Embed presentation



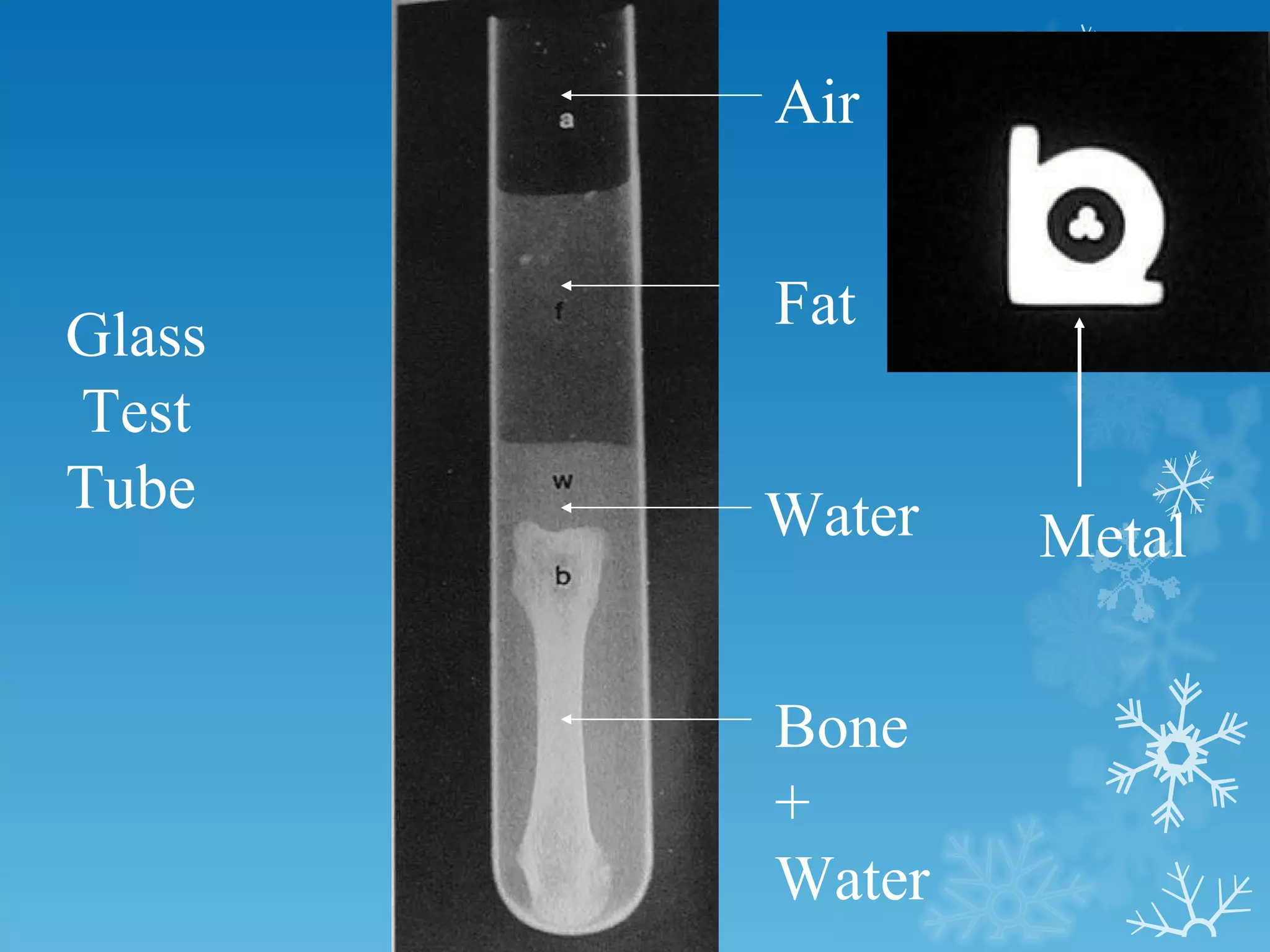
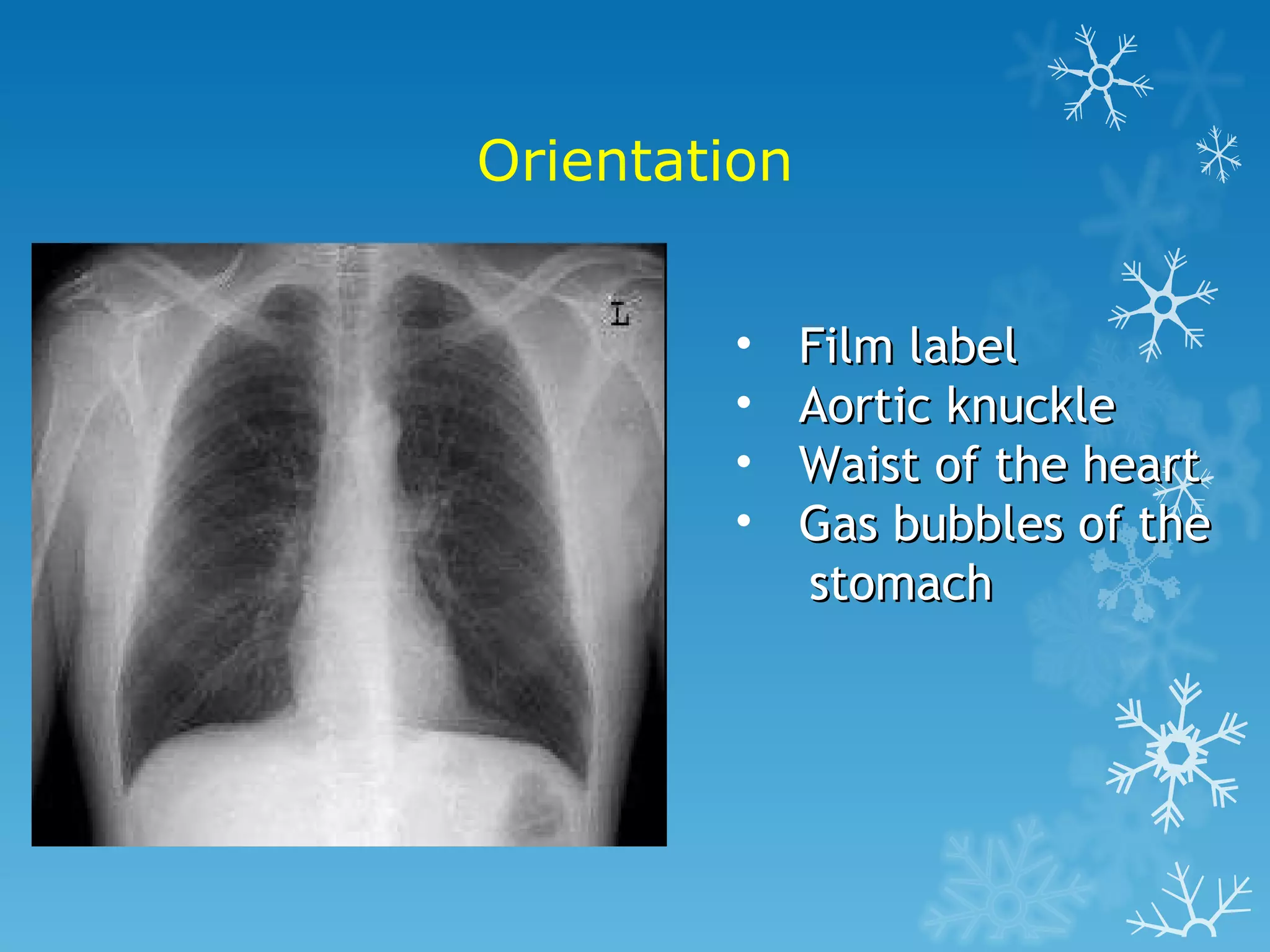
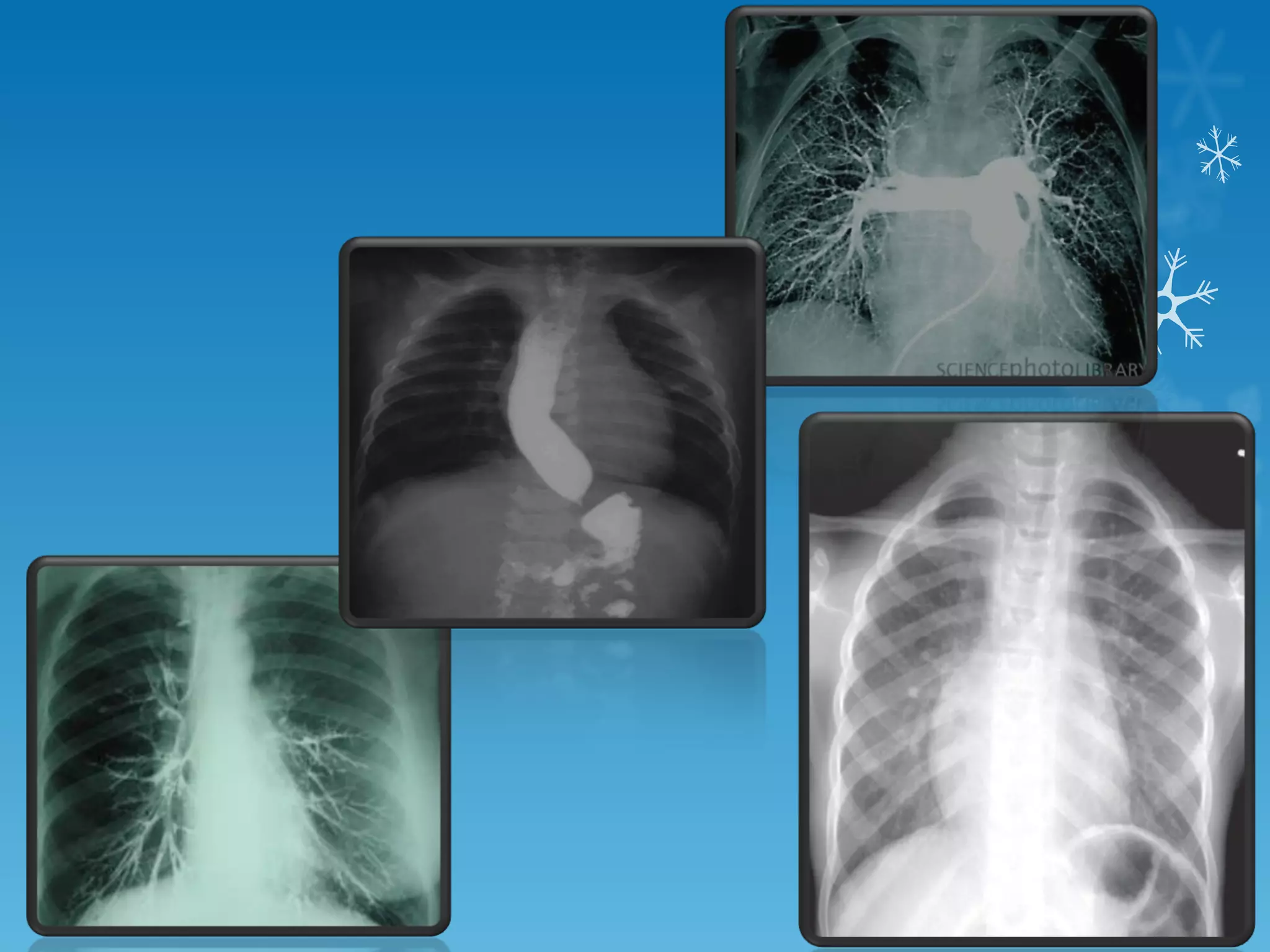

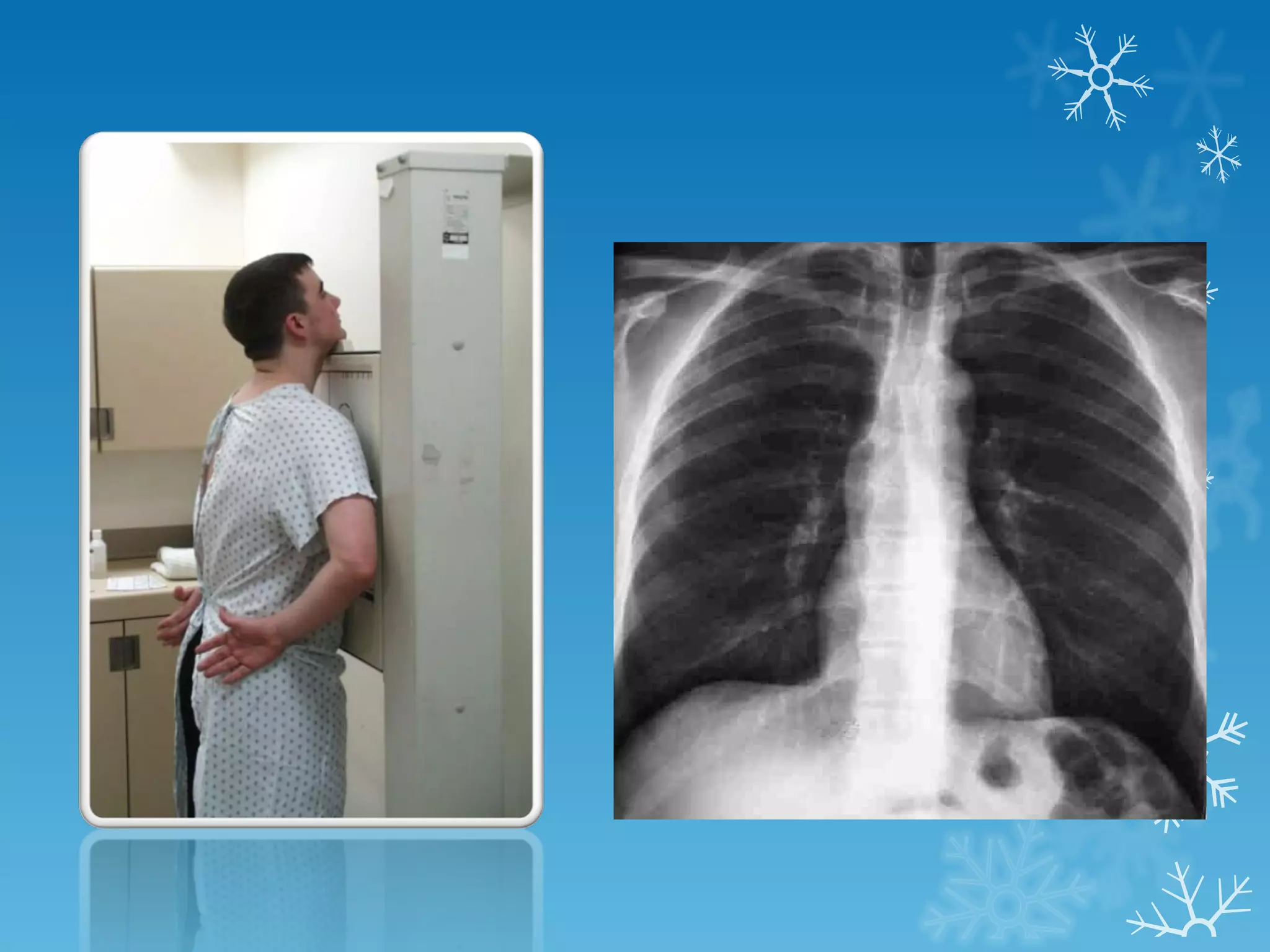
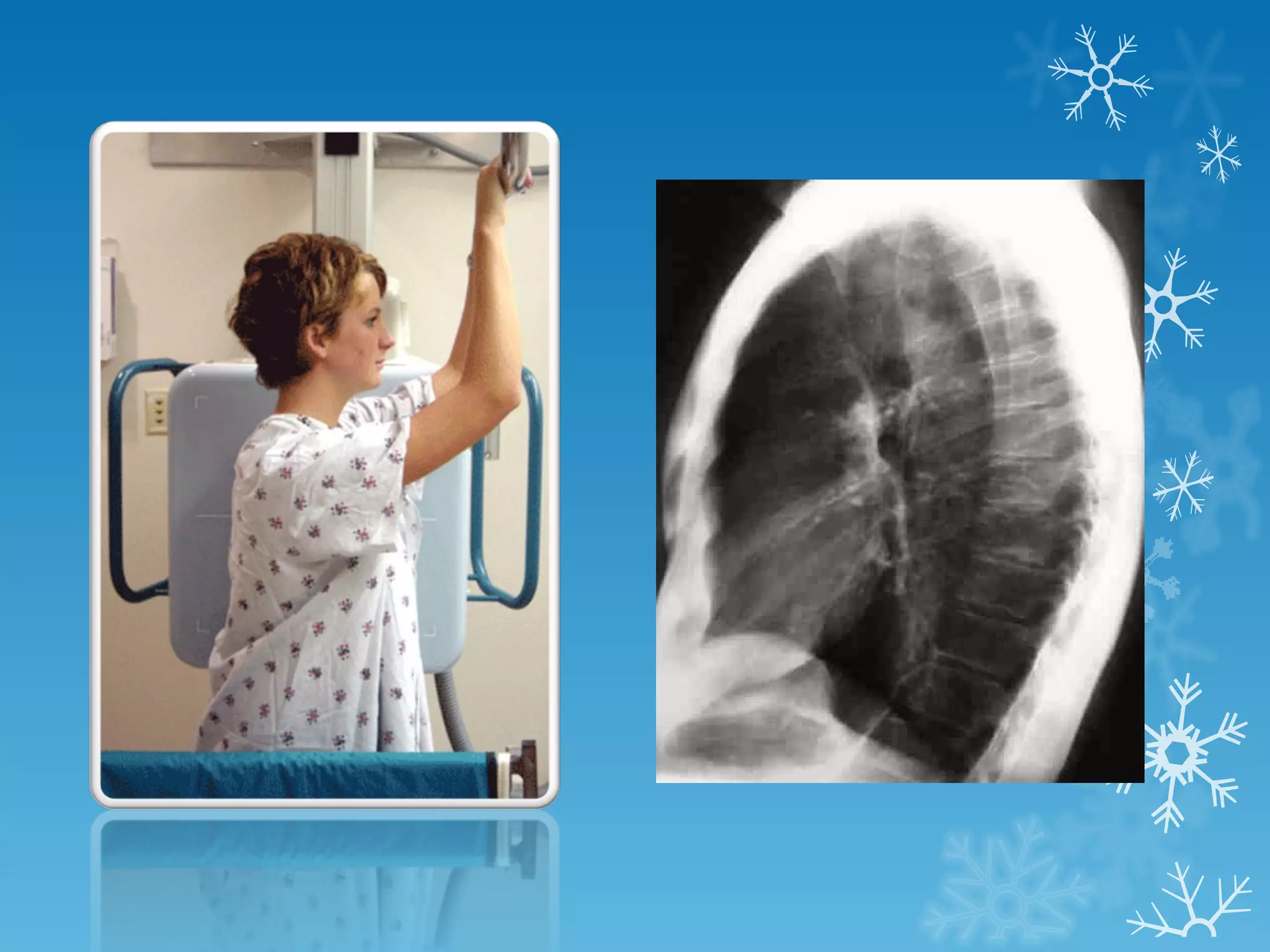
