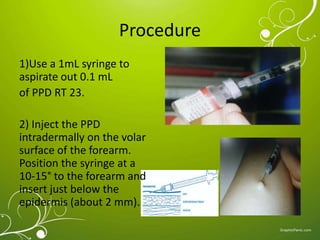
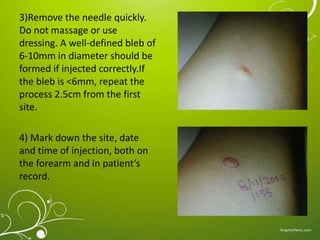
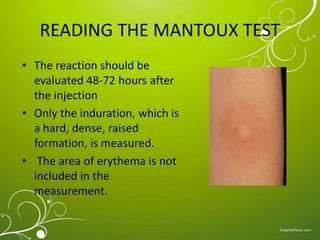
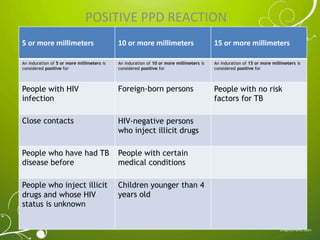
The Mantoux test, also known as the tuberculin skin test, is used to determine if a person has been infected with tuberculosis. It involves injecting a small amount of purified protein derivative into the skin on the lower arm. After 48 to 72 hours, a health care worker measures any induration, or hard, raised area that develops on the arm, which can indicate infection. A positive result is based on the size of the induration and the person's risk factors. While very accurate, the test can sometimes produce false positives or negatives, requiring further evaluation and testing to diagnose active TB disease.