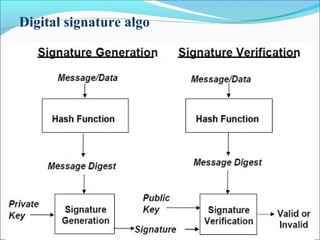
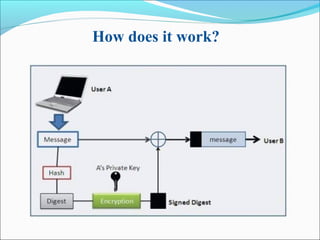
This document summarizes a colloquium on digital signatures presented by Prashant Shekhar. It introduces digital signatures as a way to authenticate electronic documents through a mathematical scheme. It discusses how digital signatures work using public and private keys along with digital certificates from a certification authority. The document also outlines some applications of digital signatures like email, data storage, funds transfer, and software distribution. It concludes by noting advantages like authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation, as well as disadvantages such as expiration of certificates and costs of software.





![Digital certificate
A subscriber of the private key and public key pair makes
the public key available to all those who are intended to
receive the signed messages from the subscriber.[1]
But in case of any dispute between the two sides, there
must be some entity with the receiver which will allow the
receiver of the message to prove that the message was sent
by the subscriber of the key pair. This can be done with the
Digital Signature Certificate.[1]
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prashant-170222165106/85/Digital-Signature-6-320.jpg)