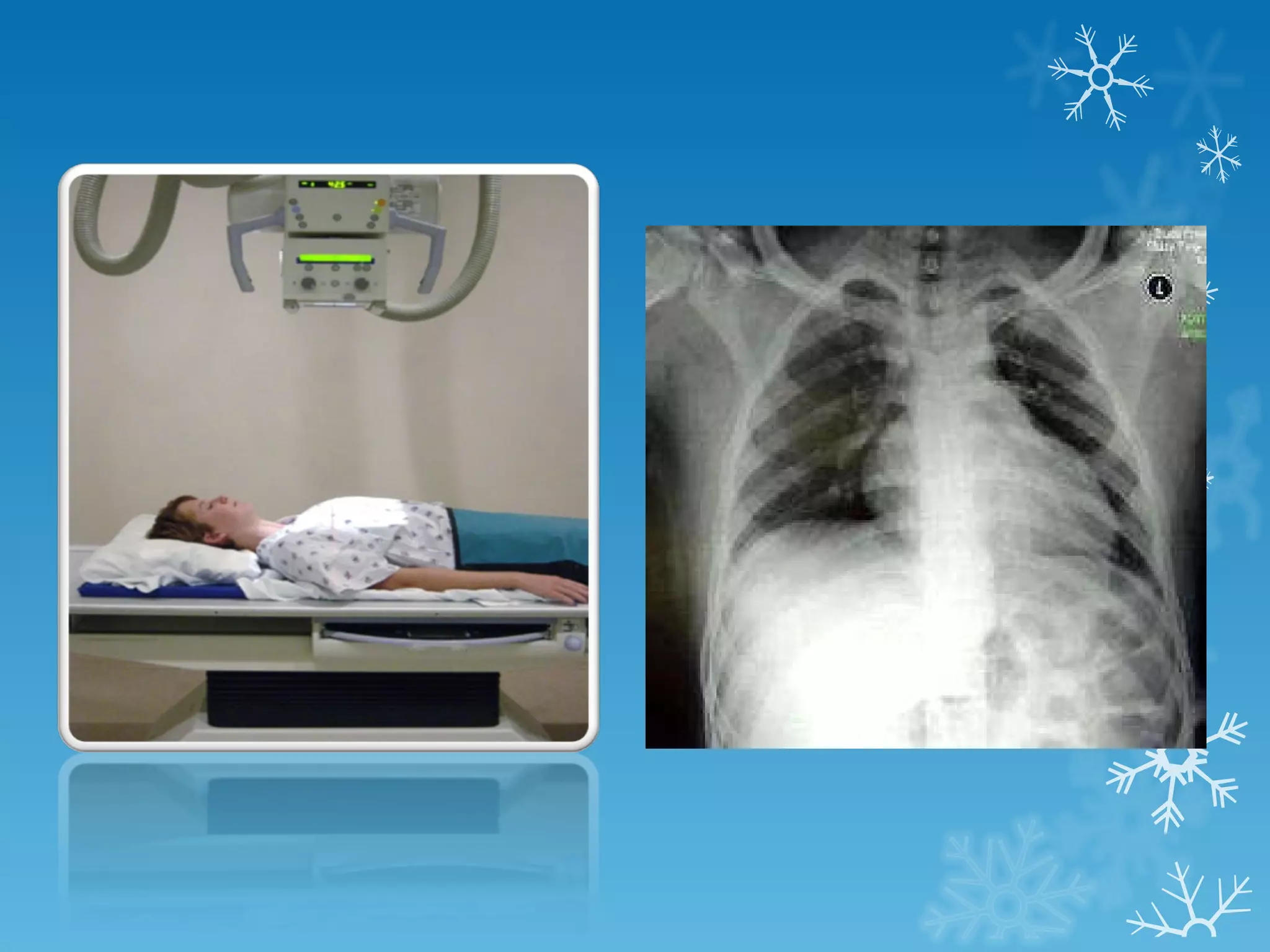
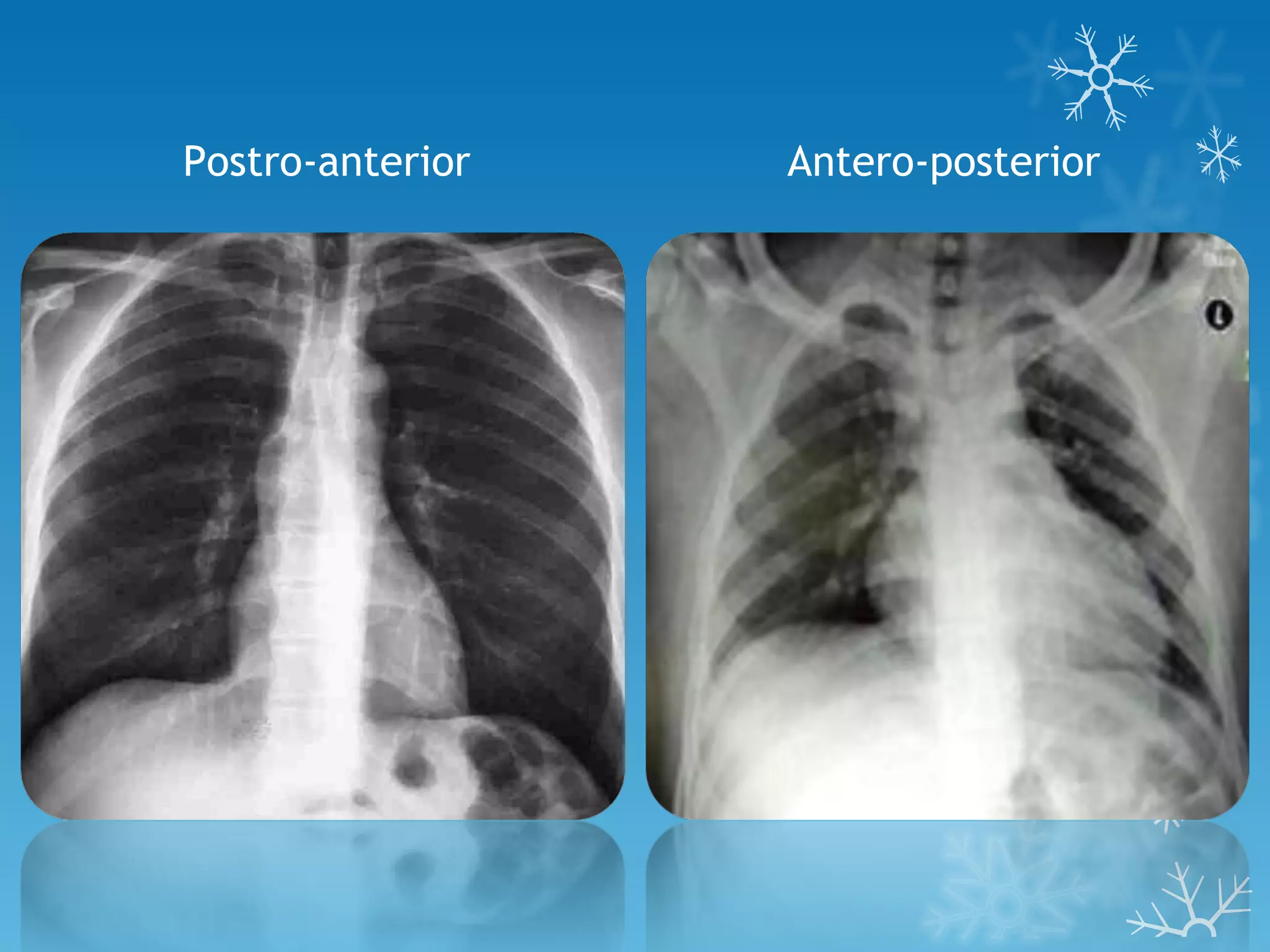
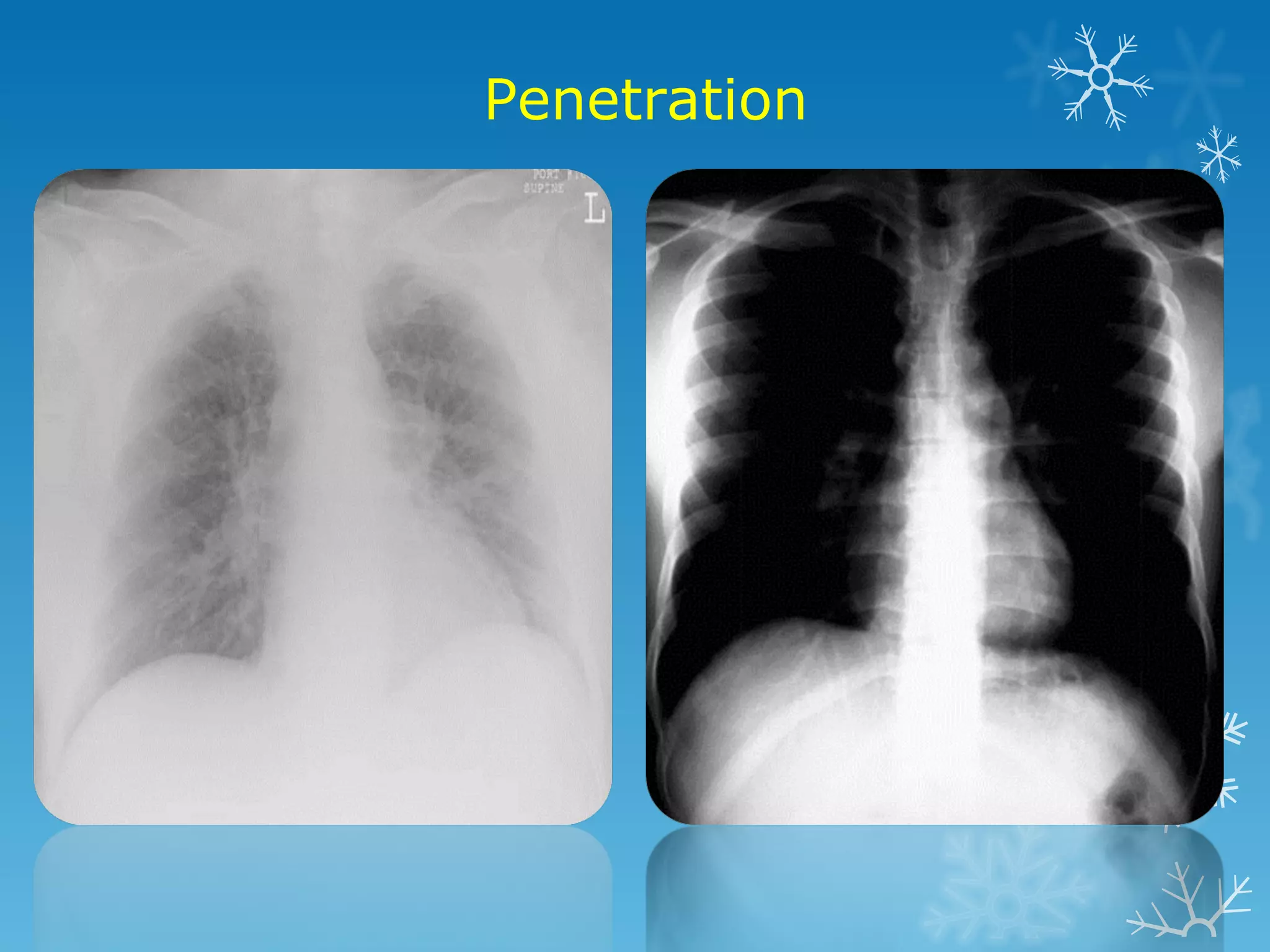
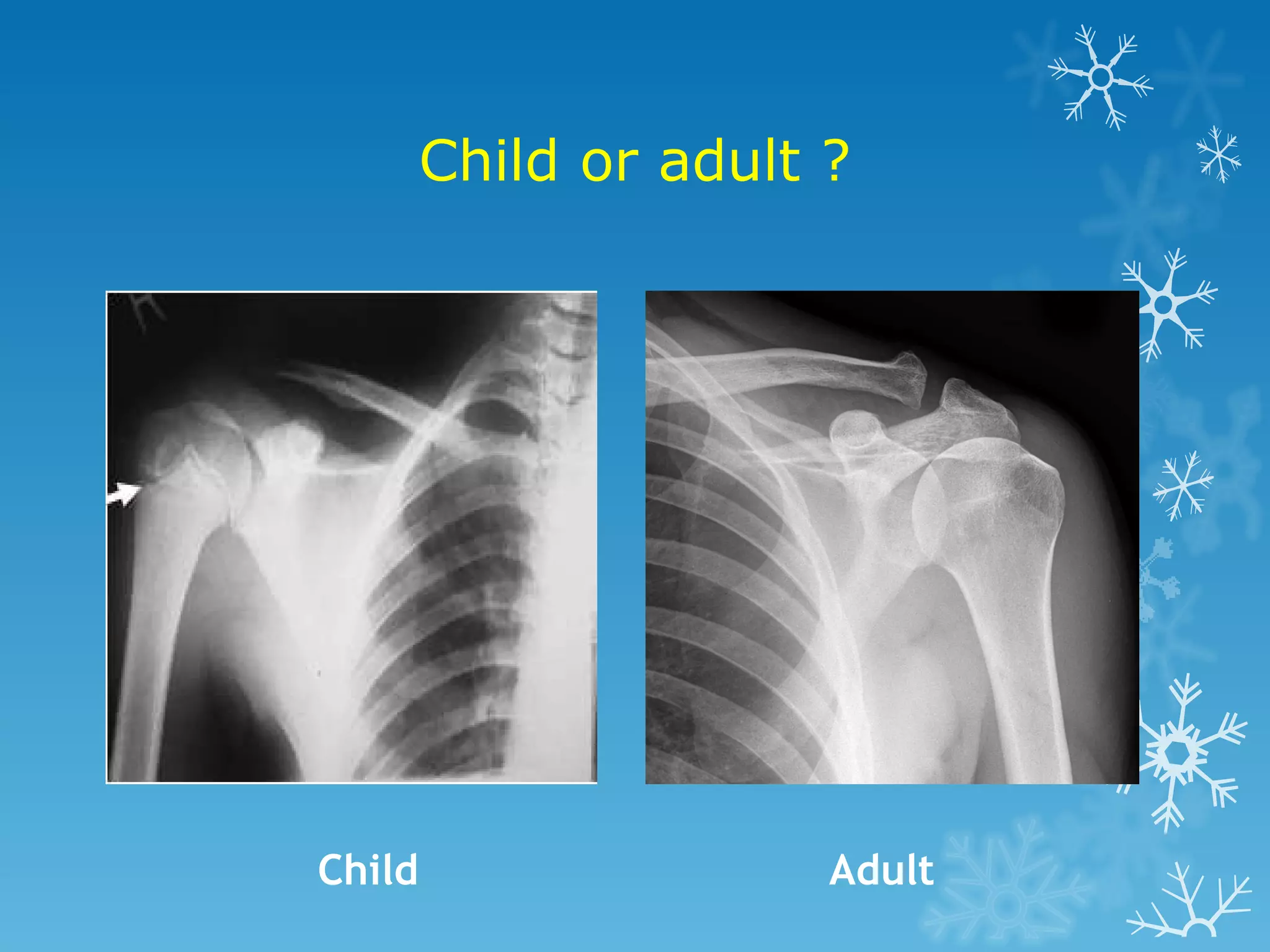
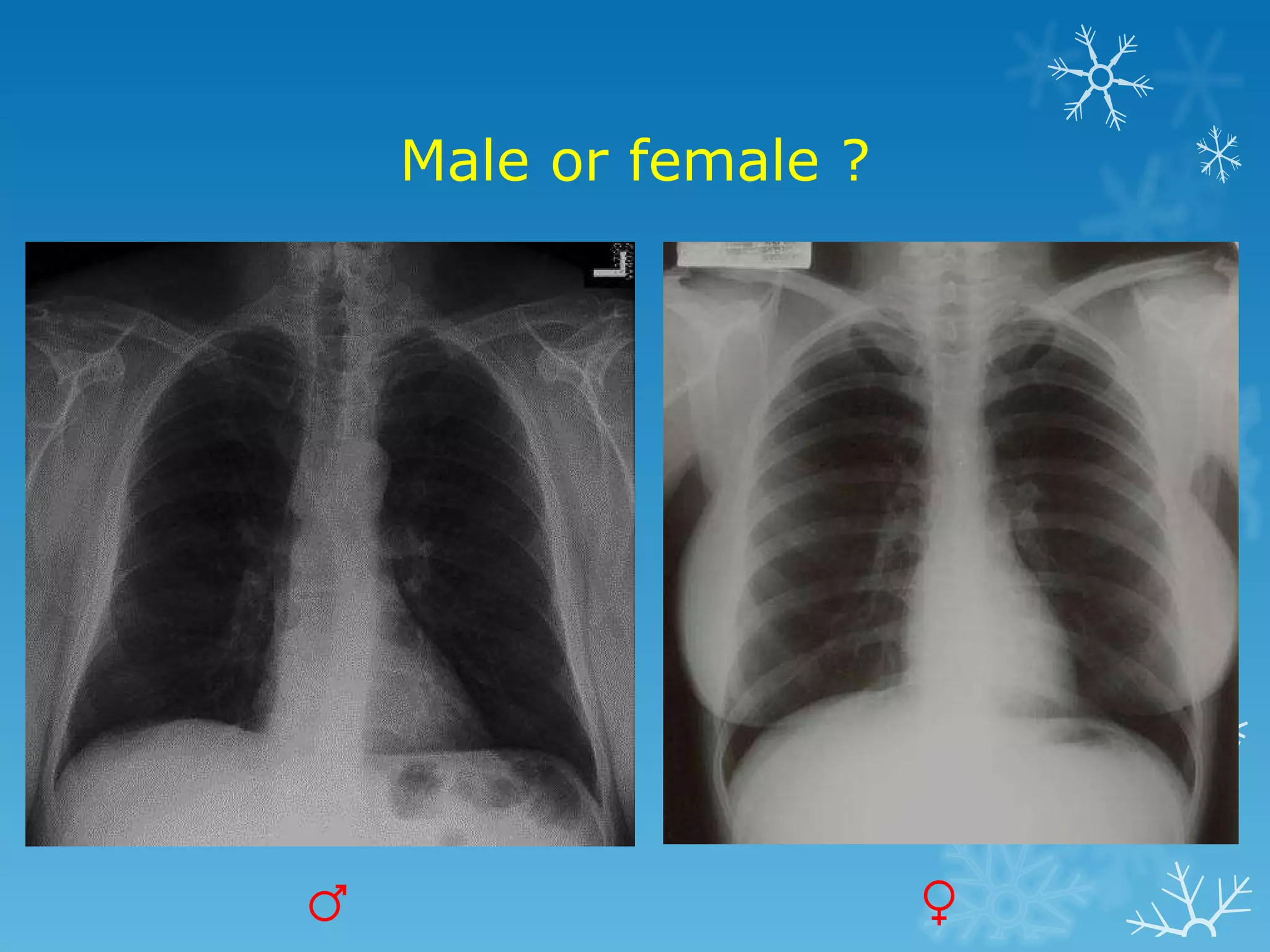
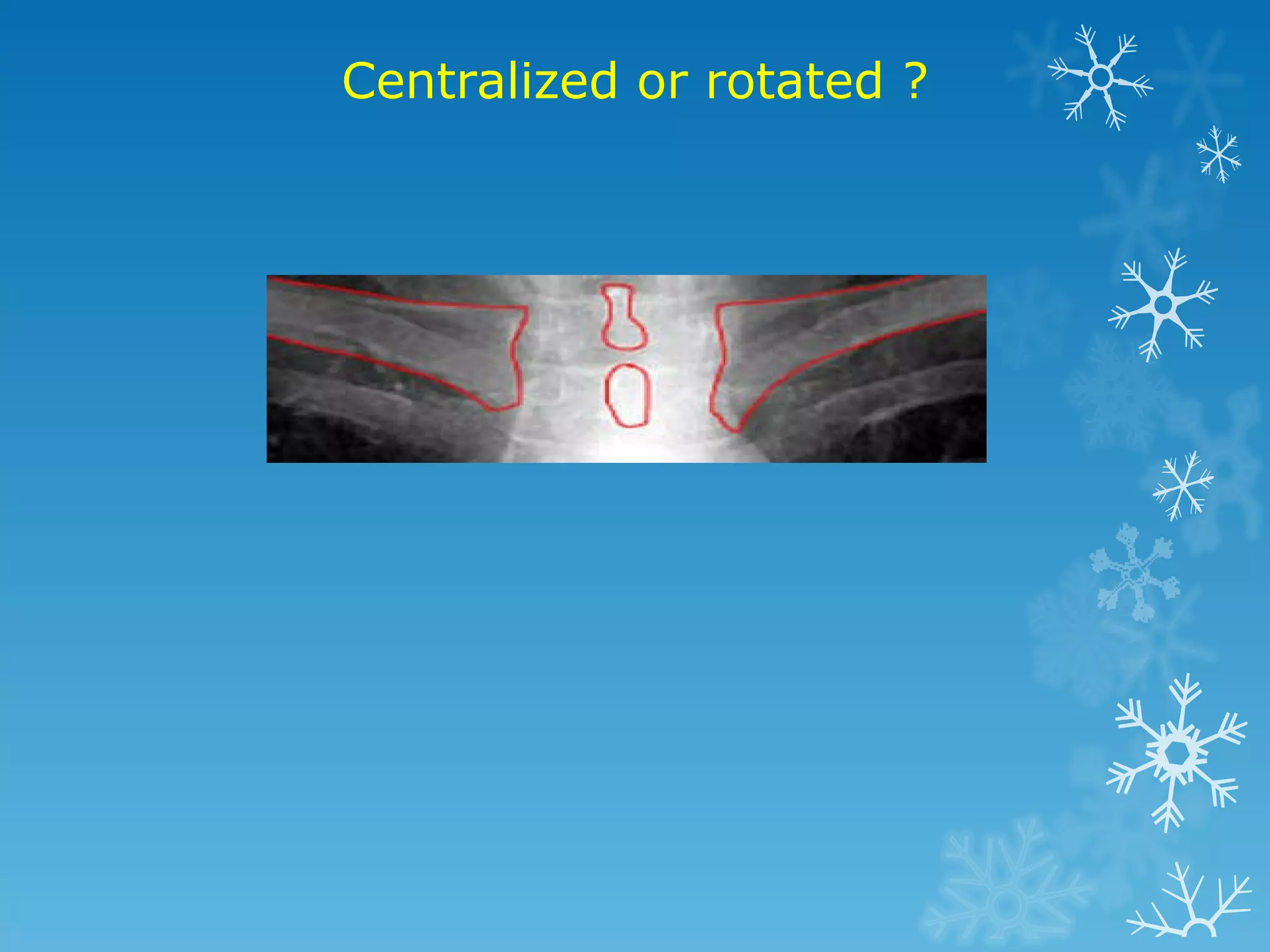
