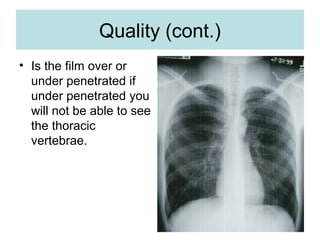
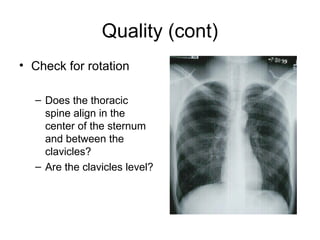
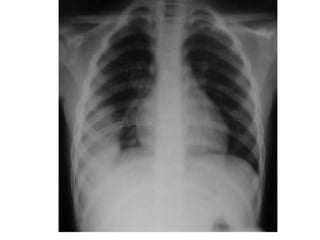
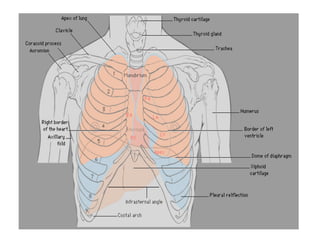
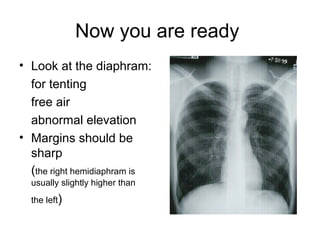
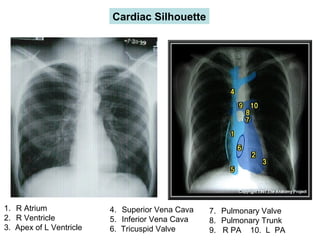
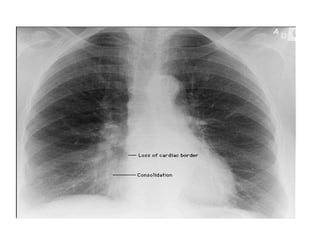
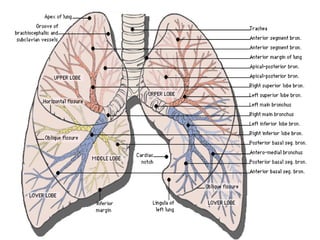
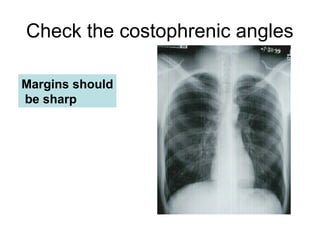
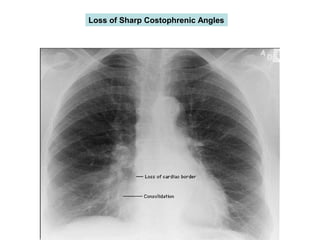
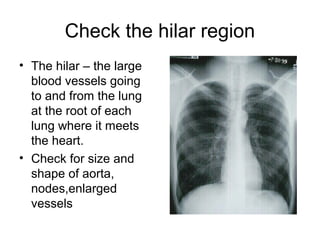
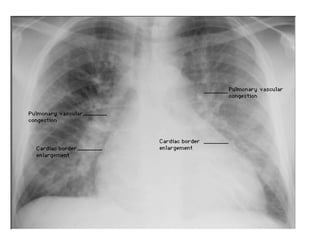
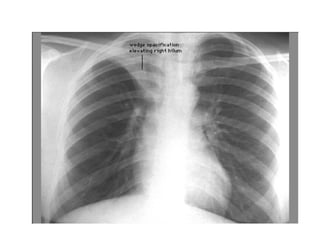
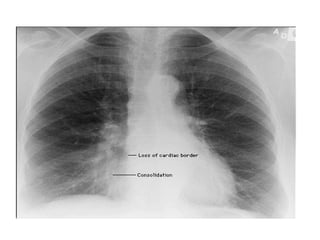
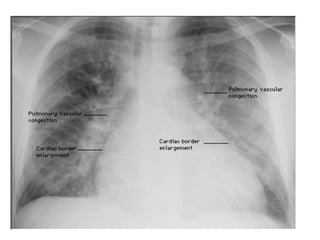
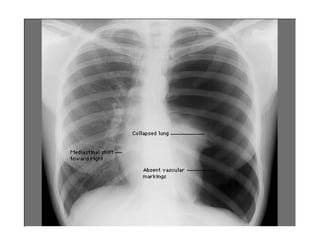
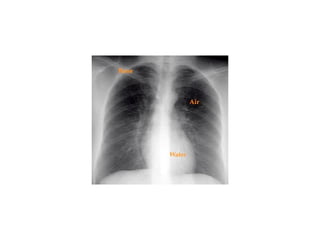
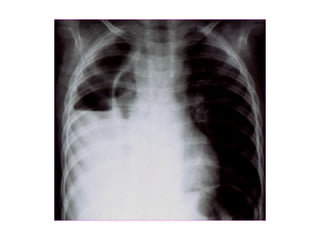
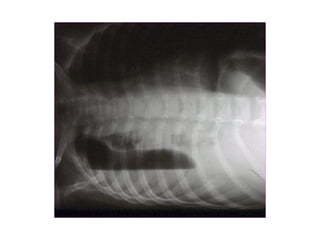
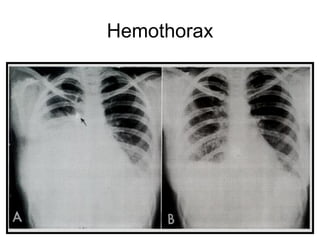
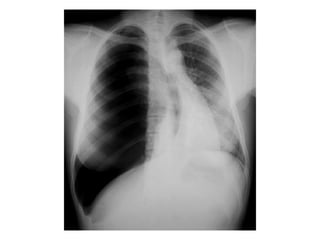
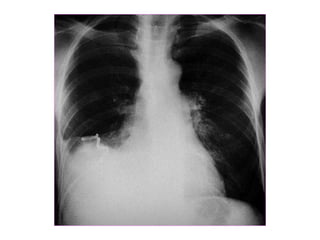
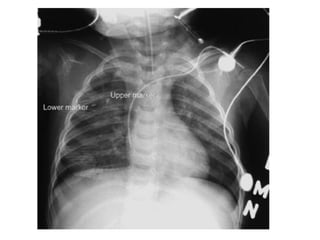
This document provides guidance on interpreting basic chest x-rays by systematically checking several key areas. It describes how x-rays produce shadows of internal body structures and how different tissues appear on film. The interpreter is advised to first check film quality, orientation and inspiration before examining the diaphragm, heart, costophrenic angles, hilar region, and lung fields for any abnormalities.