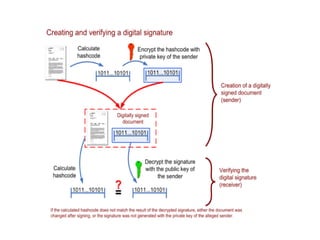
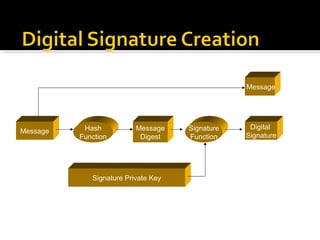
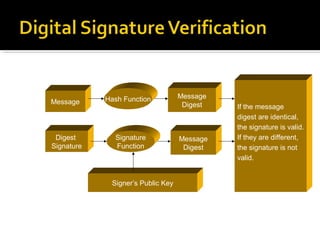
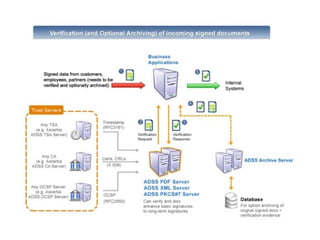
The document discusses the importance of digital signatures in e-business, highlighting their role in preventing counterfeiting and multiple spending. It defines digital signatures, outlines their properties, and explains the processes of digital signature creation and verification, emphasizing their ability to ensure authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation. Additionally, it addresses the benefits of digital signatures, such as source authentication and message integrity, as well as drawbacks and best practices for secure usage.






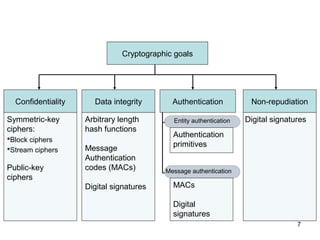







![Digital SignaturesDigital Signatures
Each individual generates his own key pair
[Public key known to everyone
&
Private key only to the owner]
Private Key – Used for making Digital Signature
Public Key – Used to verify the Digital Signature](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digsig-150305202903-conversion-gate01/85/Digital-signature-15-320.jpg)