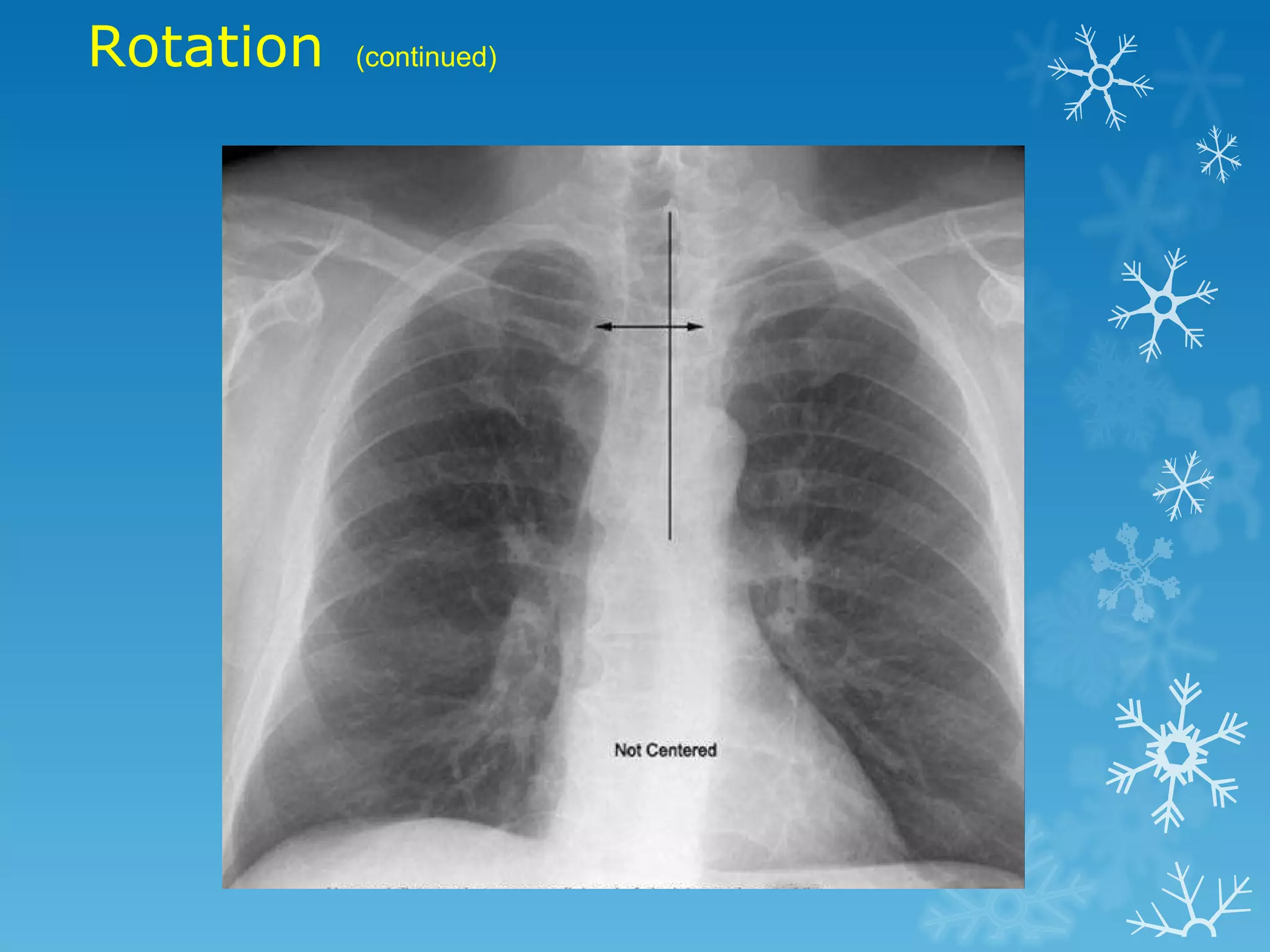
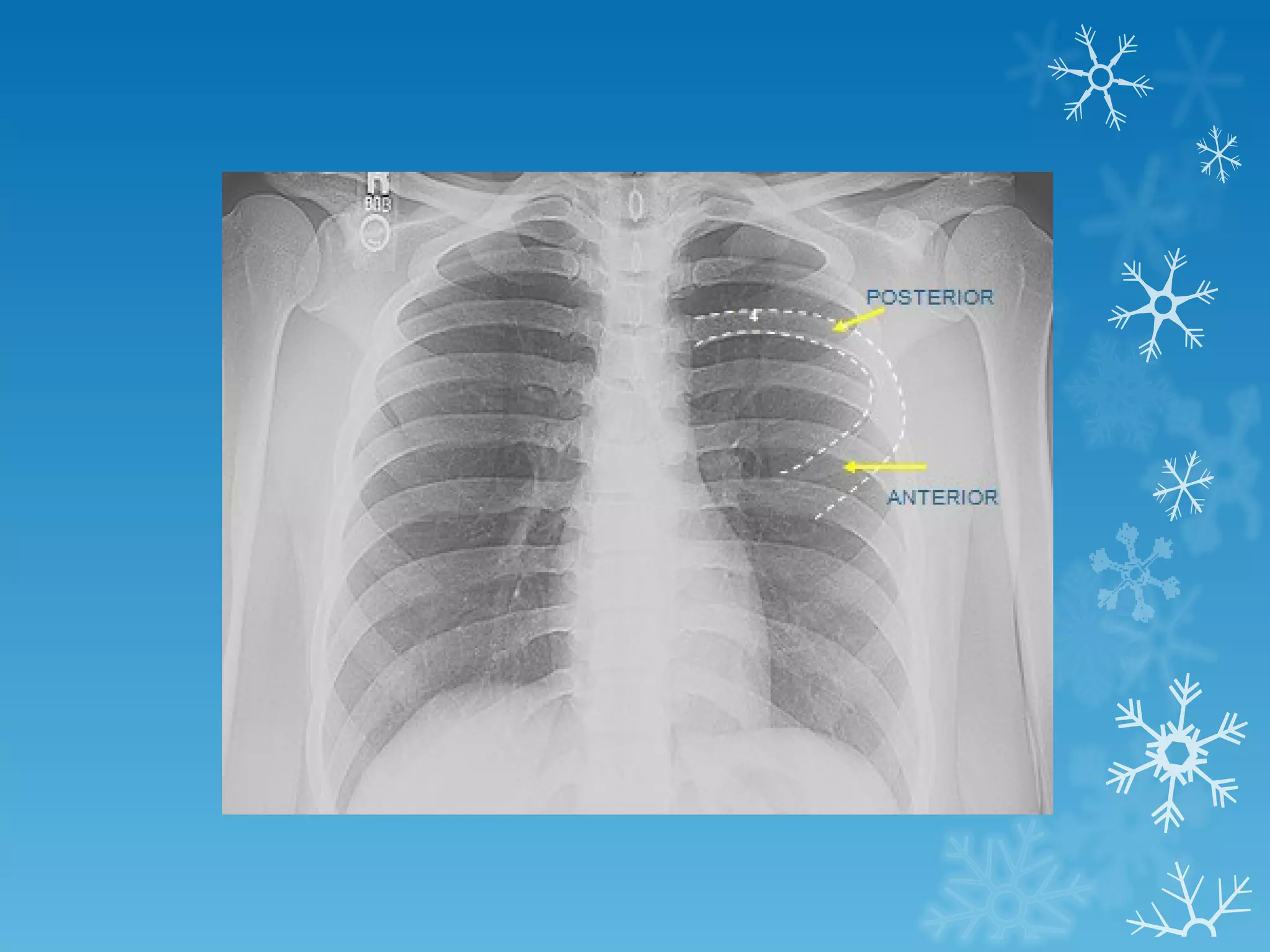
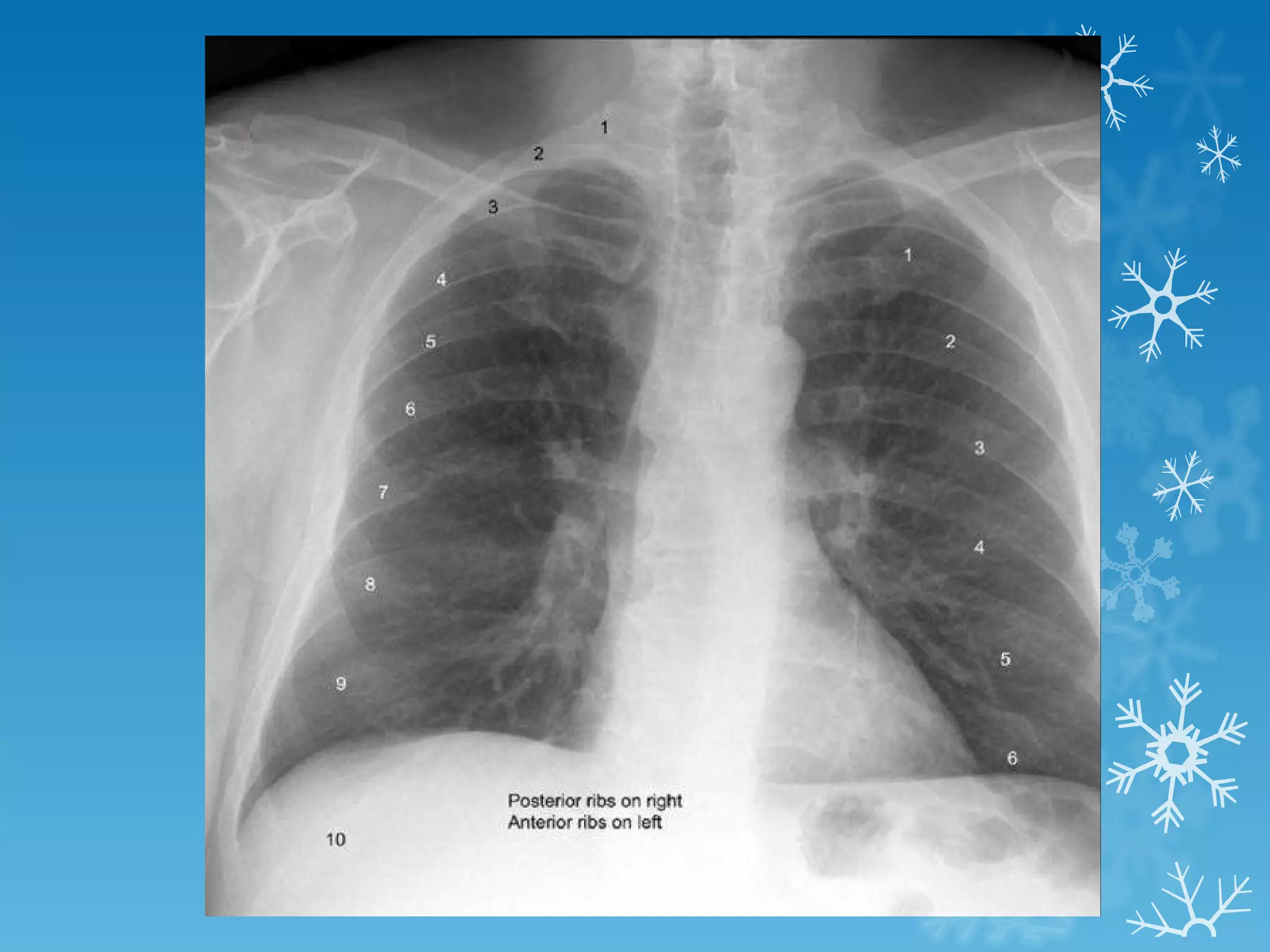
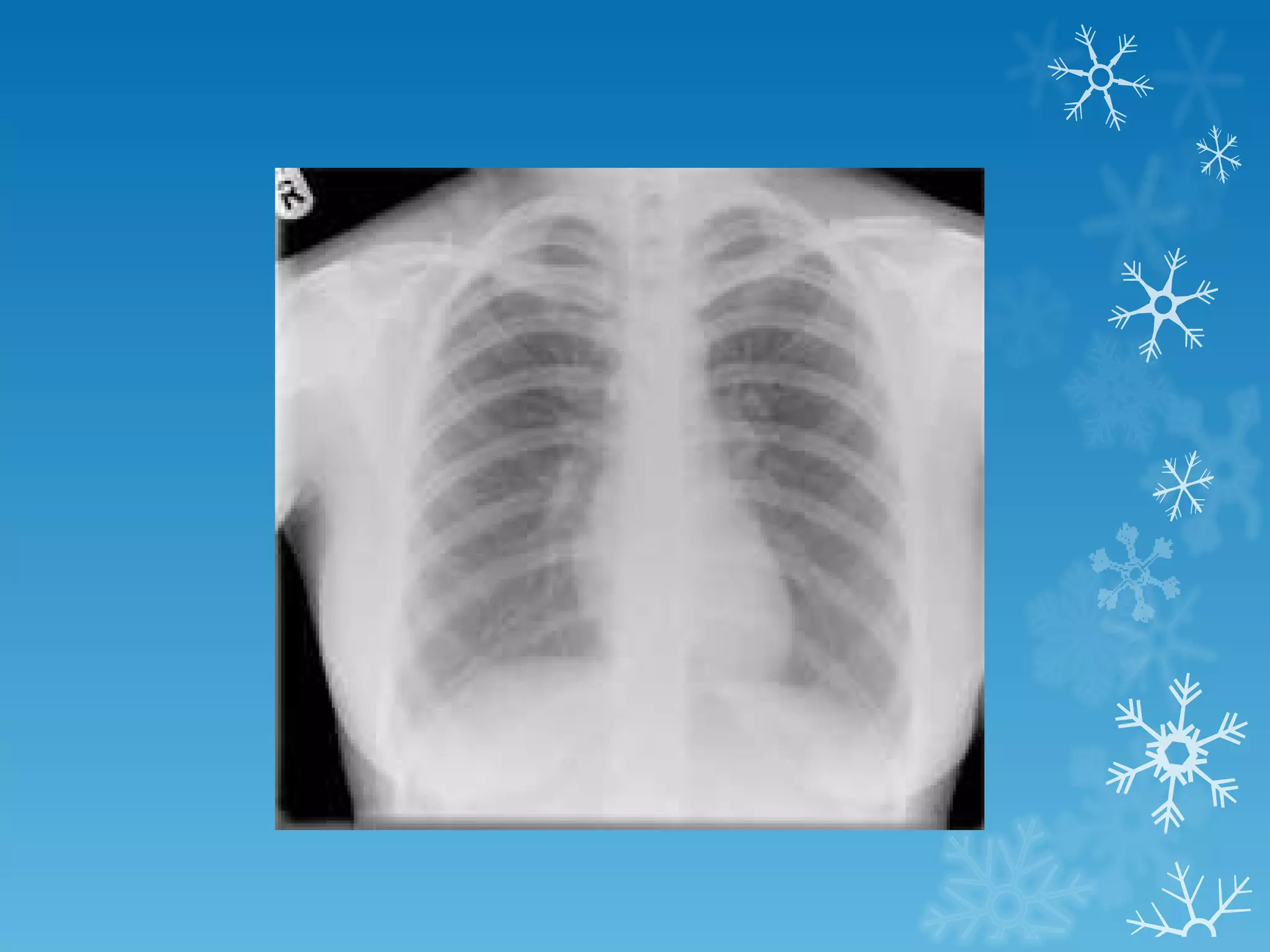
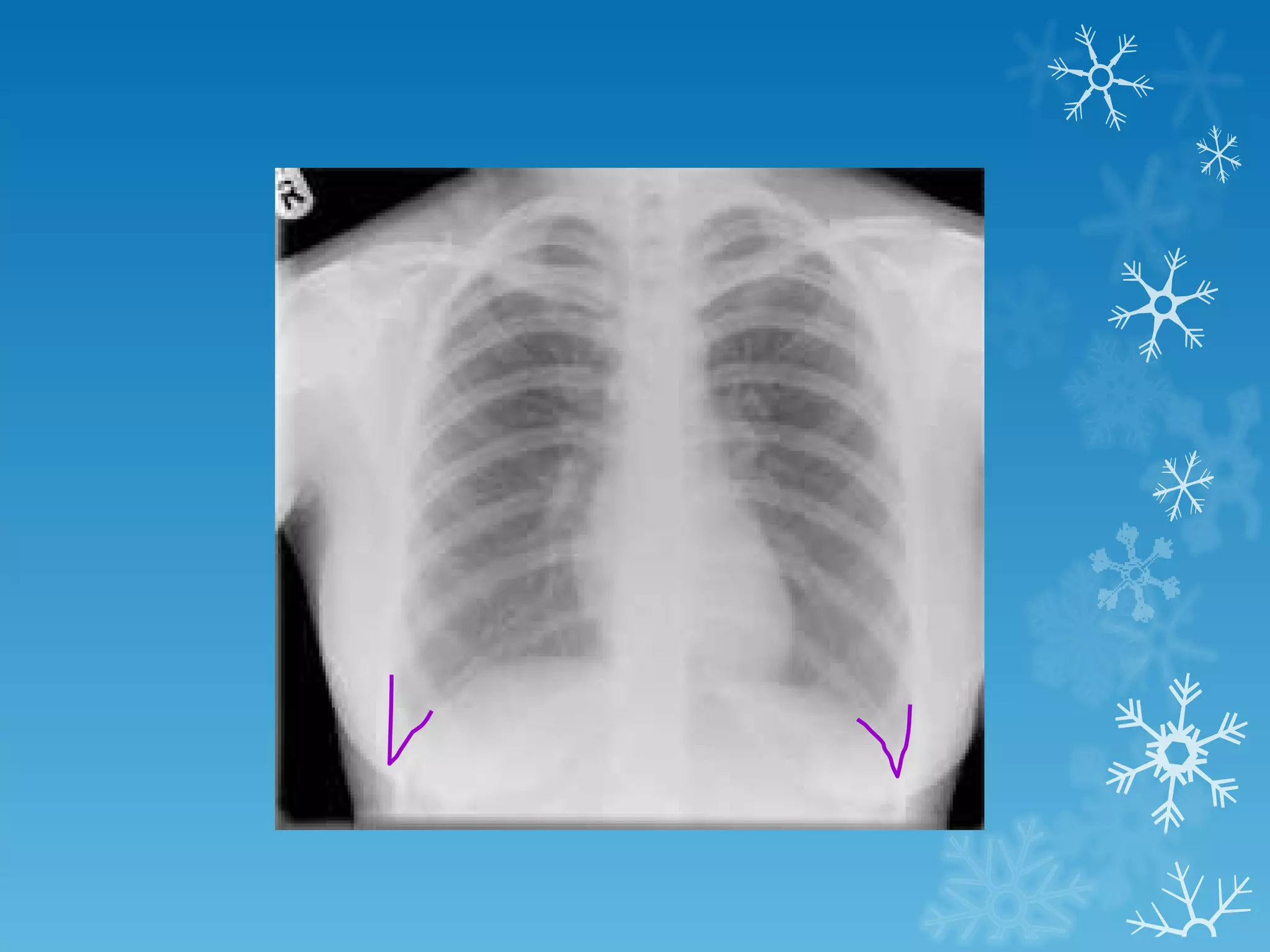
