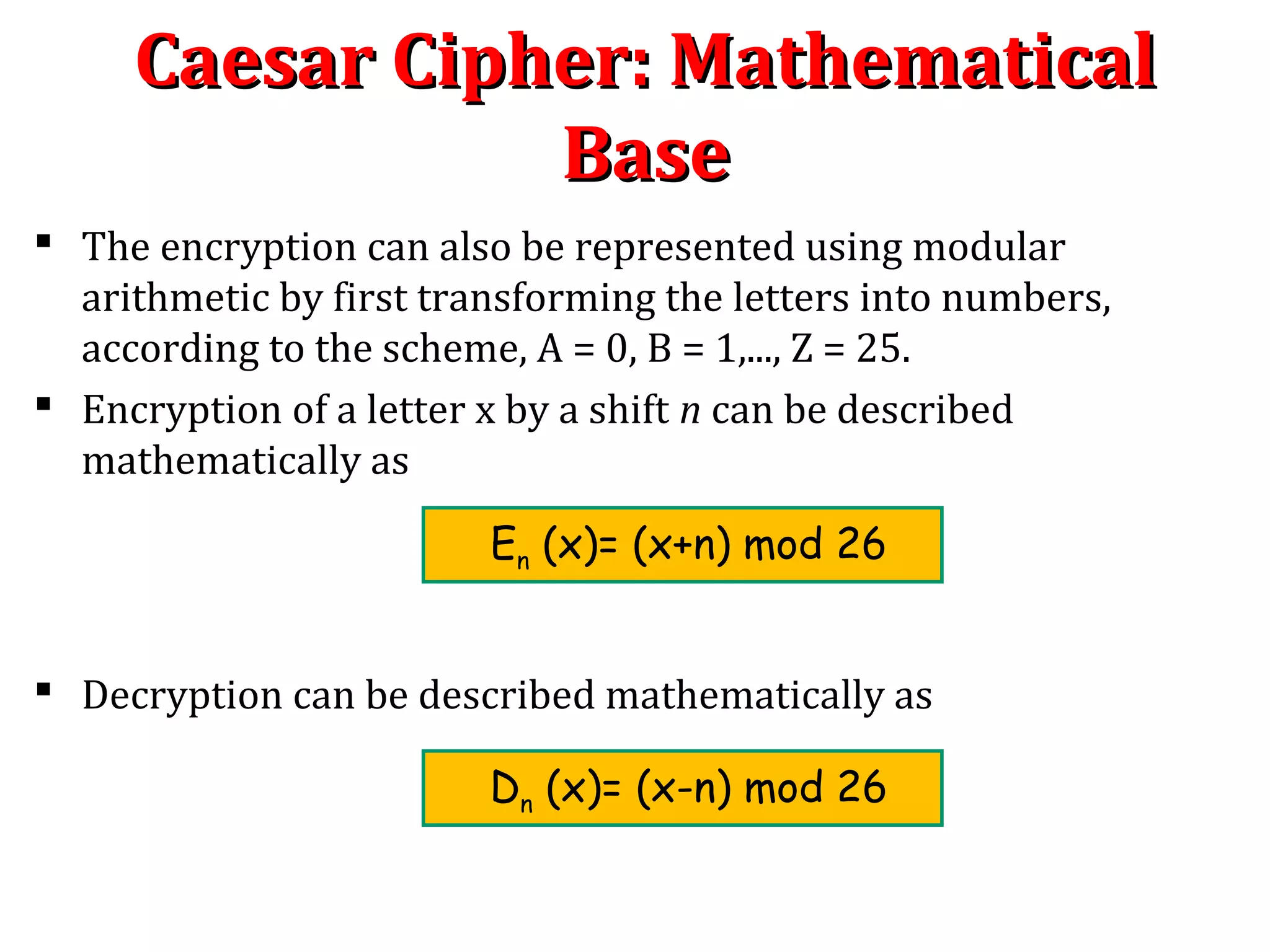
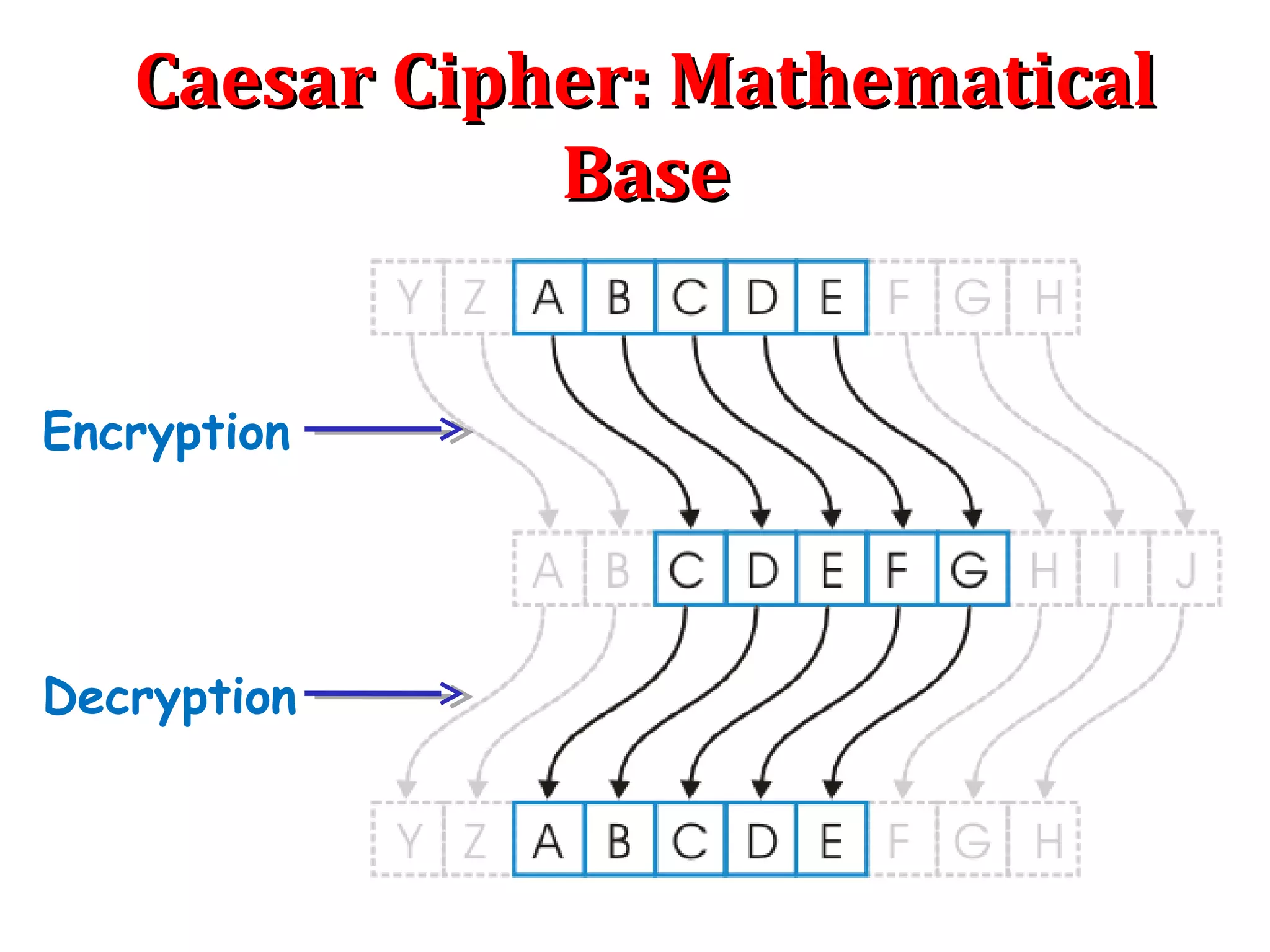
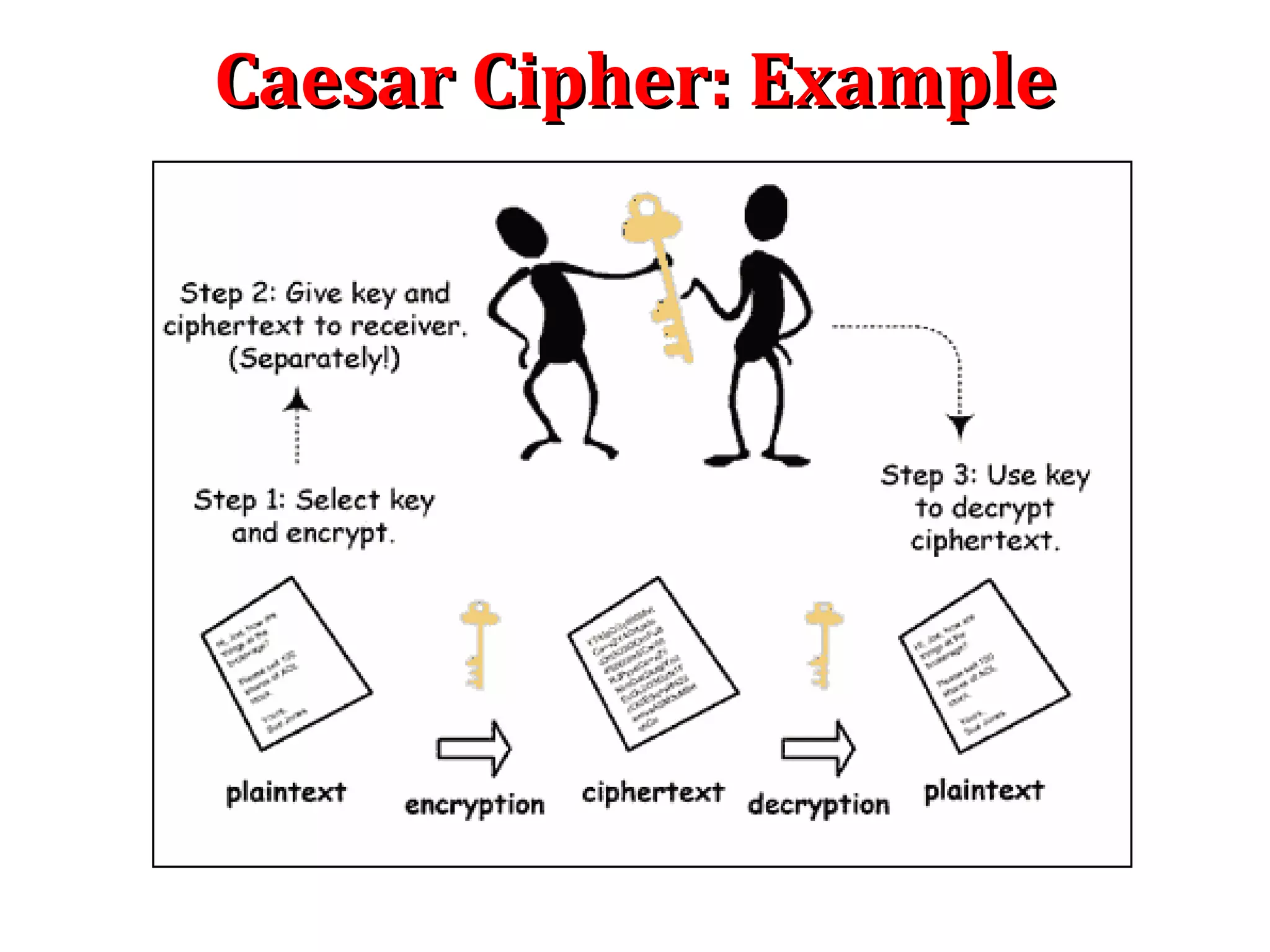
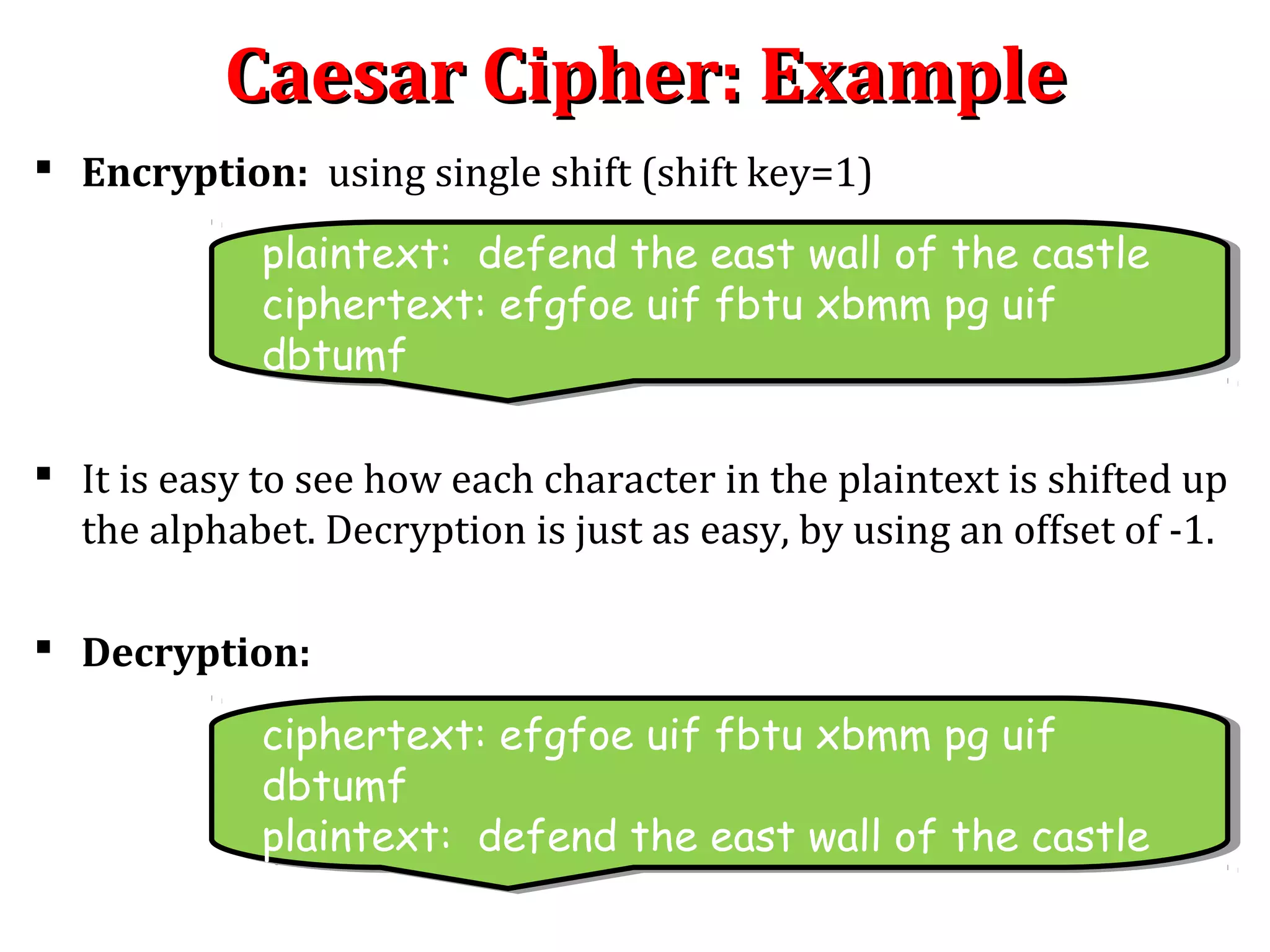
The Caesar cipher is a simple encryption technique where each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example, with a shift of 1, A would be replaced by B, and so on. It is one of the earliest known ciphers and is still used in modern ROT13 encryption. While simple, the Caesar cipher has no security against decryption by brute force since there are only 26 possible keys. More complex ciphers are needed to securely encrypt messages.