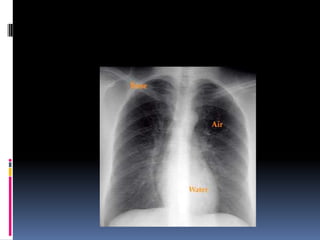
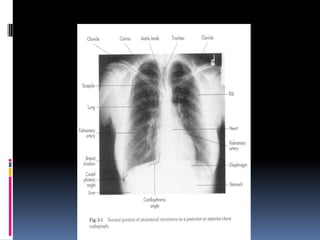
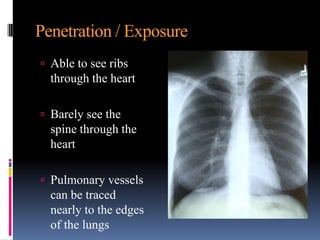
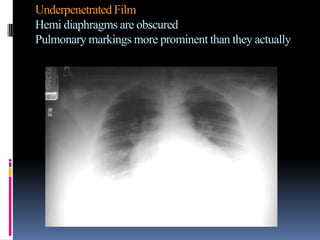
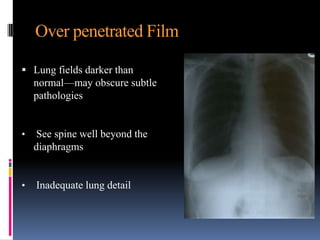
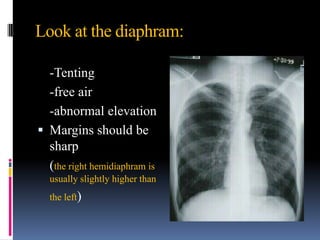
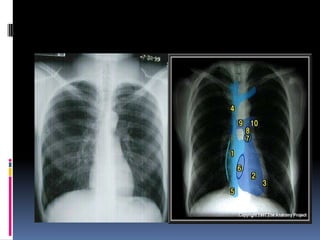
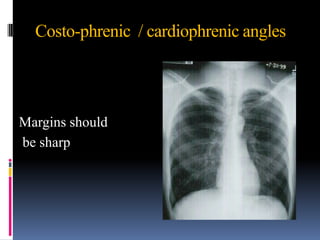
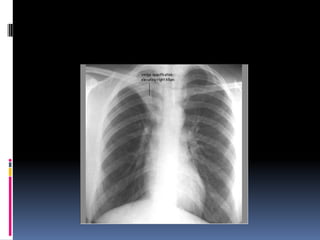
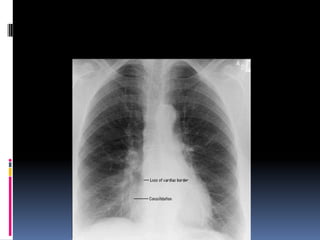
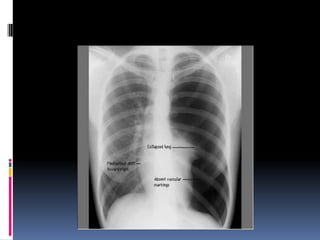
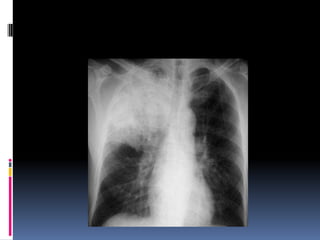
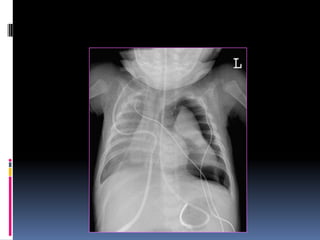
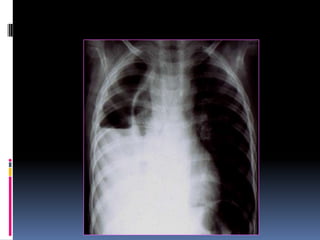
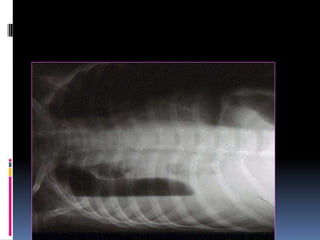
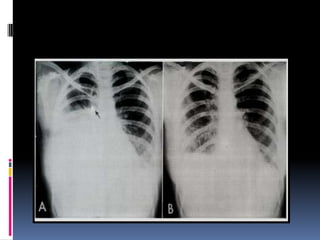
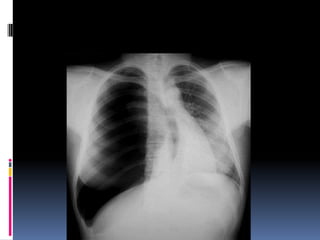
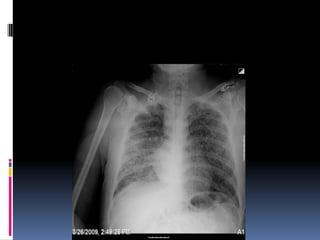
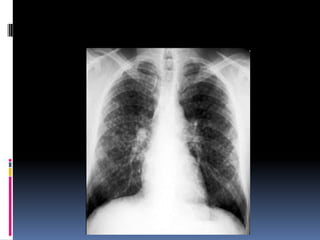
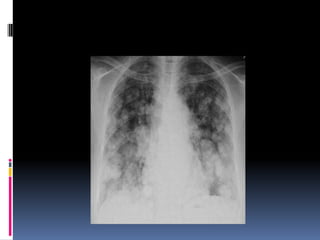
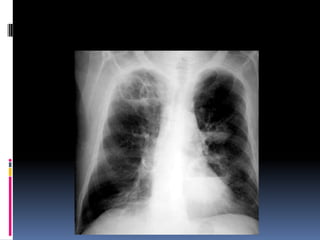
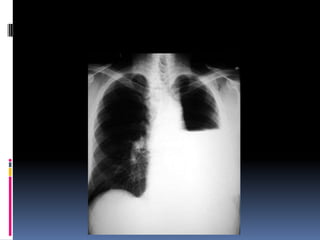
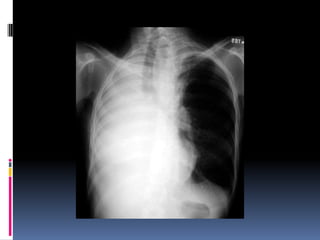
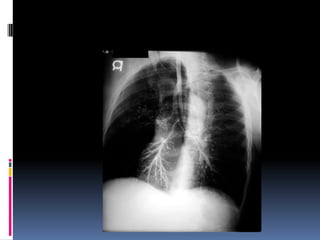
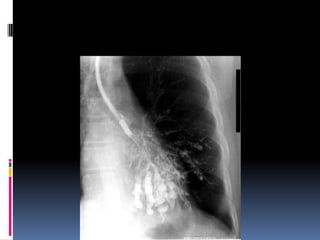
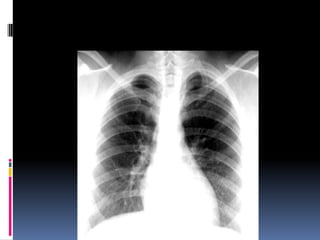