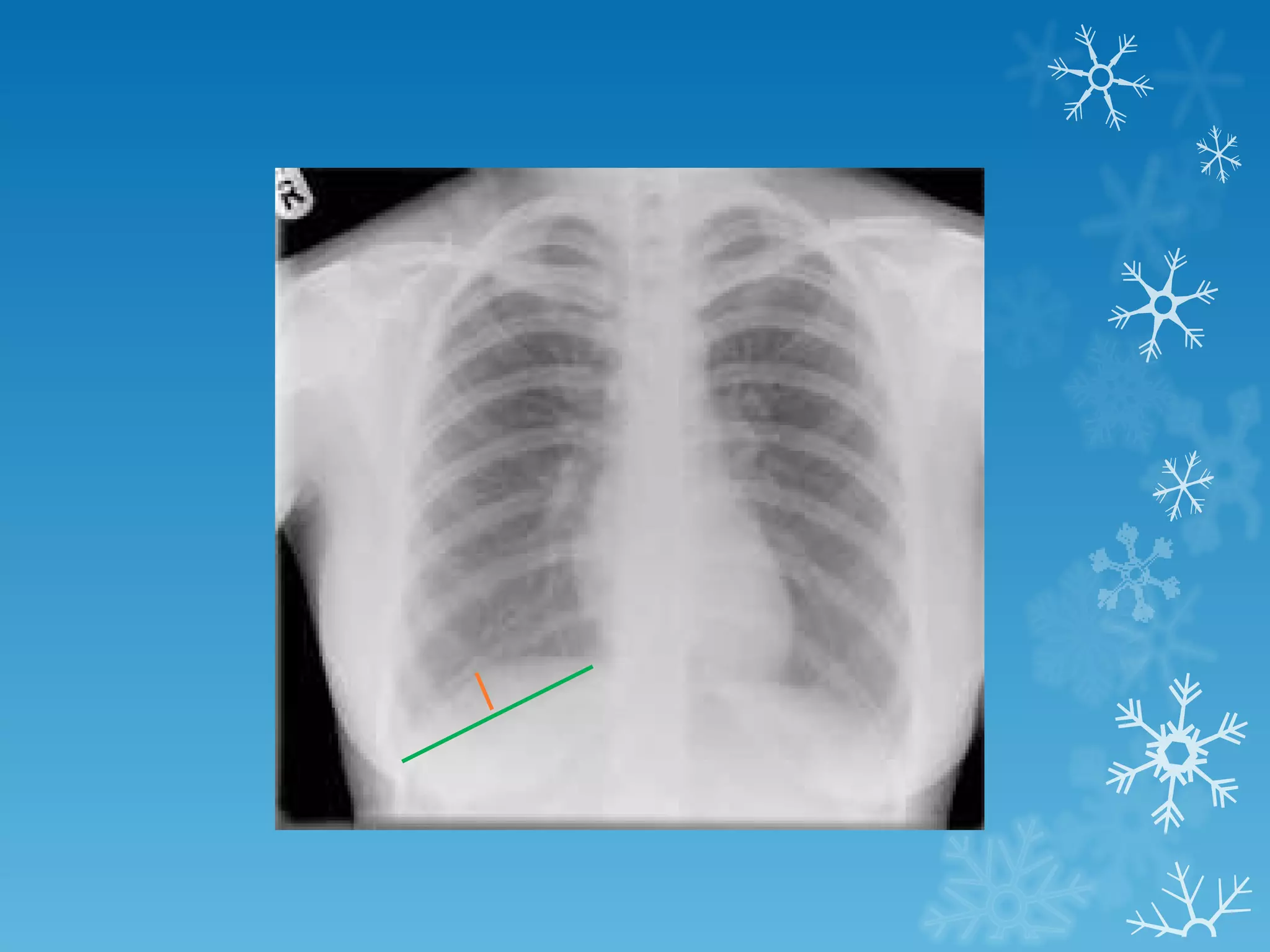
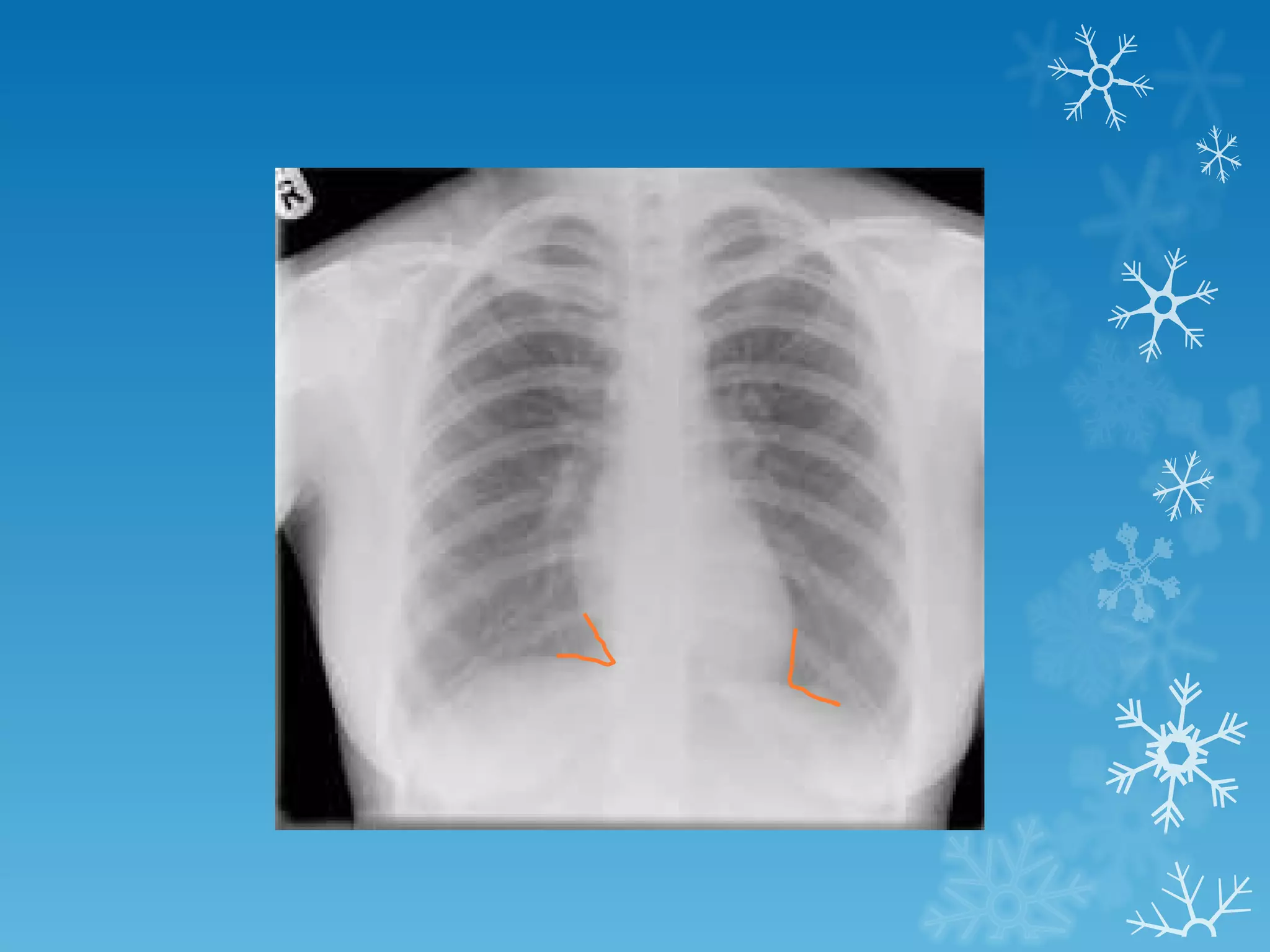
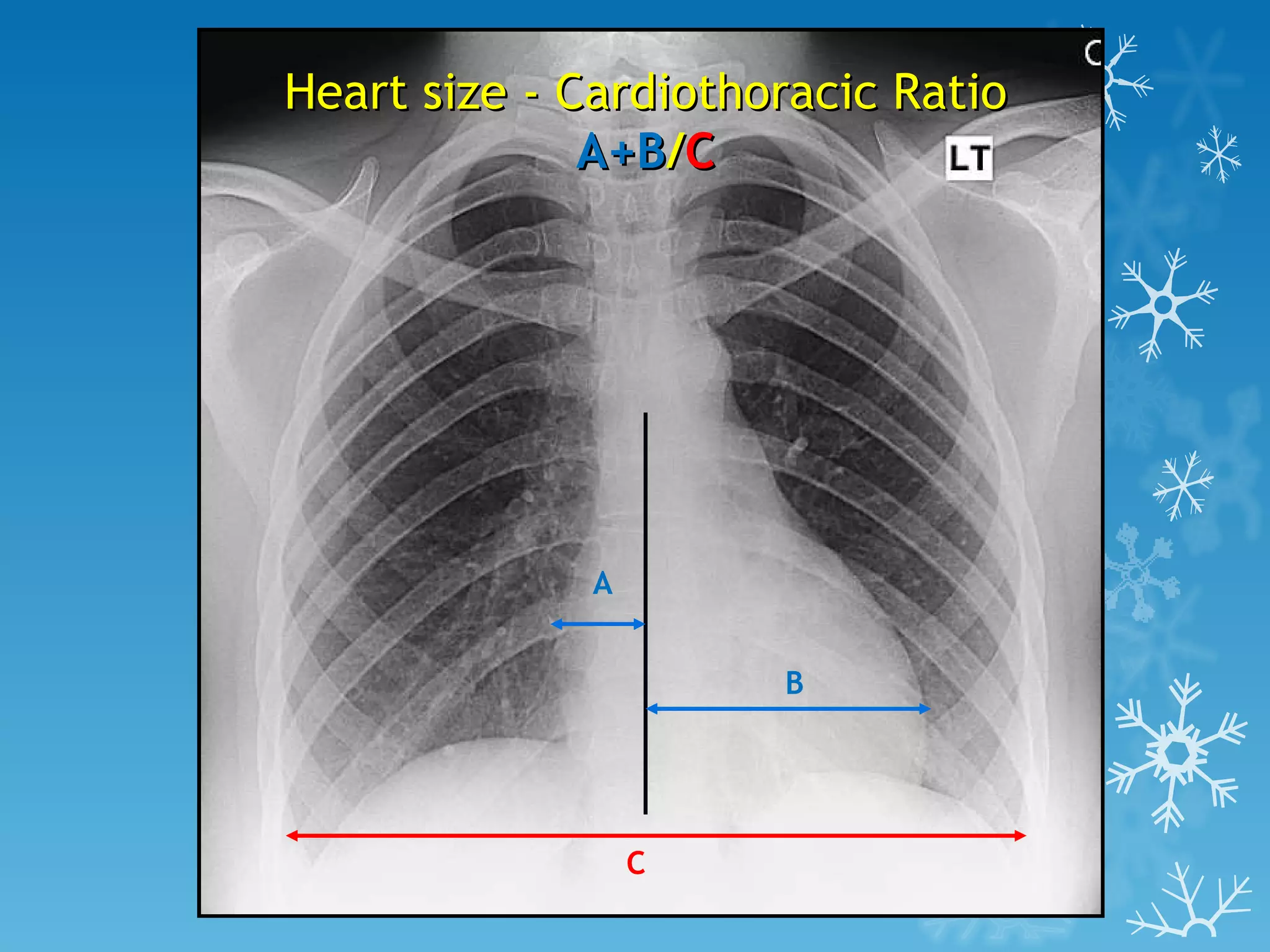
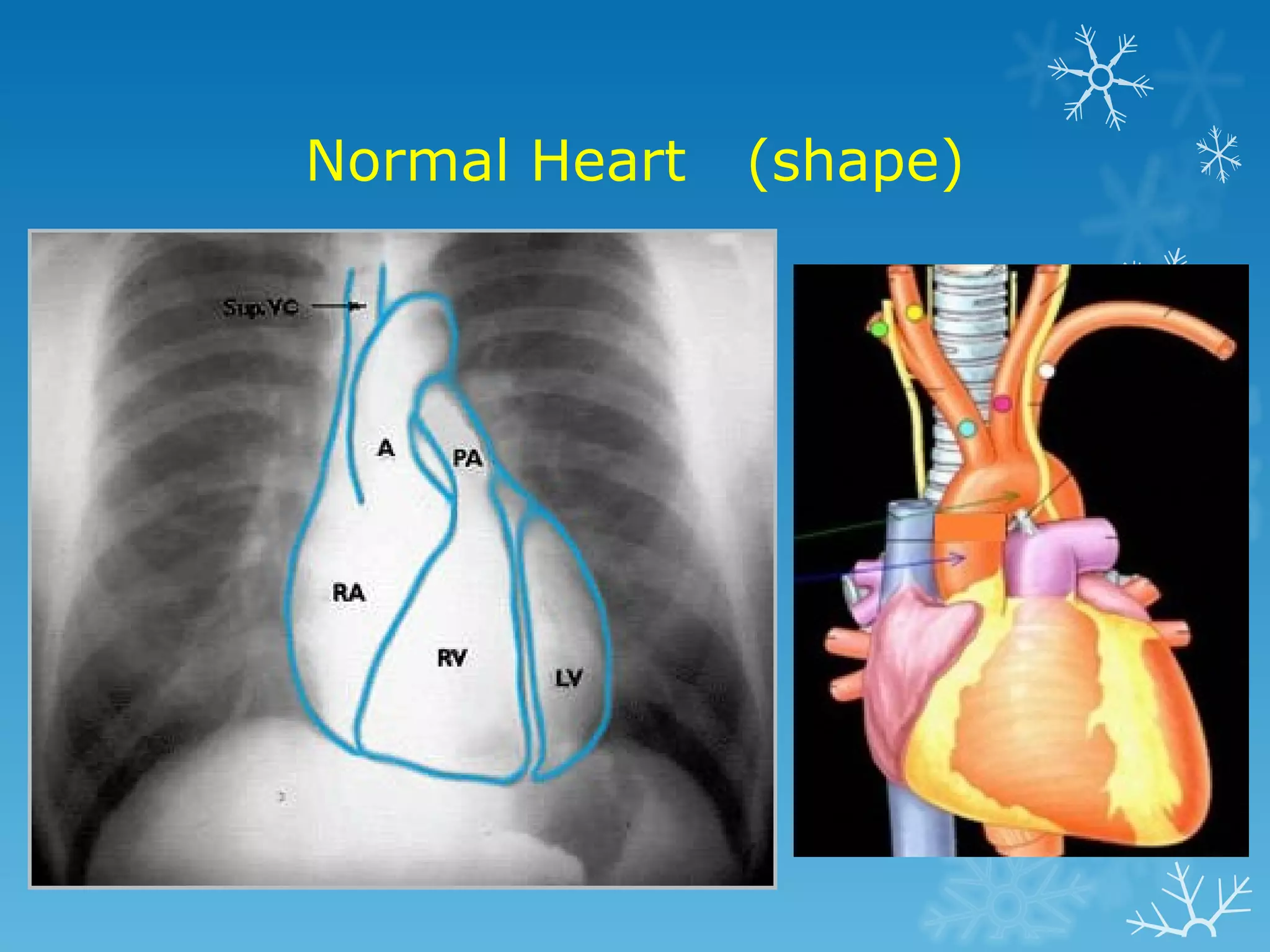
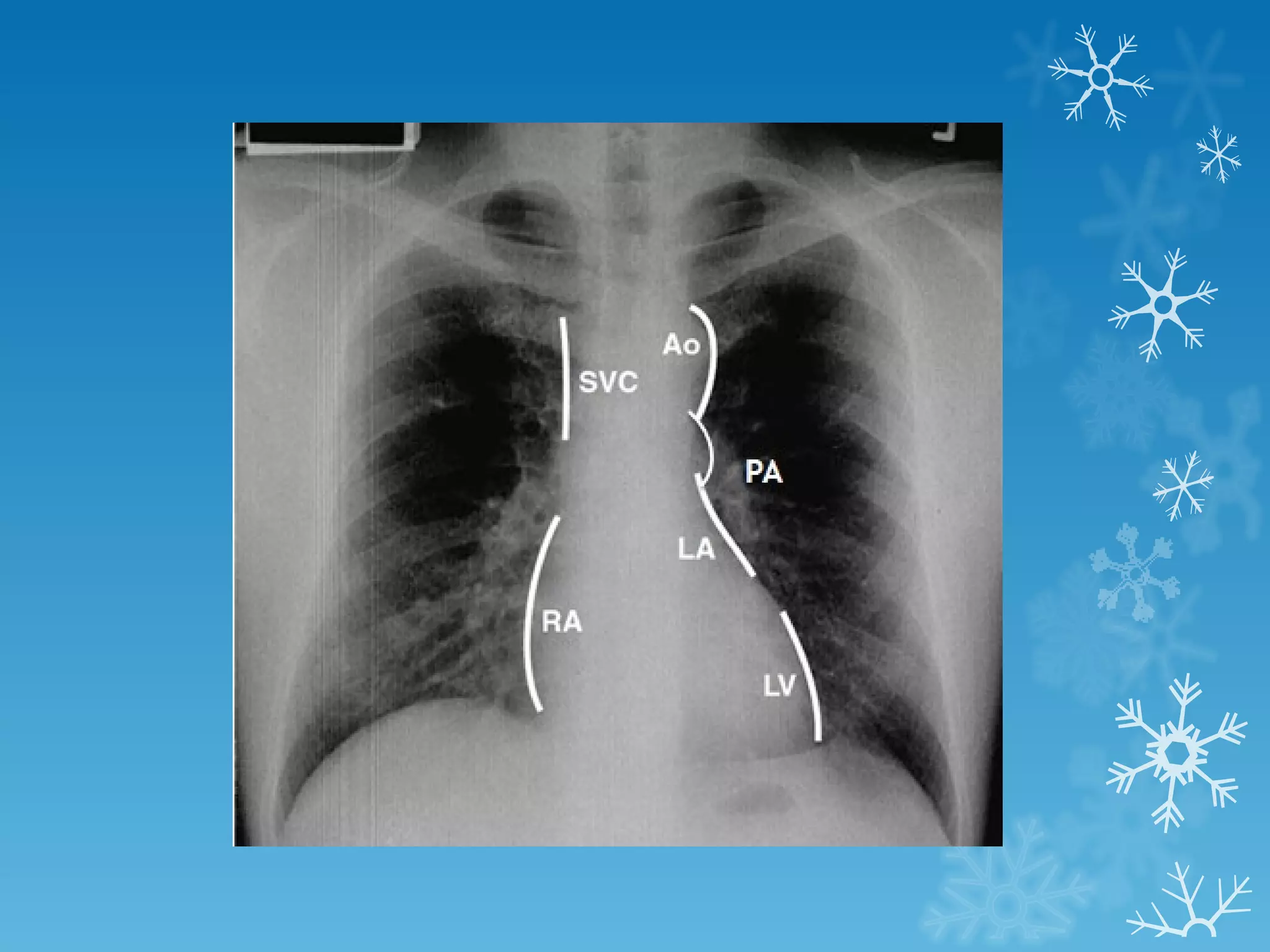
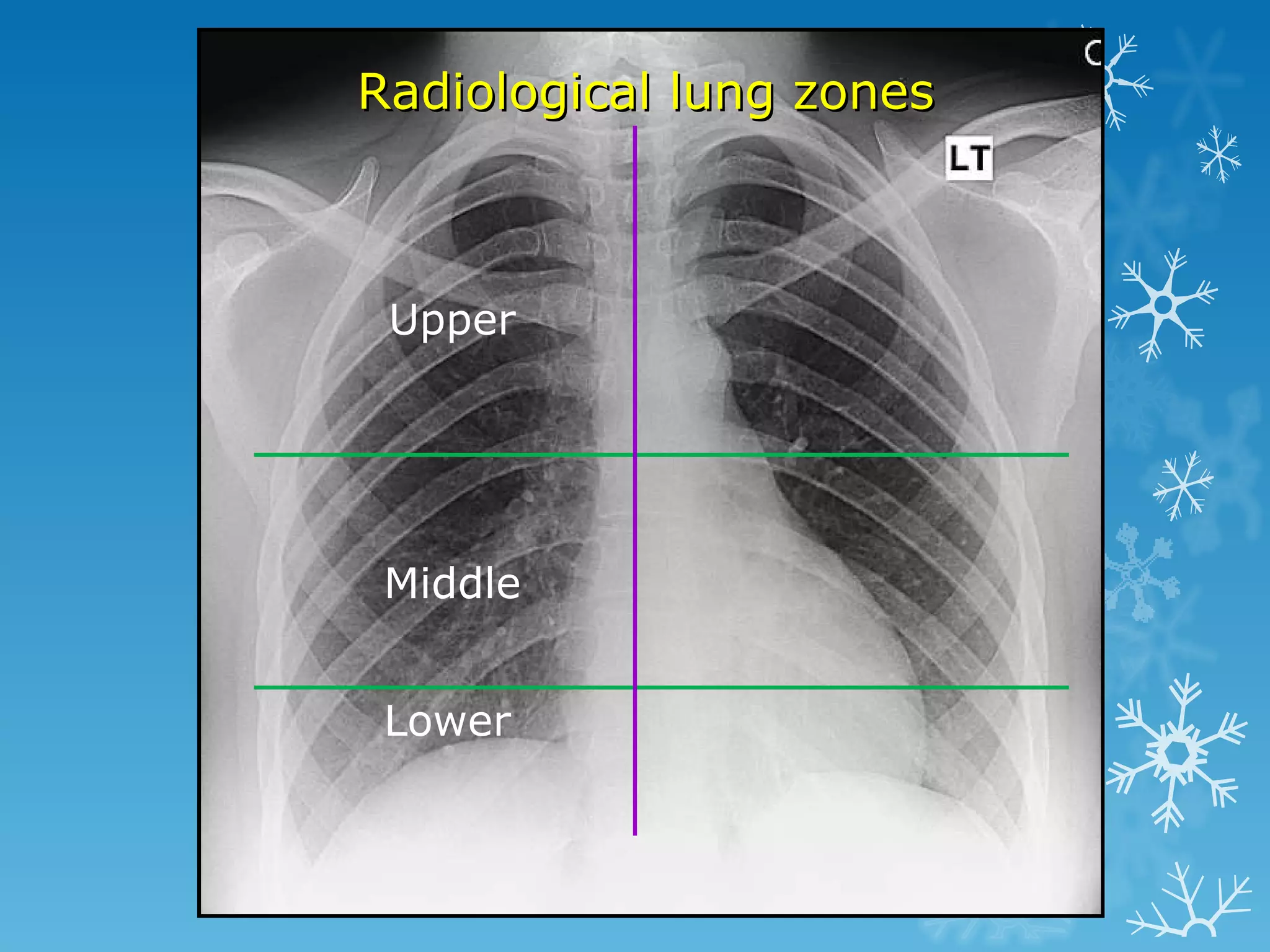


