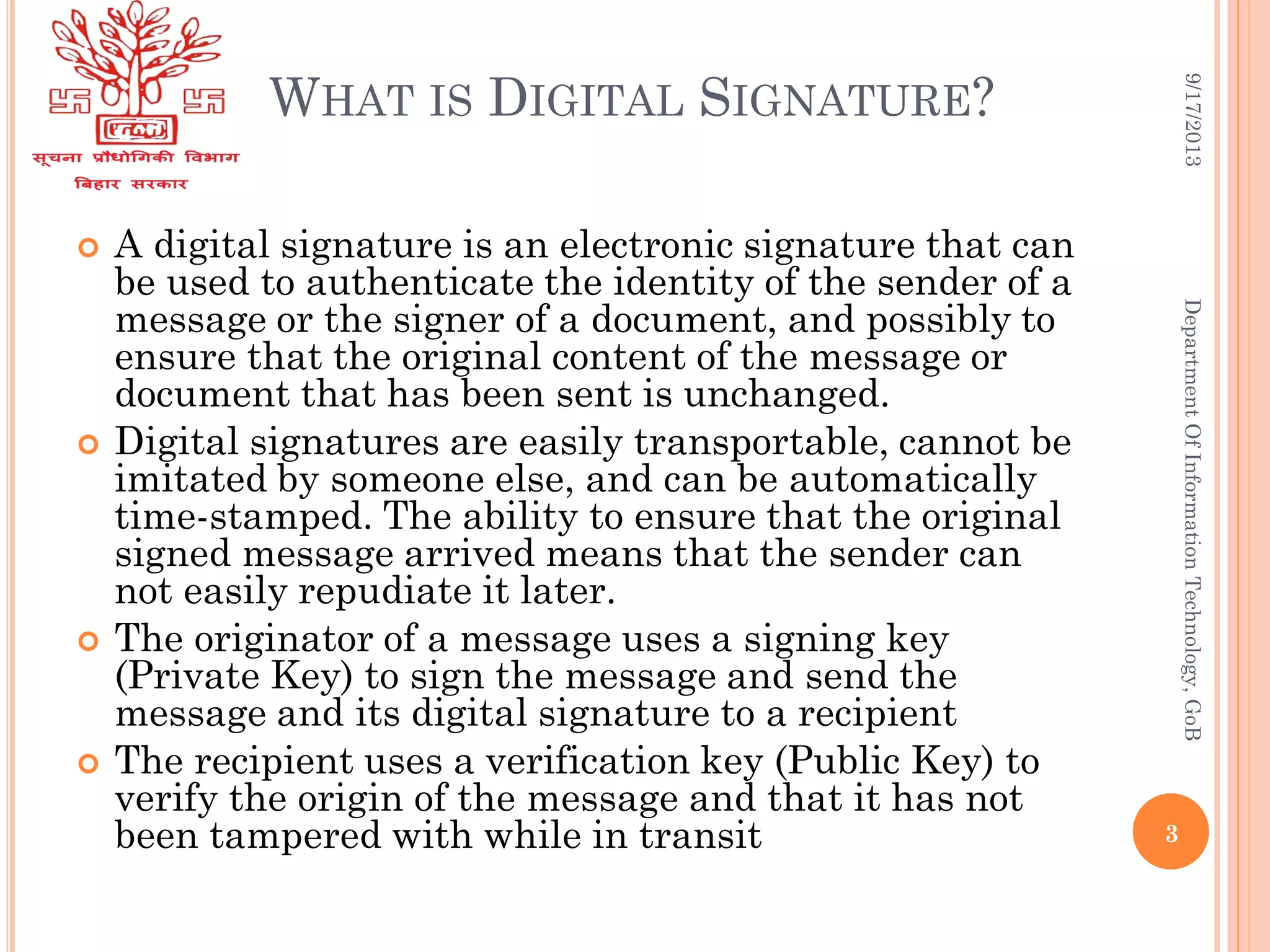

![DIGITAL SIGNATURES
9/17/2013DepartmentOfInformationTechnology,GoB
Each individual generates his own key pair
[Public key known to everyone
&
Private key only to the owner]
Private Key – Used for making Digital Signature
Public Key – Used to verify the Digital Signature
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalsignatures-130918004306-phpapp01/75/Digital-signatures-5-2048.jpg)