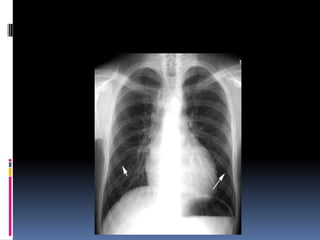
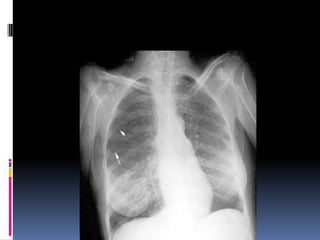
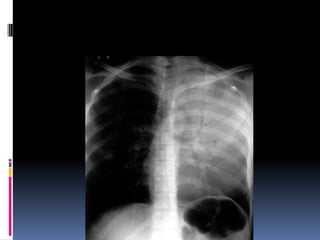
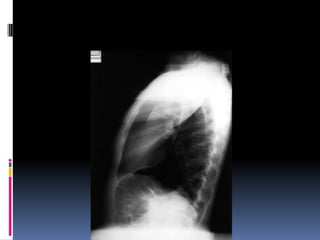
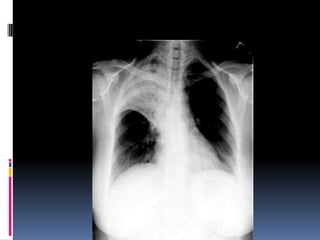
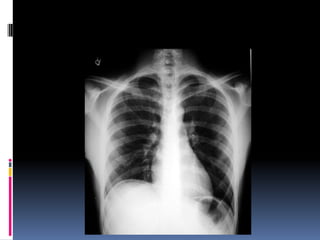
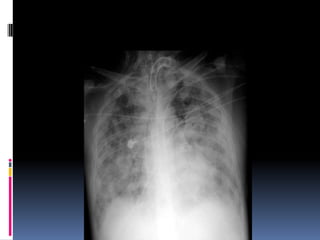
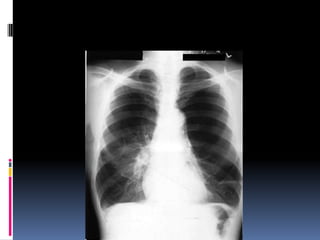
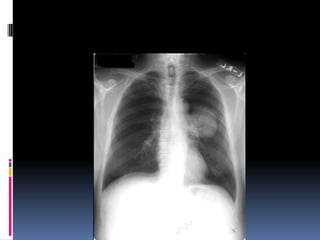
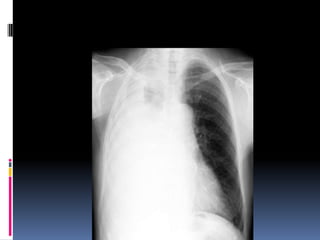
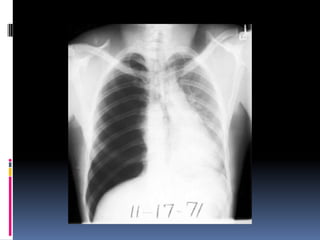
The document discusses how chest X-rays work and what they can show. Different tissues absorb X-rays at different rates, with bone appearing white, soft tissue grey, and air black. A PA view has X-rays enter through the back while an AP view is from the front. Proper exposure level is needed to see details in the lungs and heart without being over or under penetrated. Positioning is important to evaluate symmetry and check for abnormalities in soft tissues and bones like the ribs, spine, diaphragm and heart. Lung fields and costophrenic angles should have sharp margins and be checked for issues like infiltrates or masses.