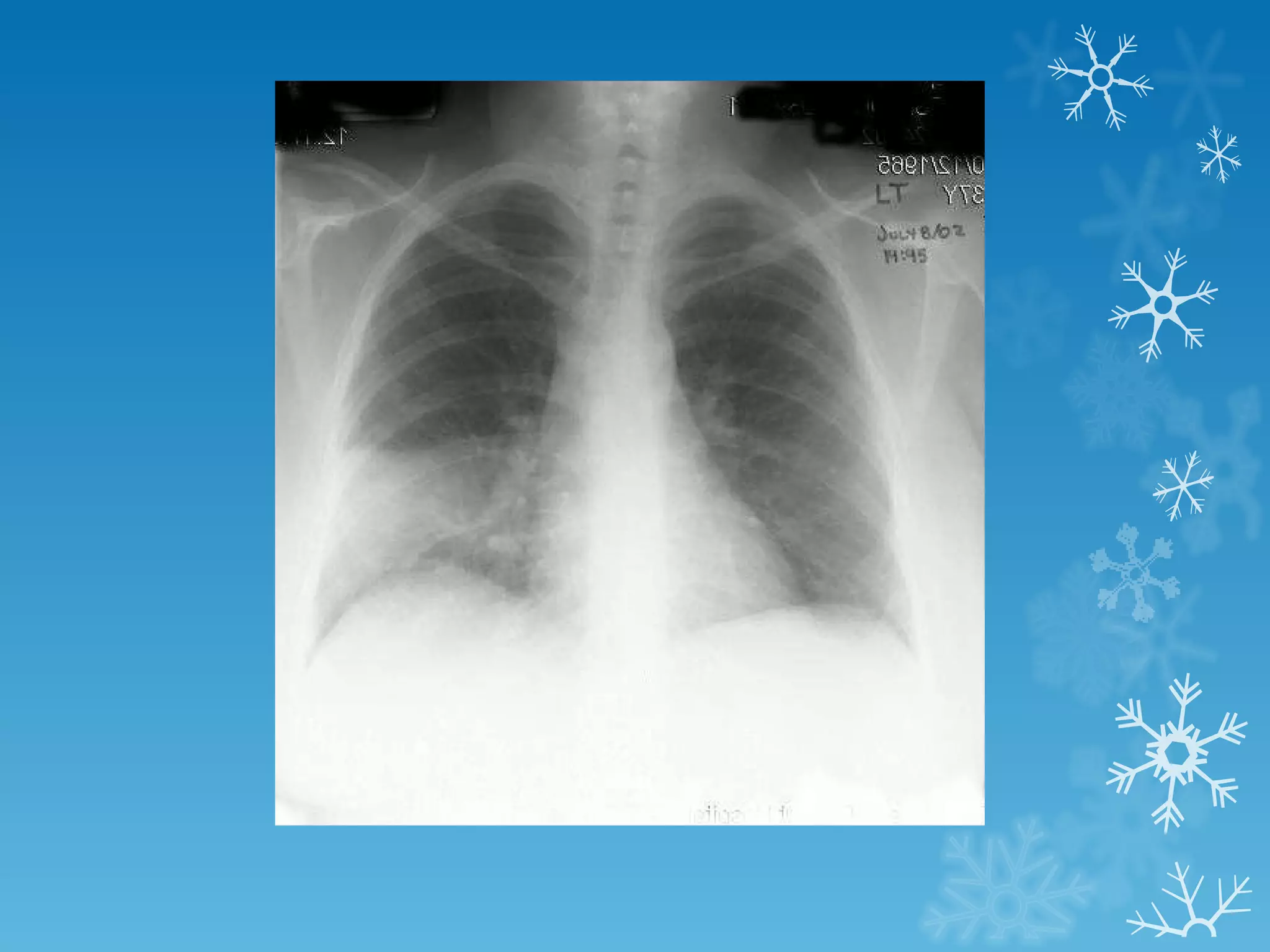
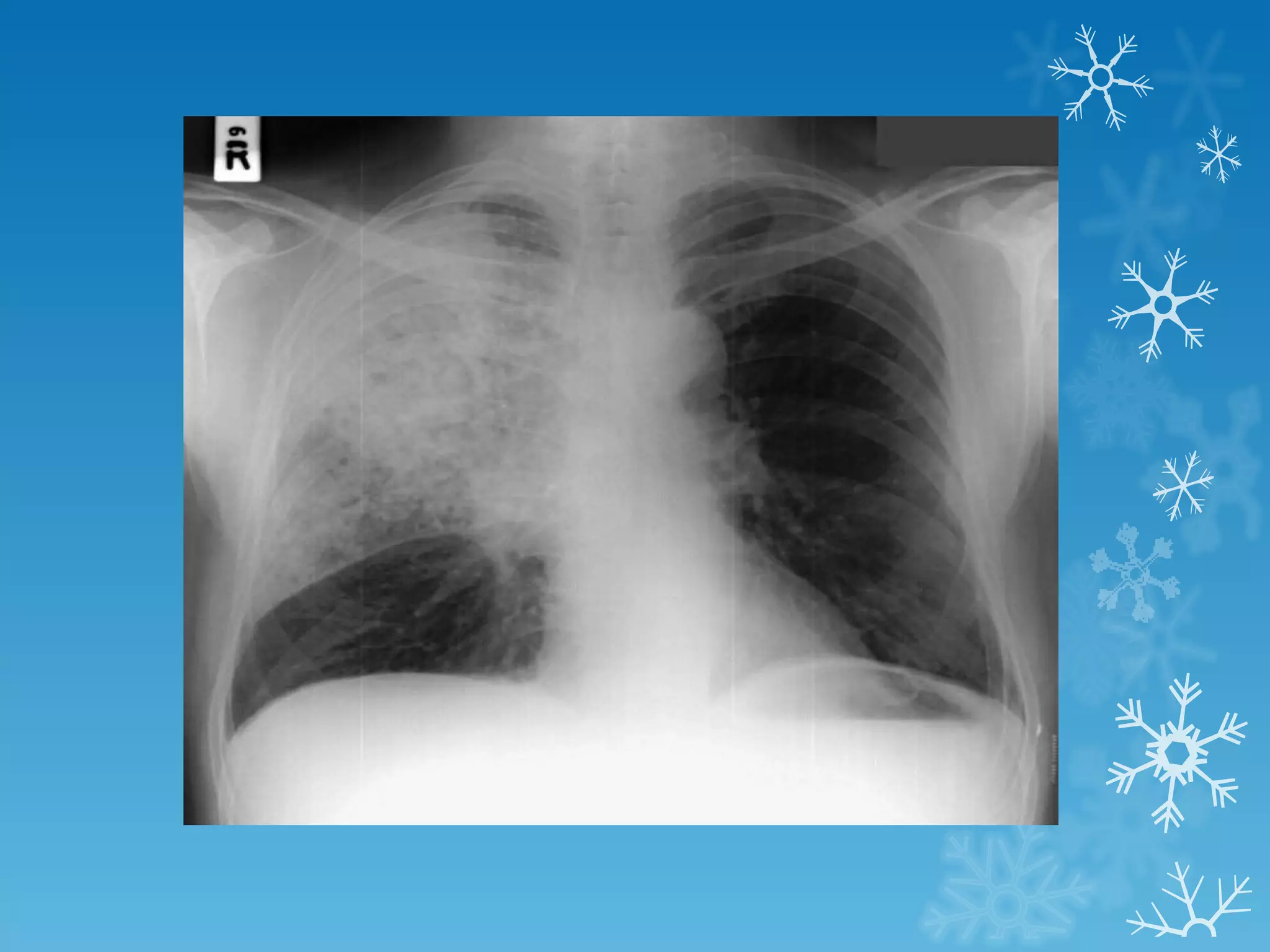
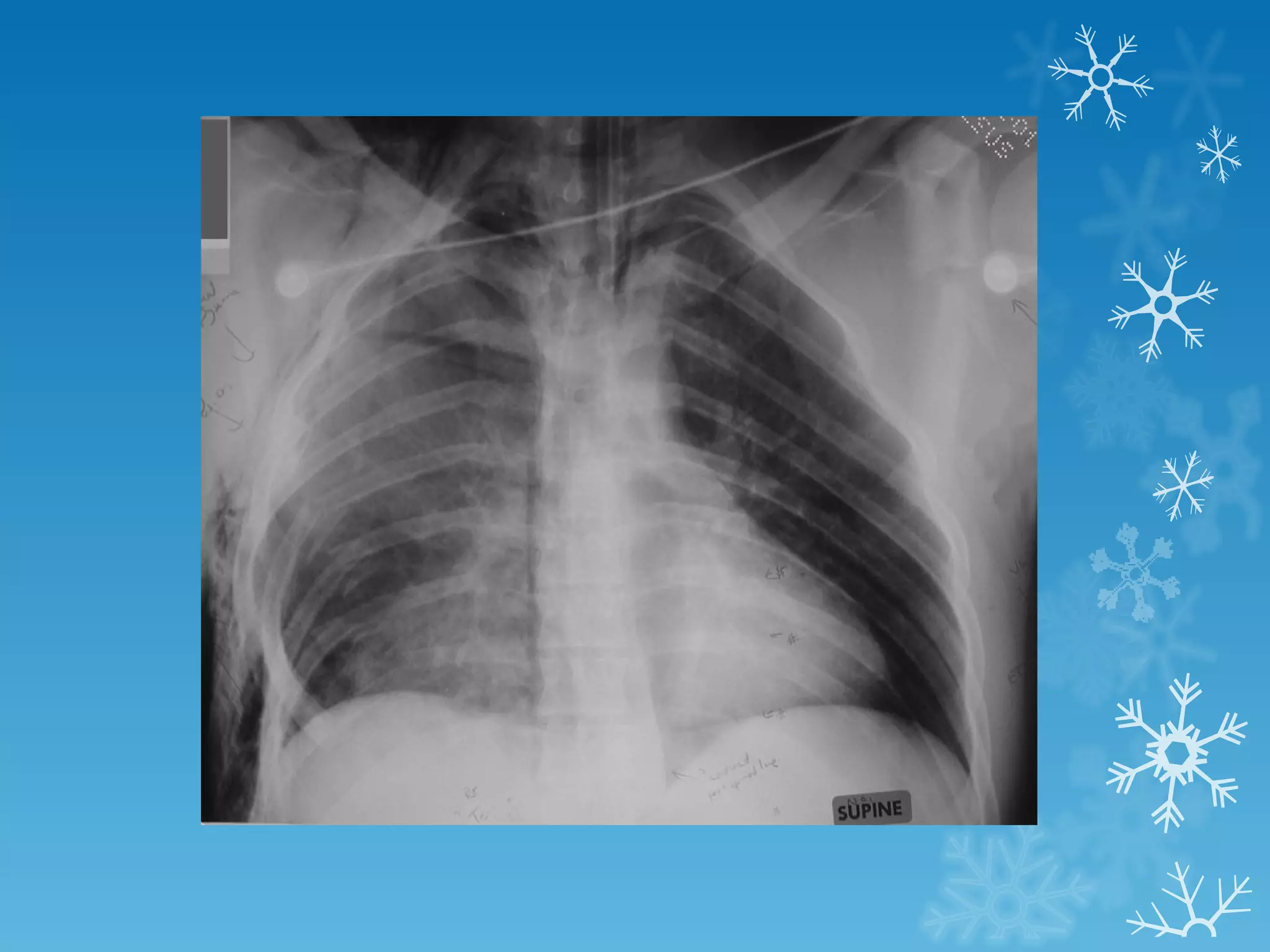
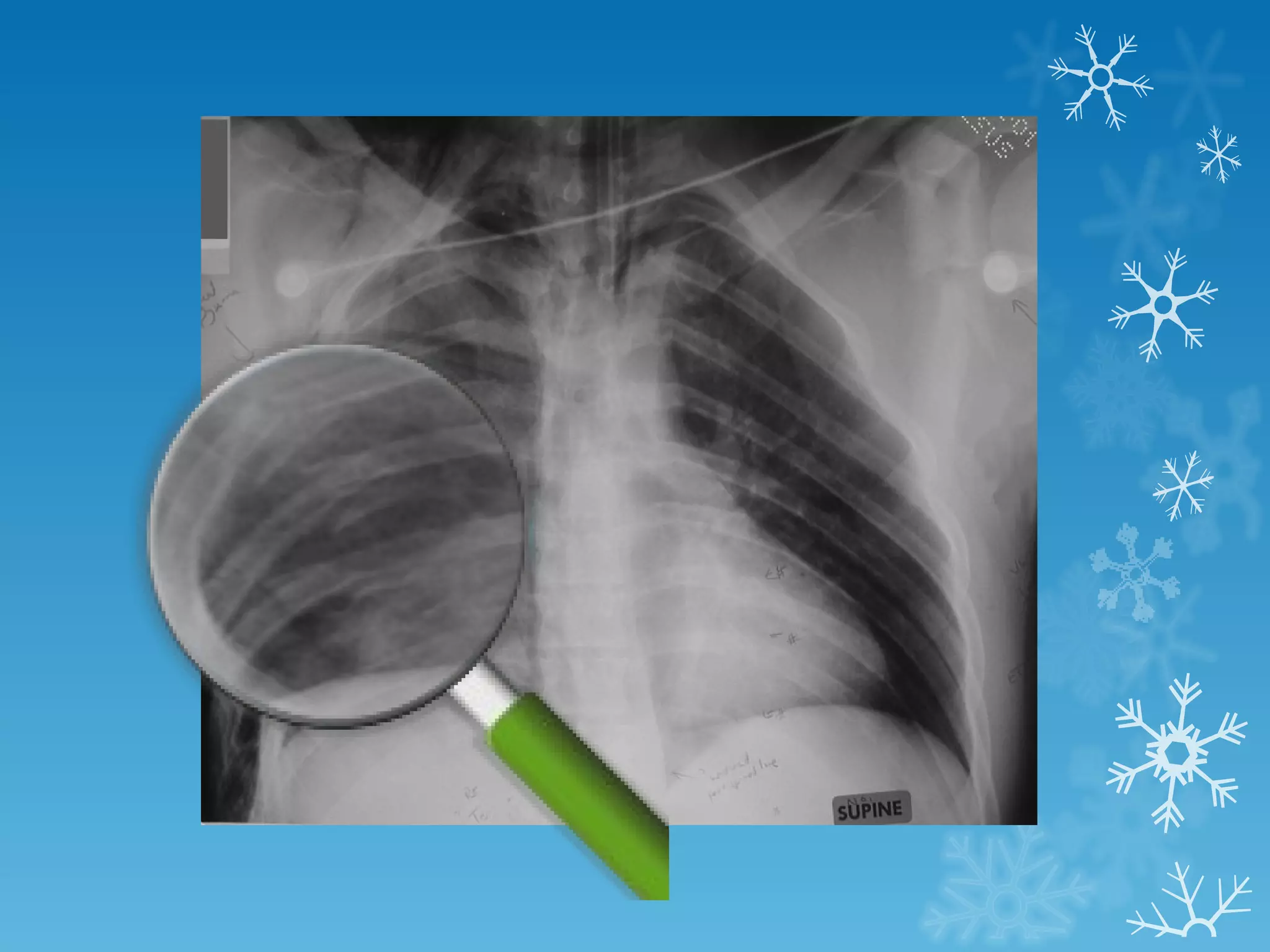
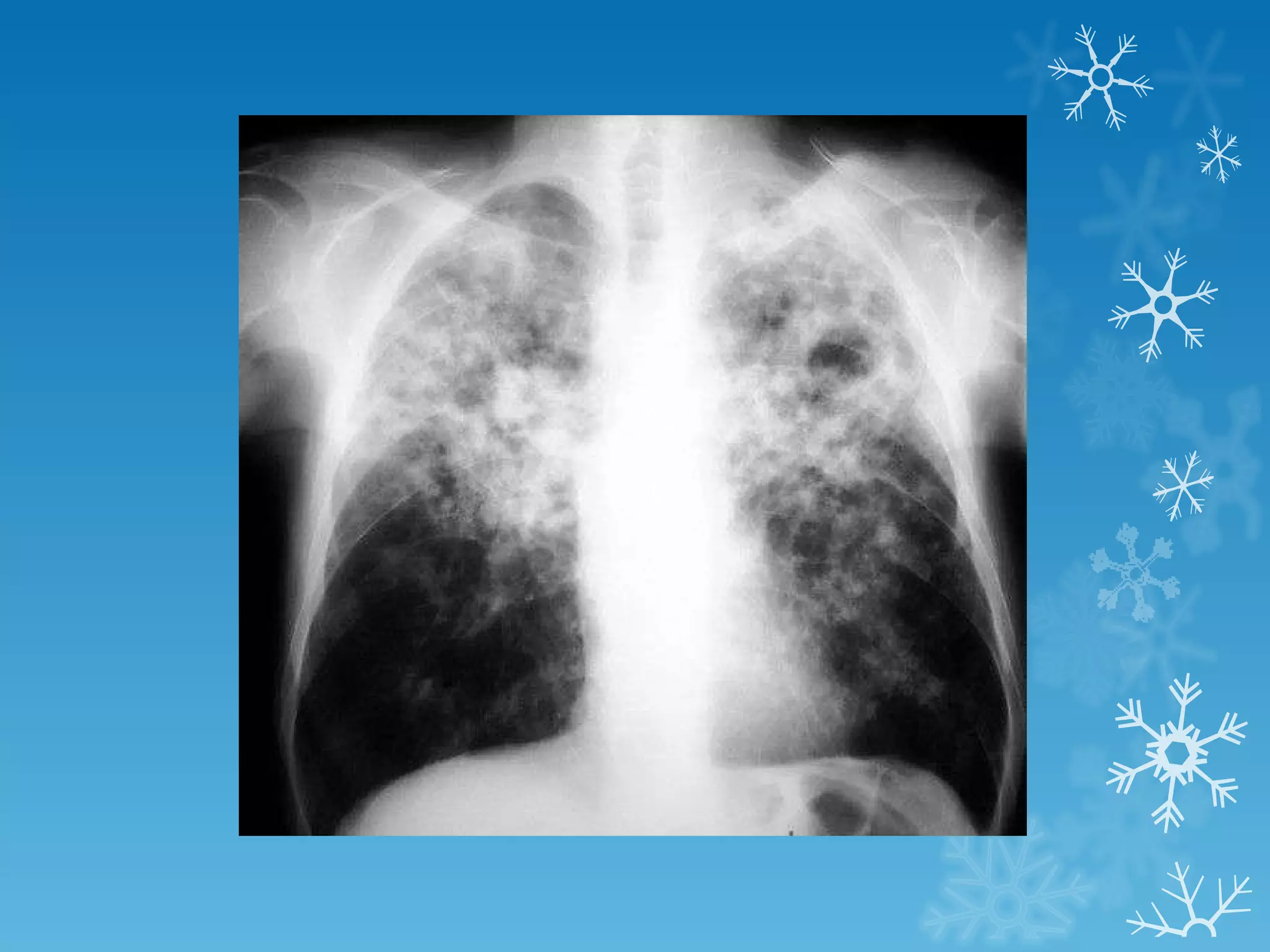
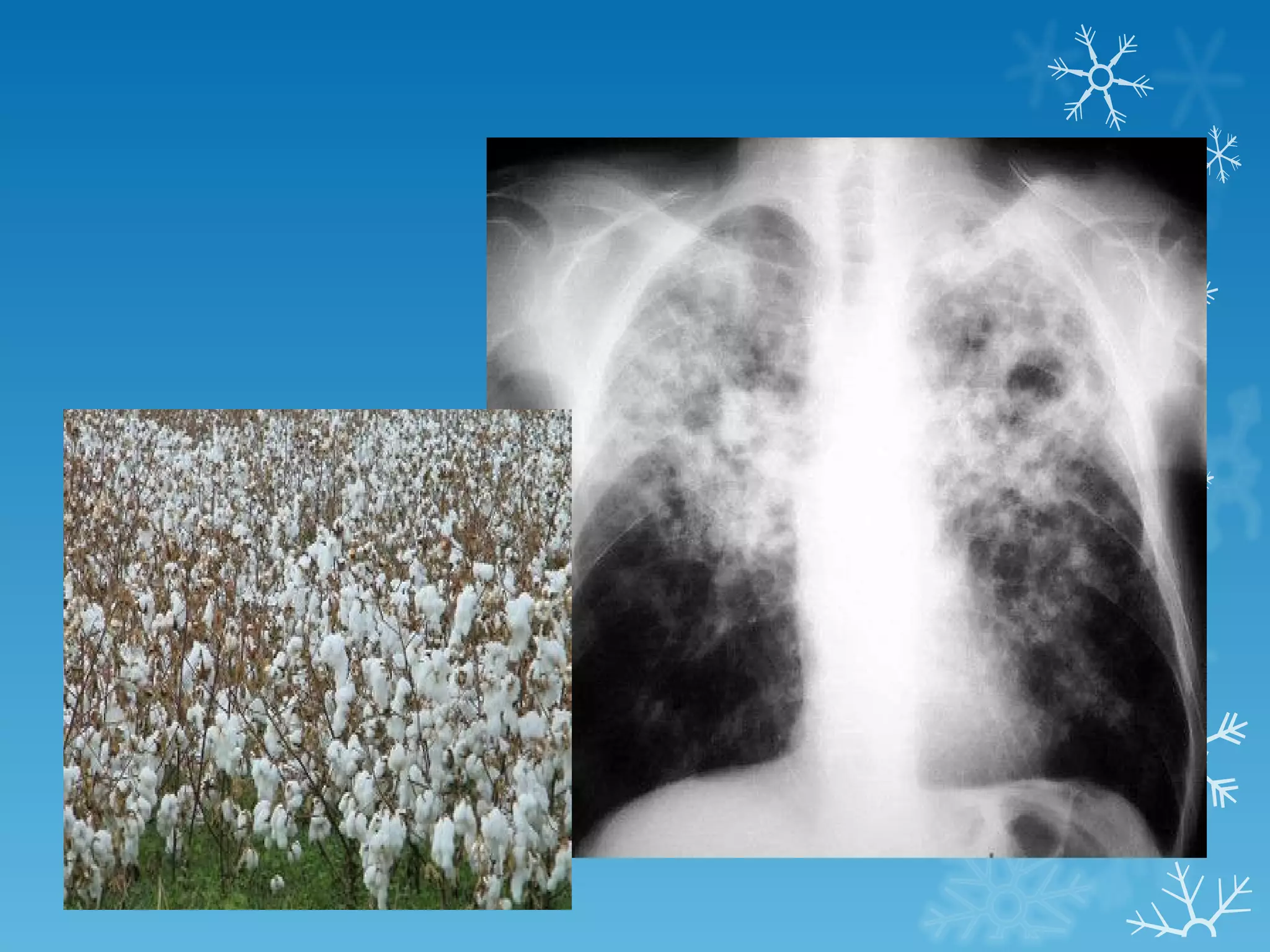
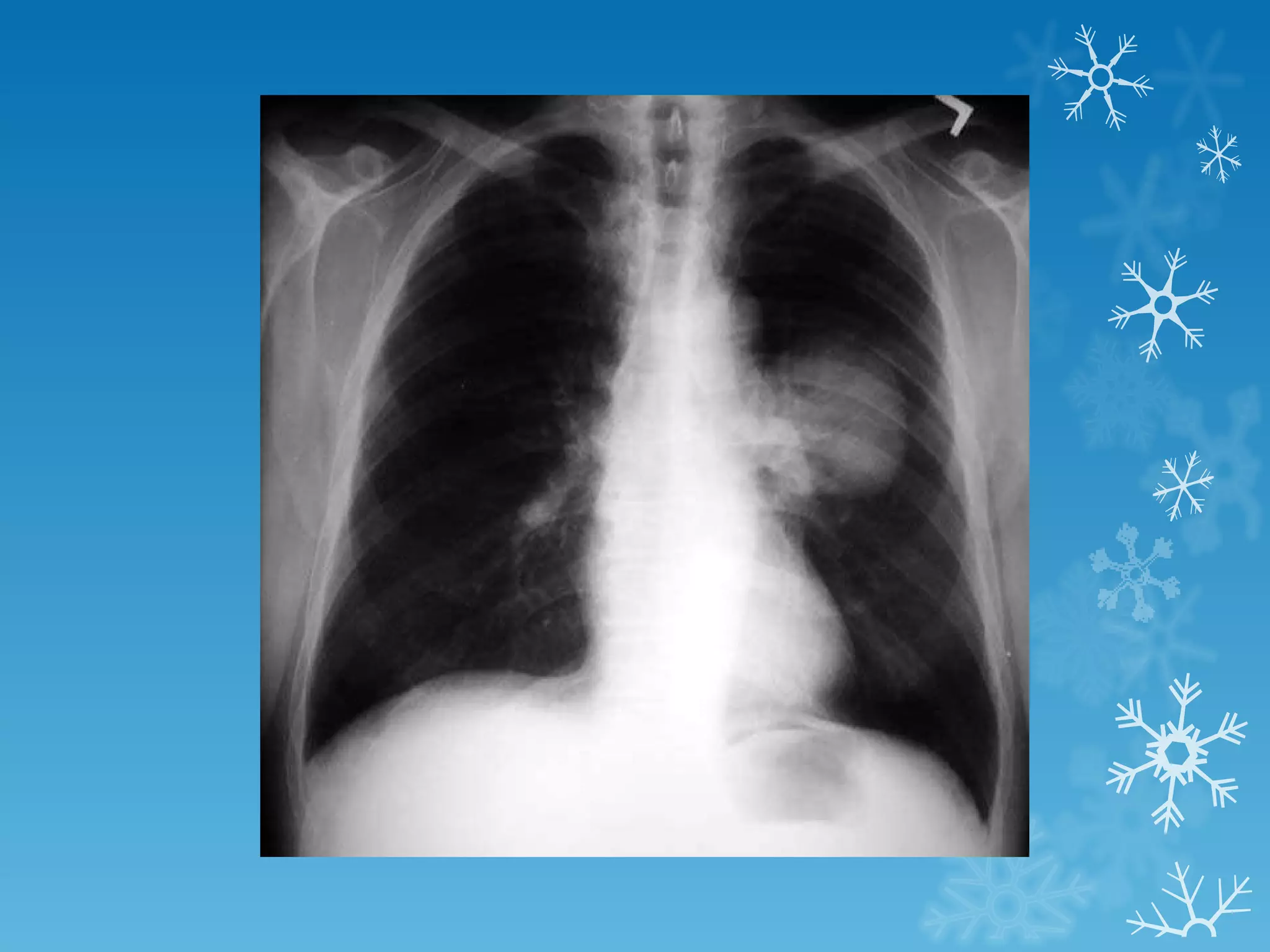
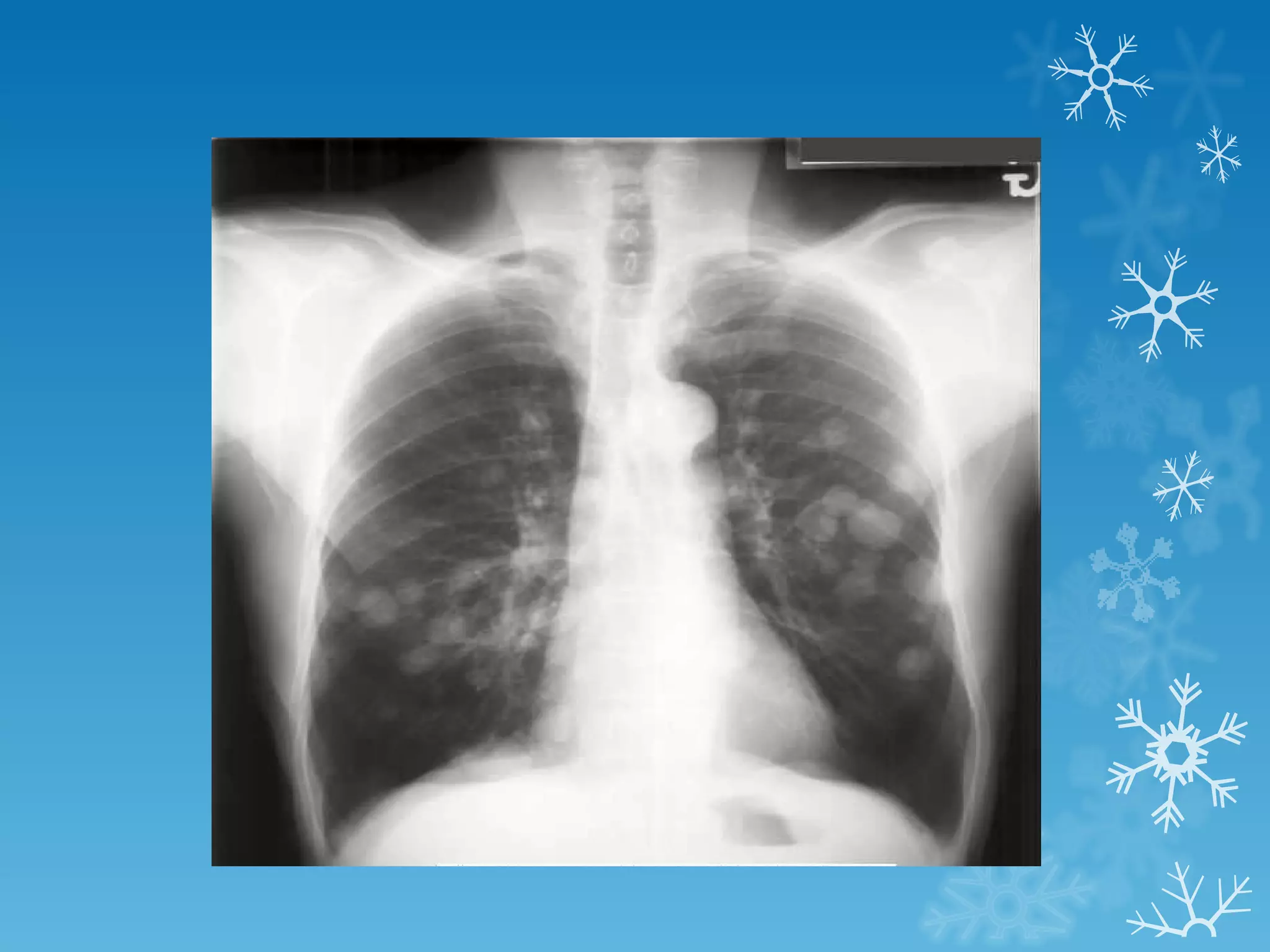
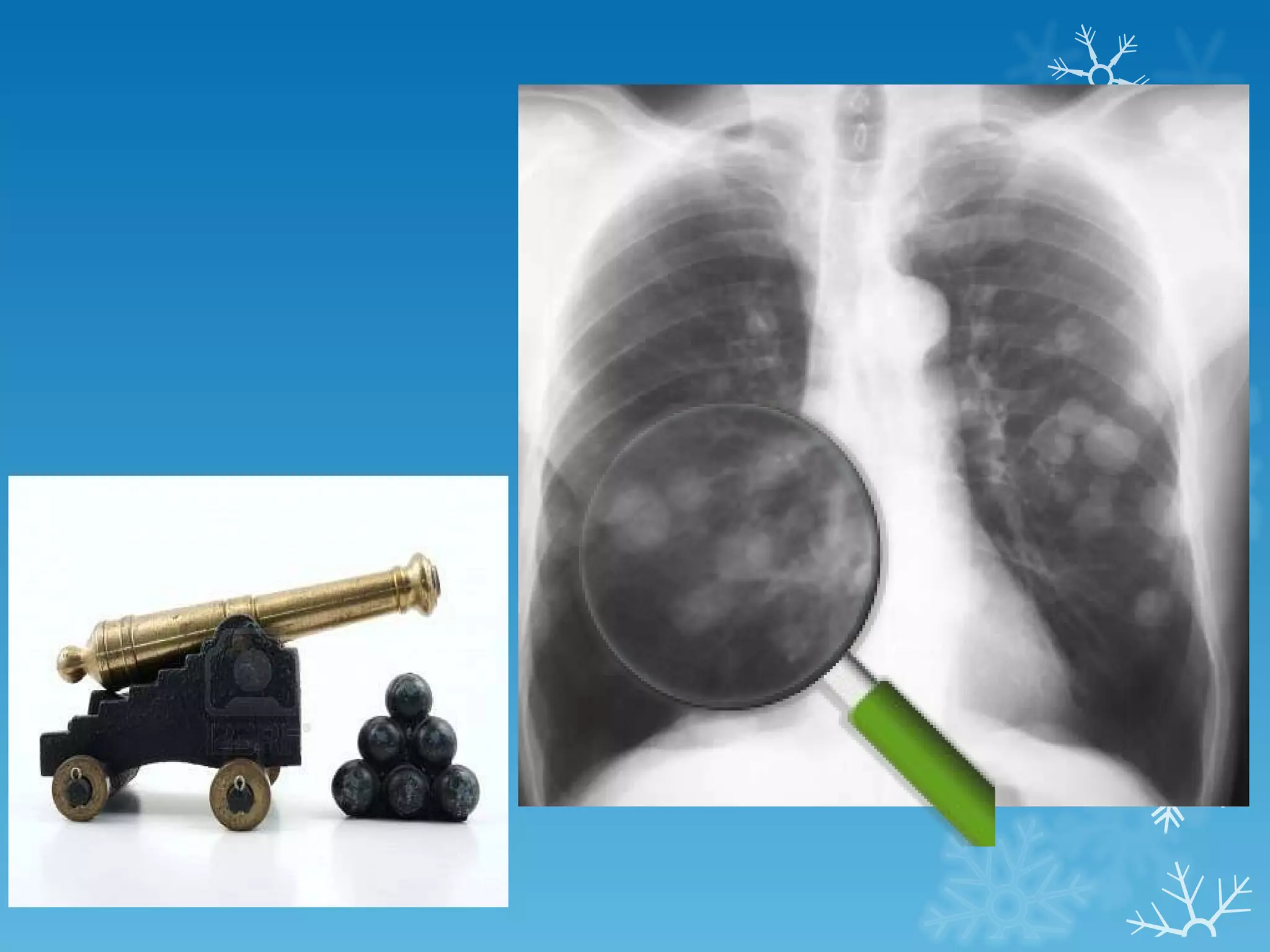
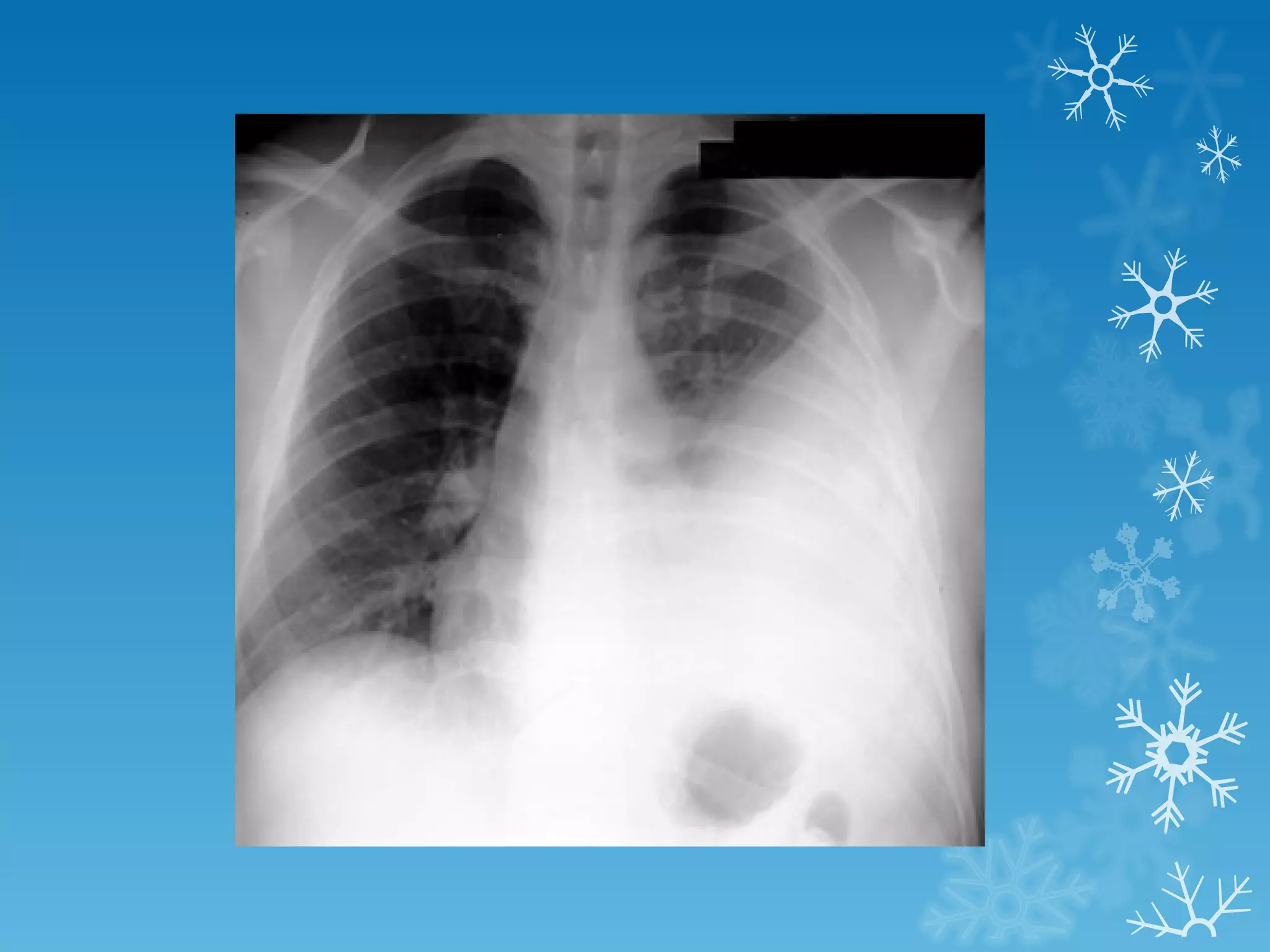
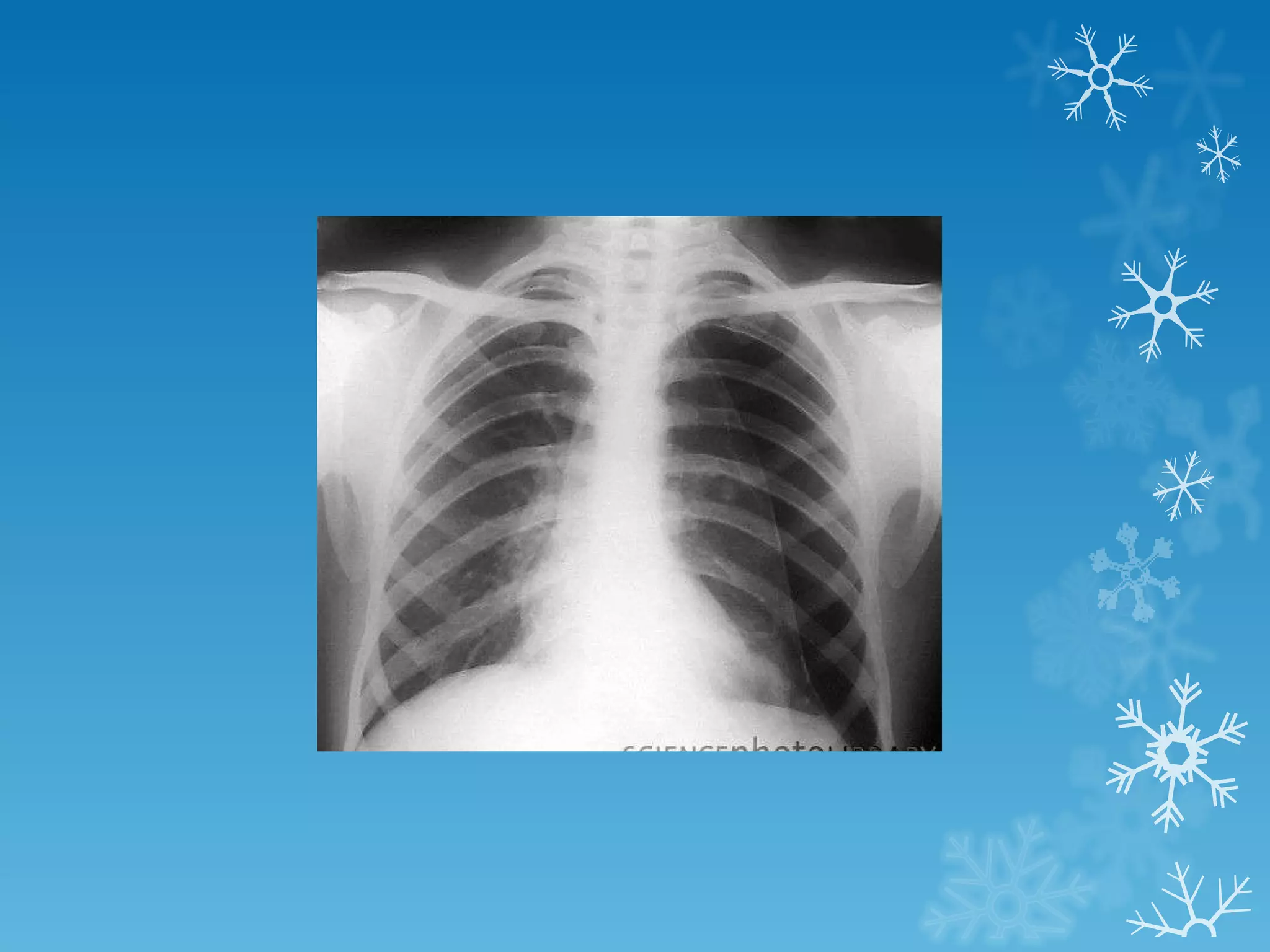
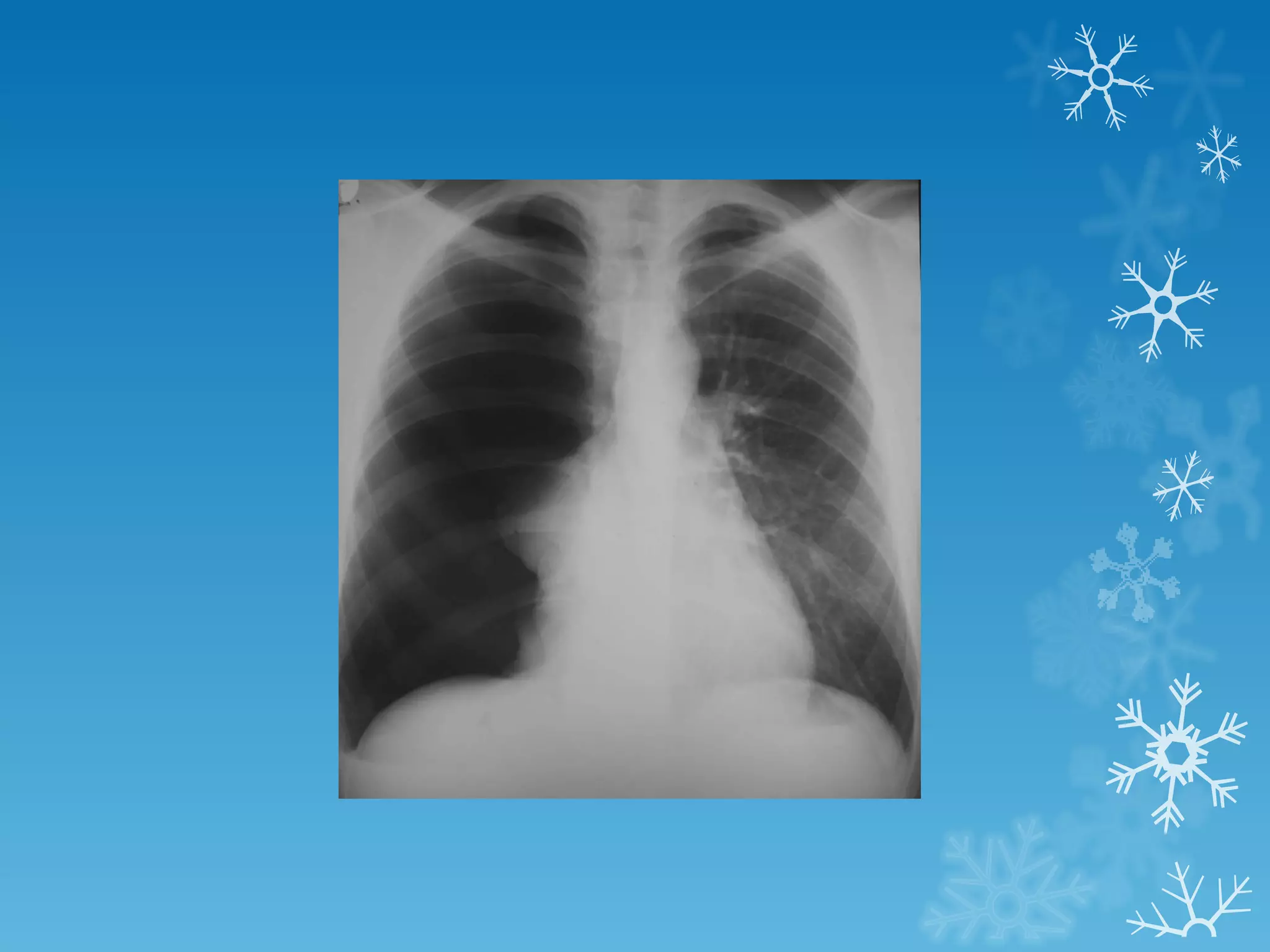
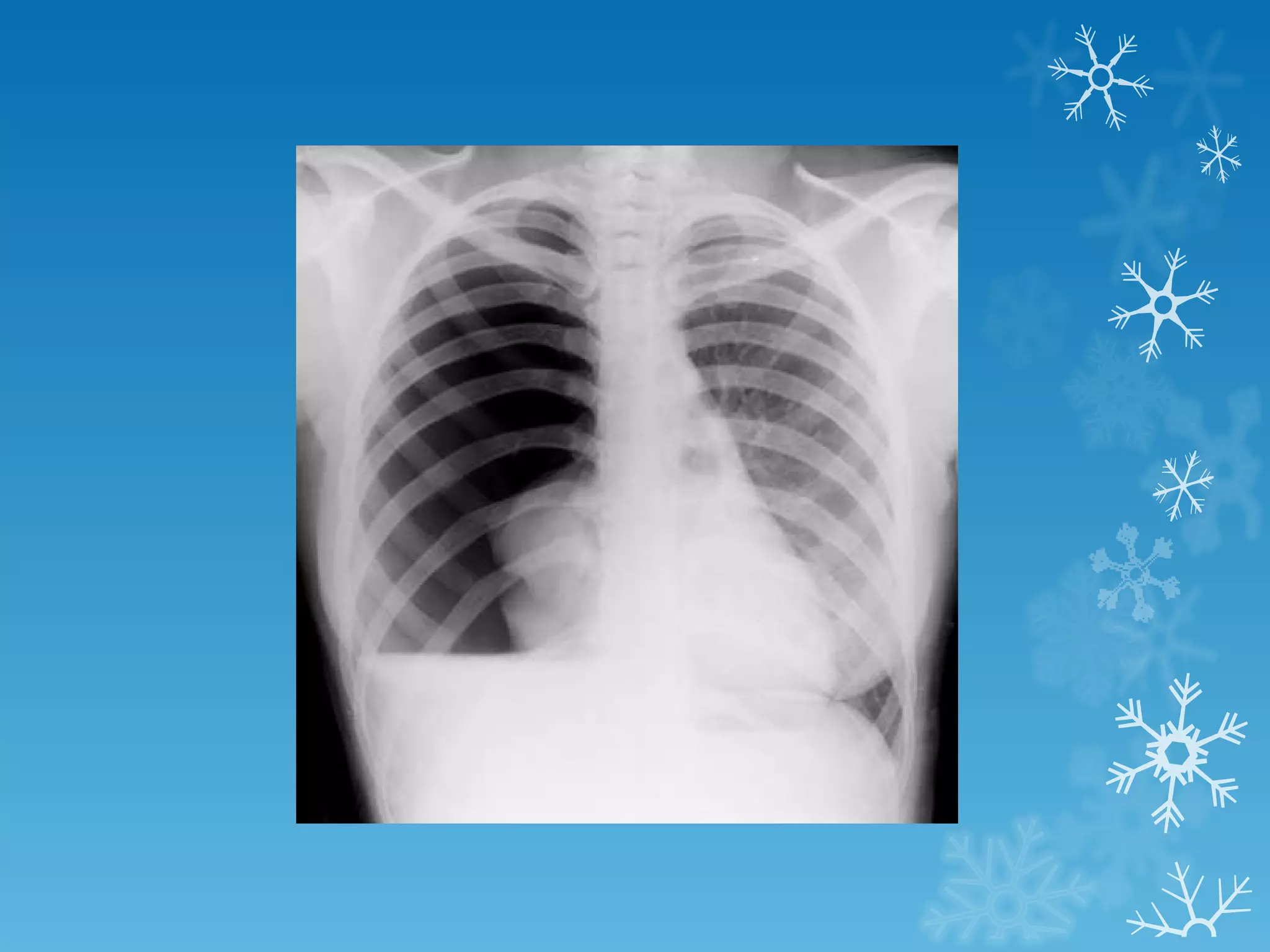
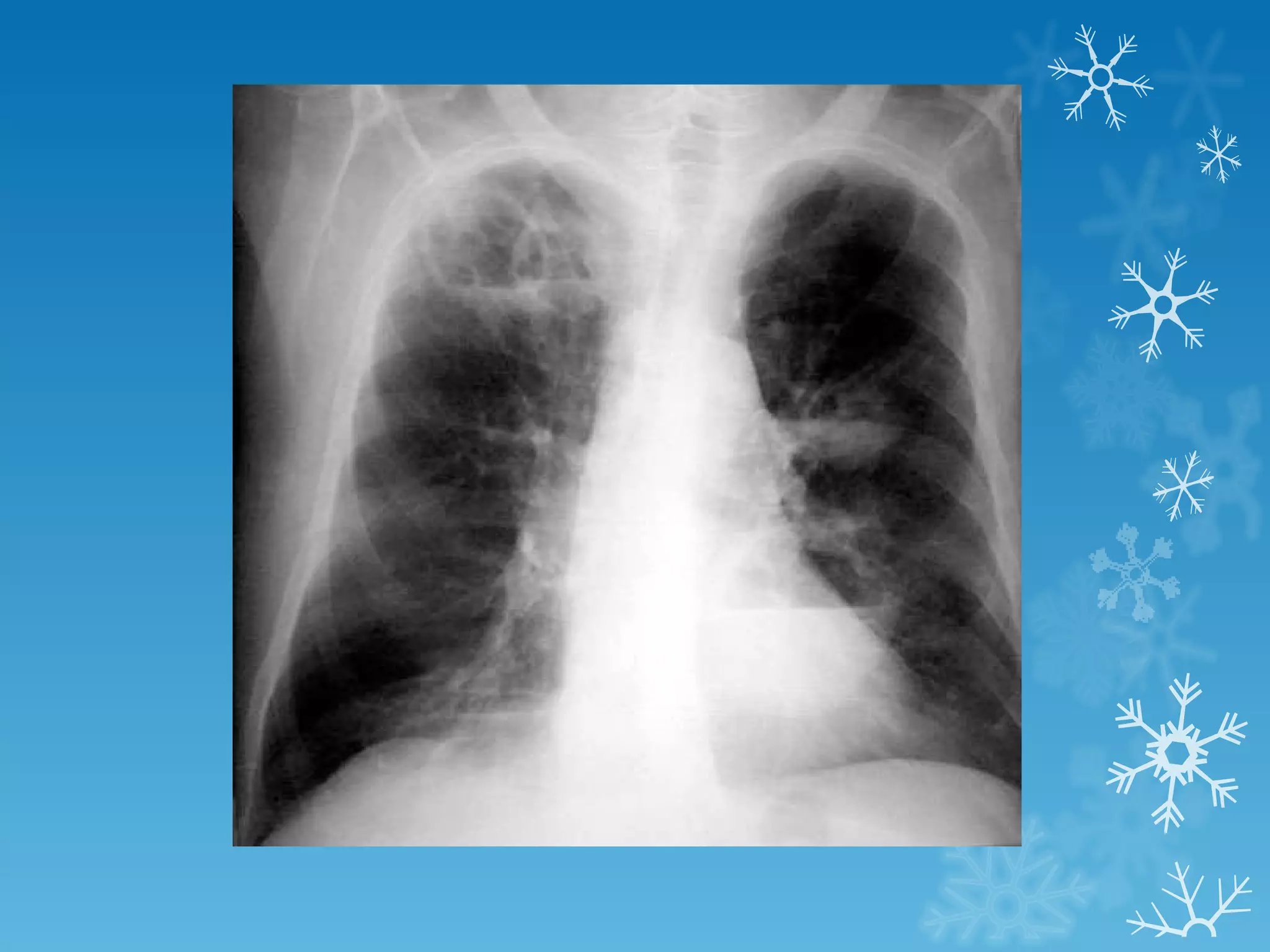
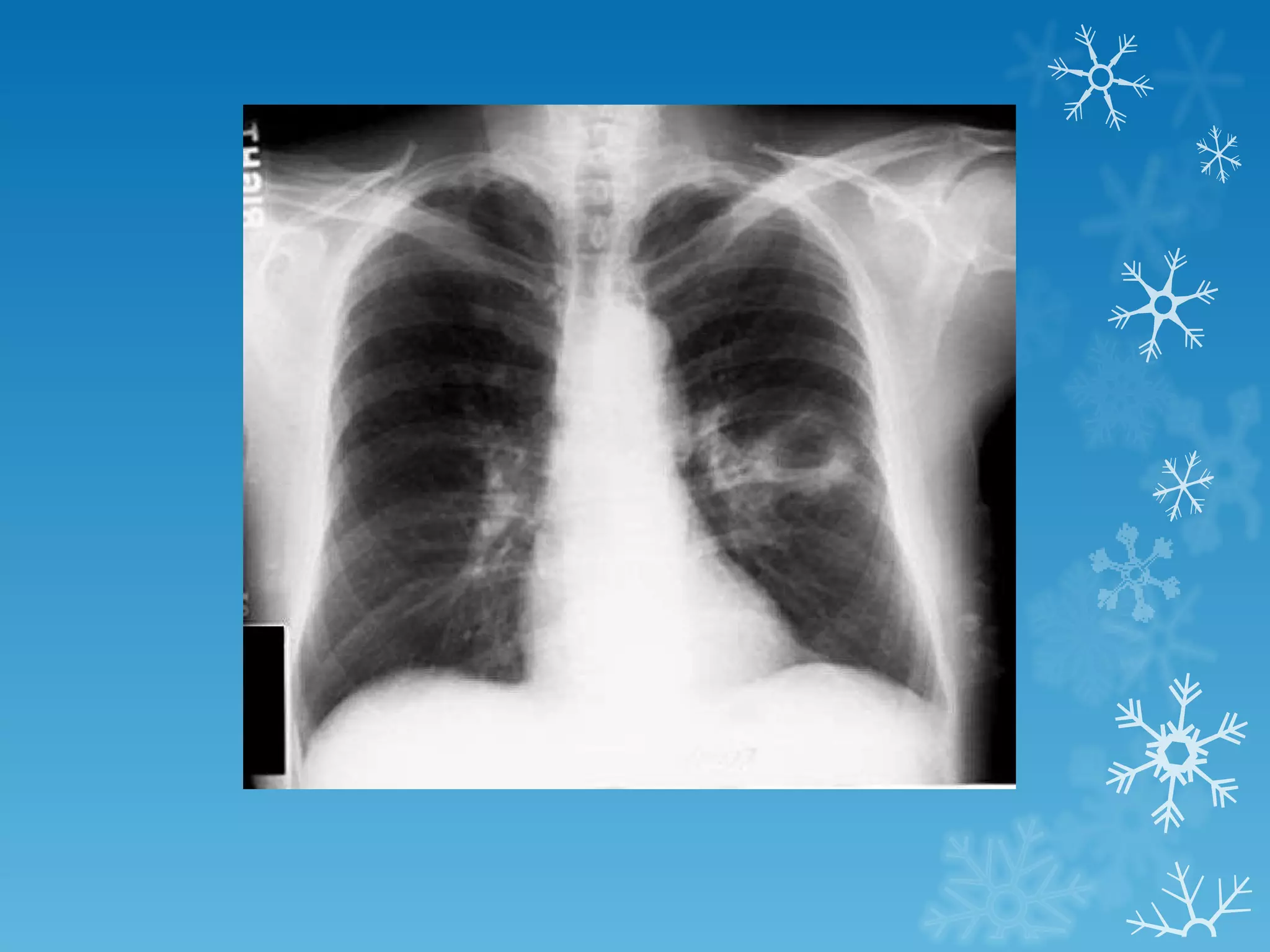
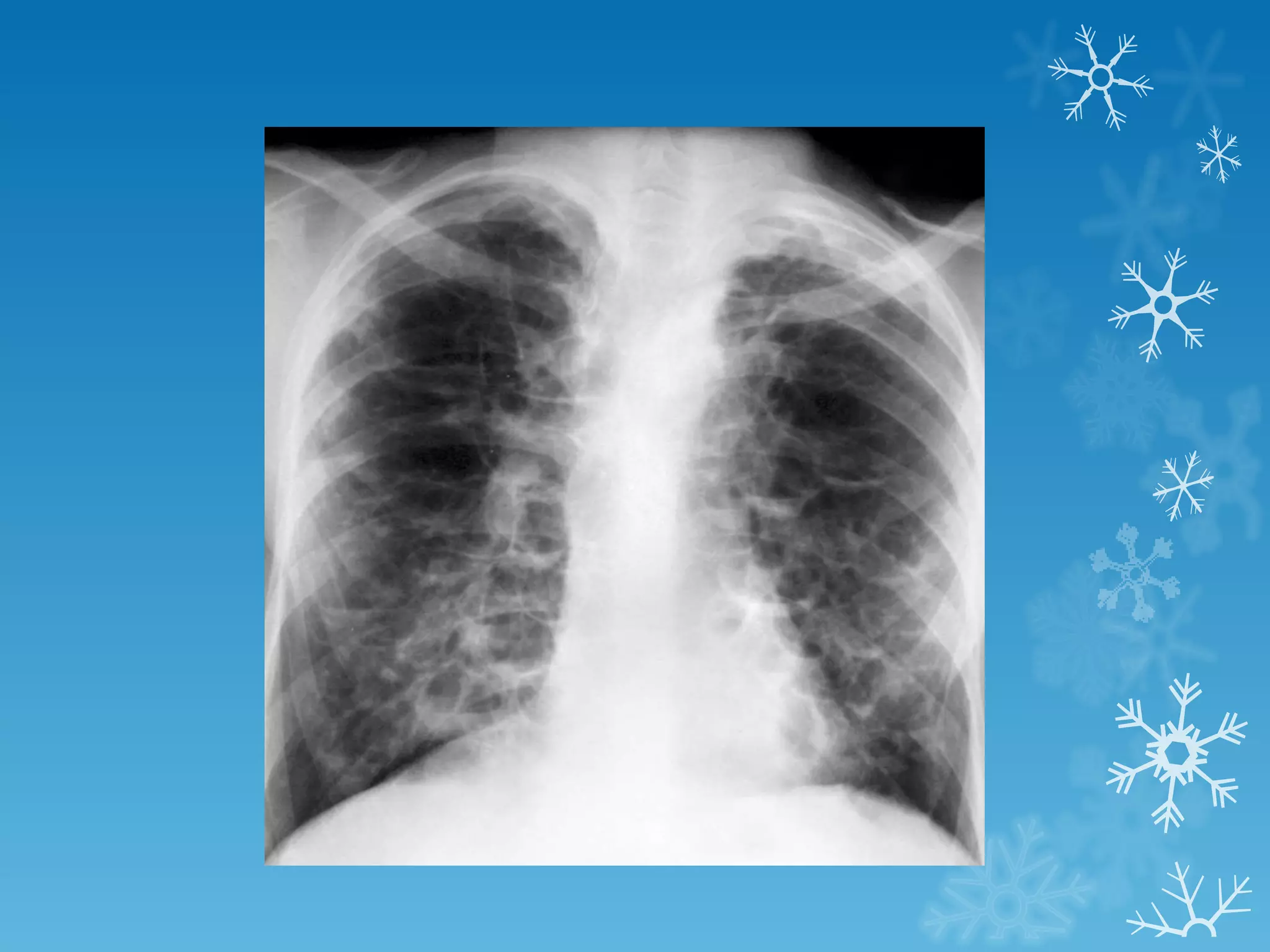
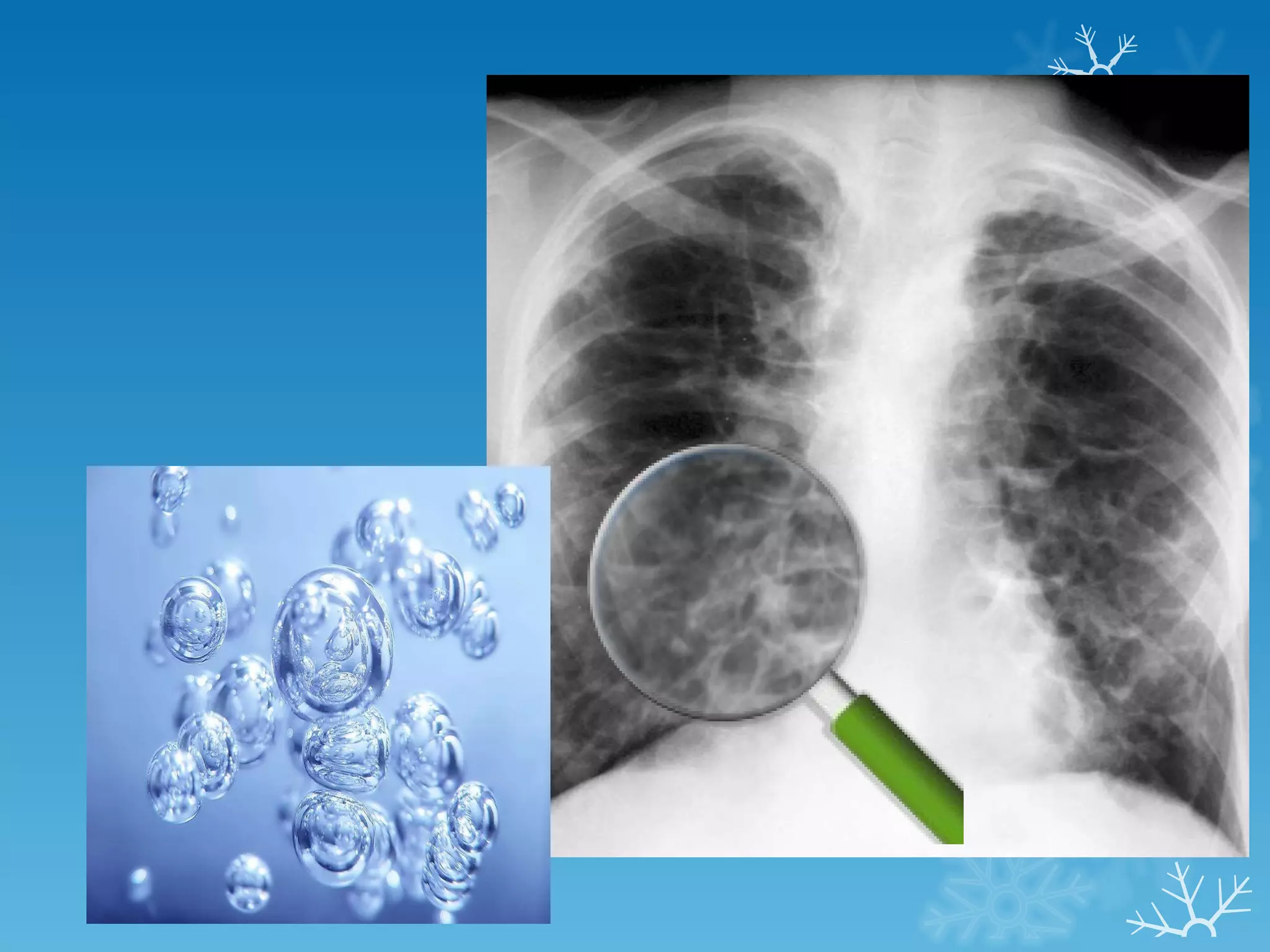
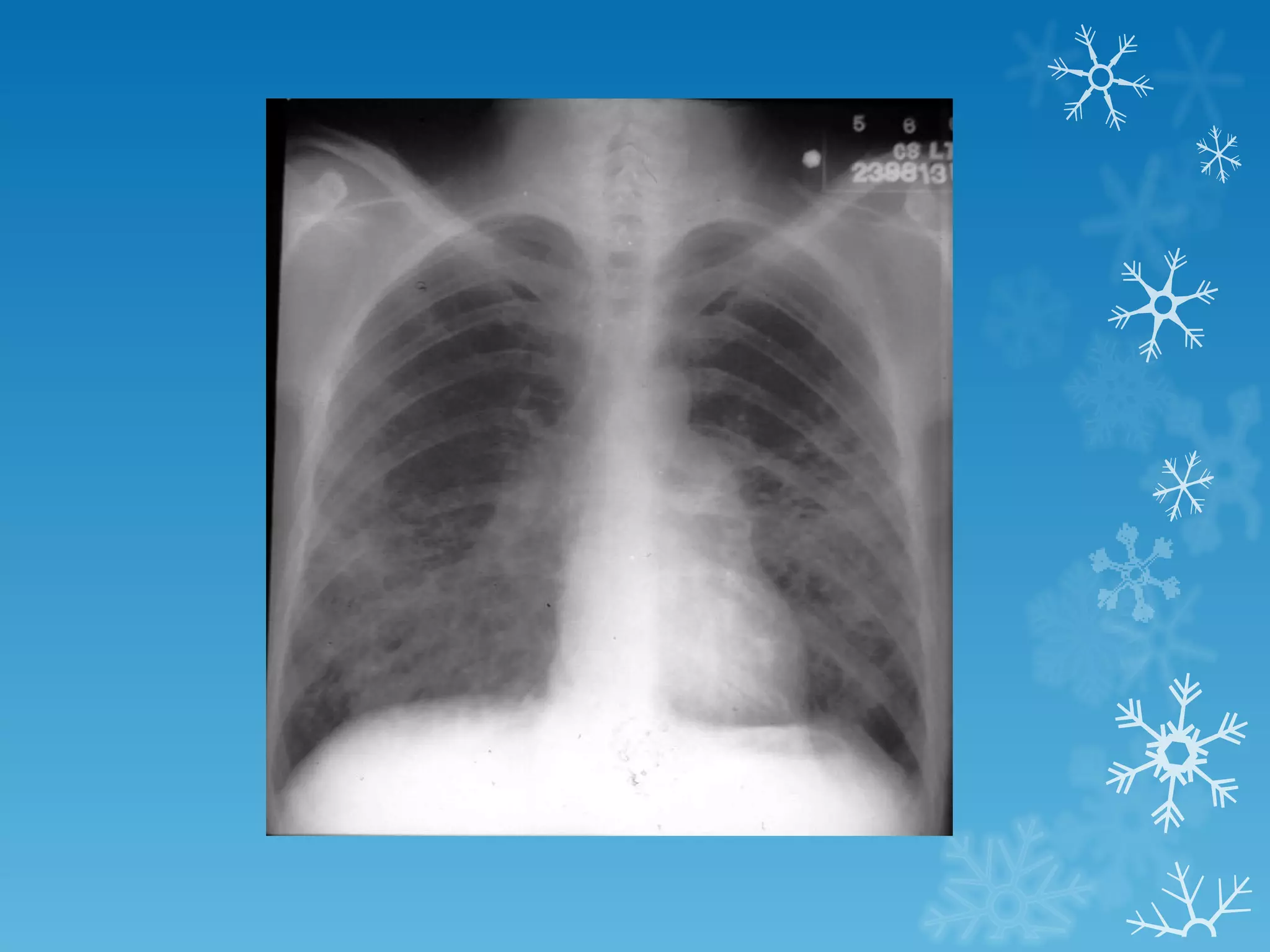
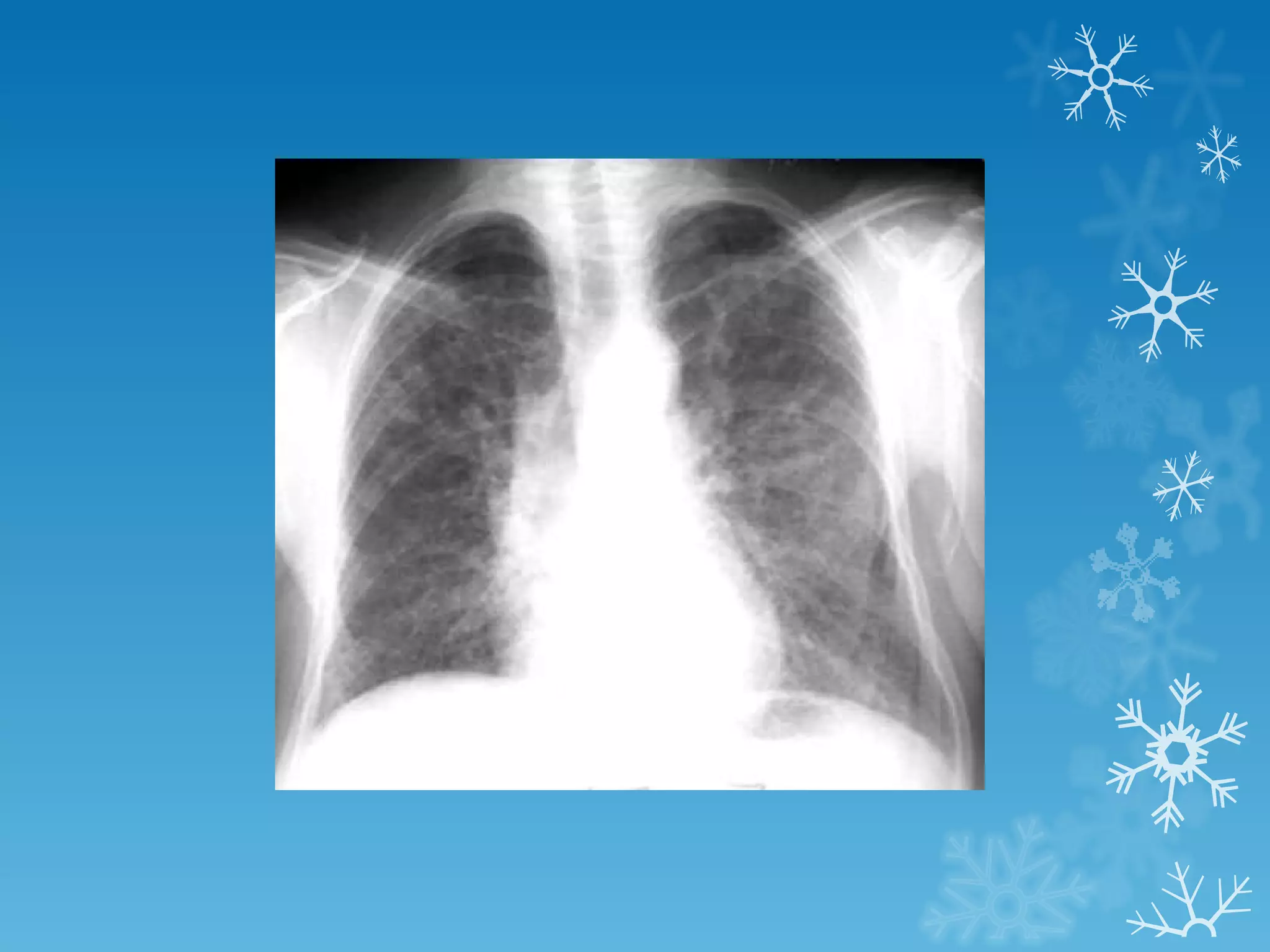
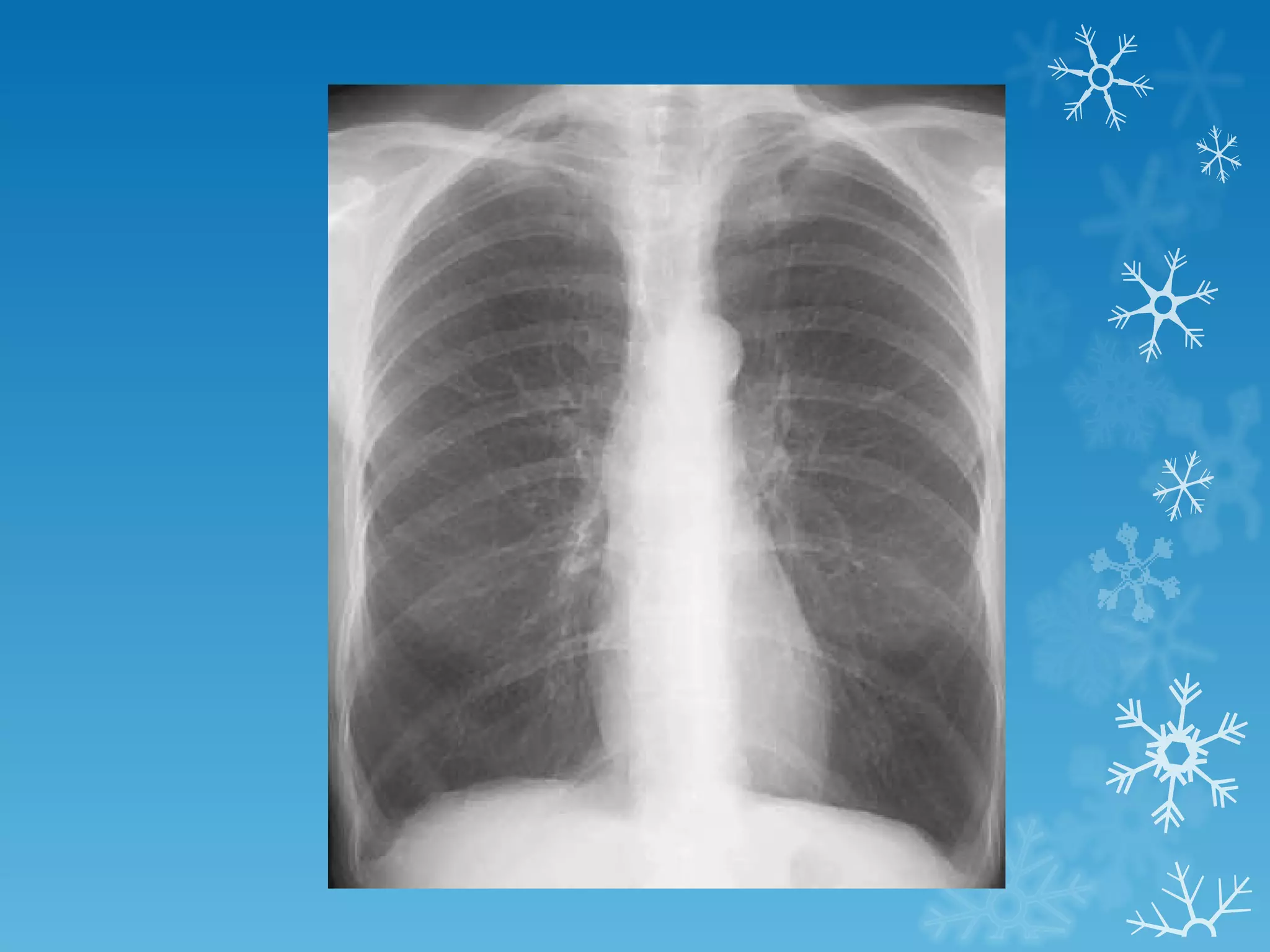
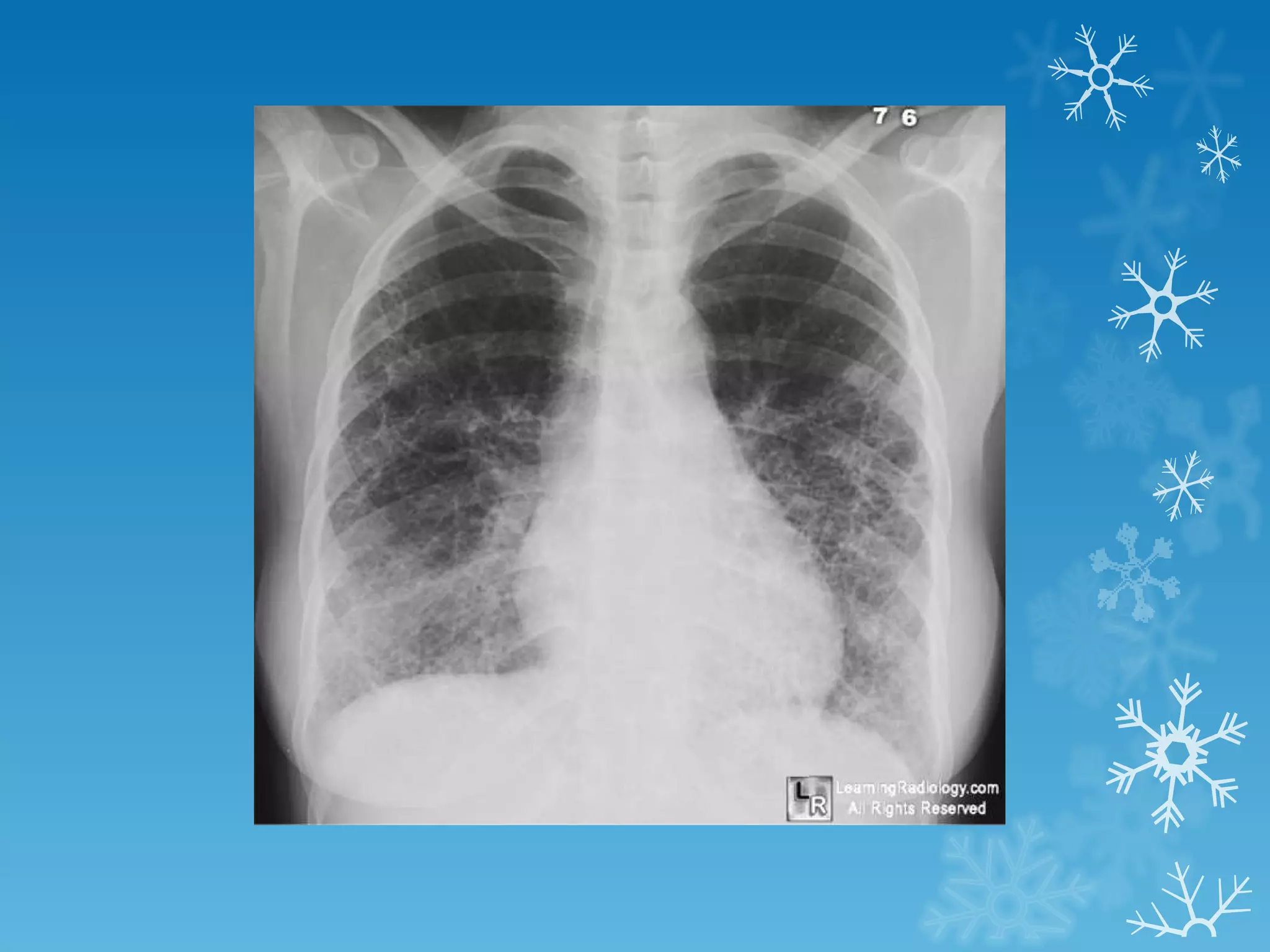
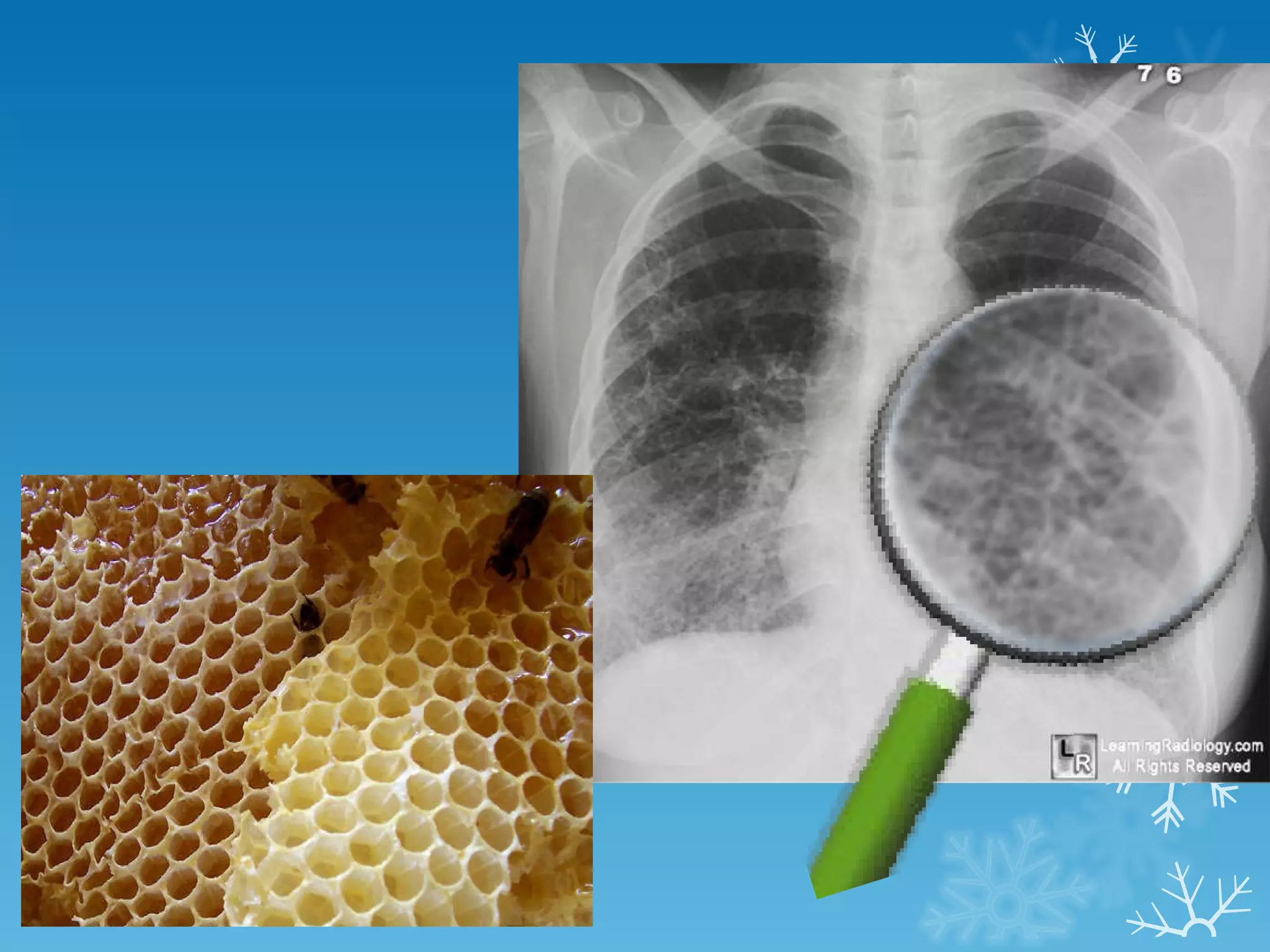
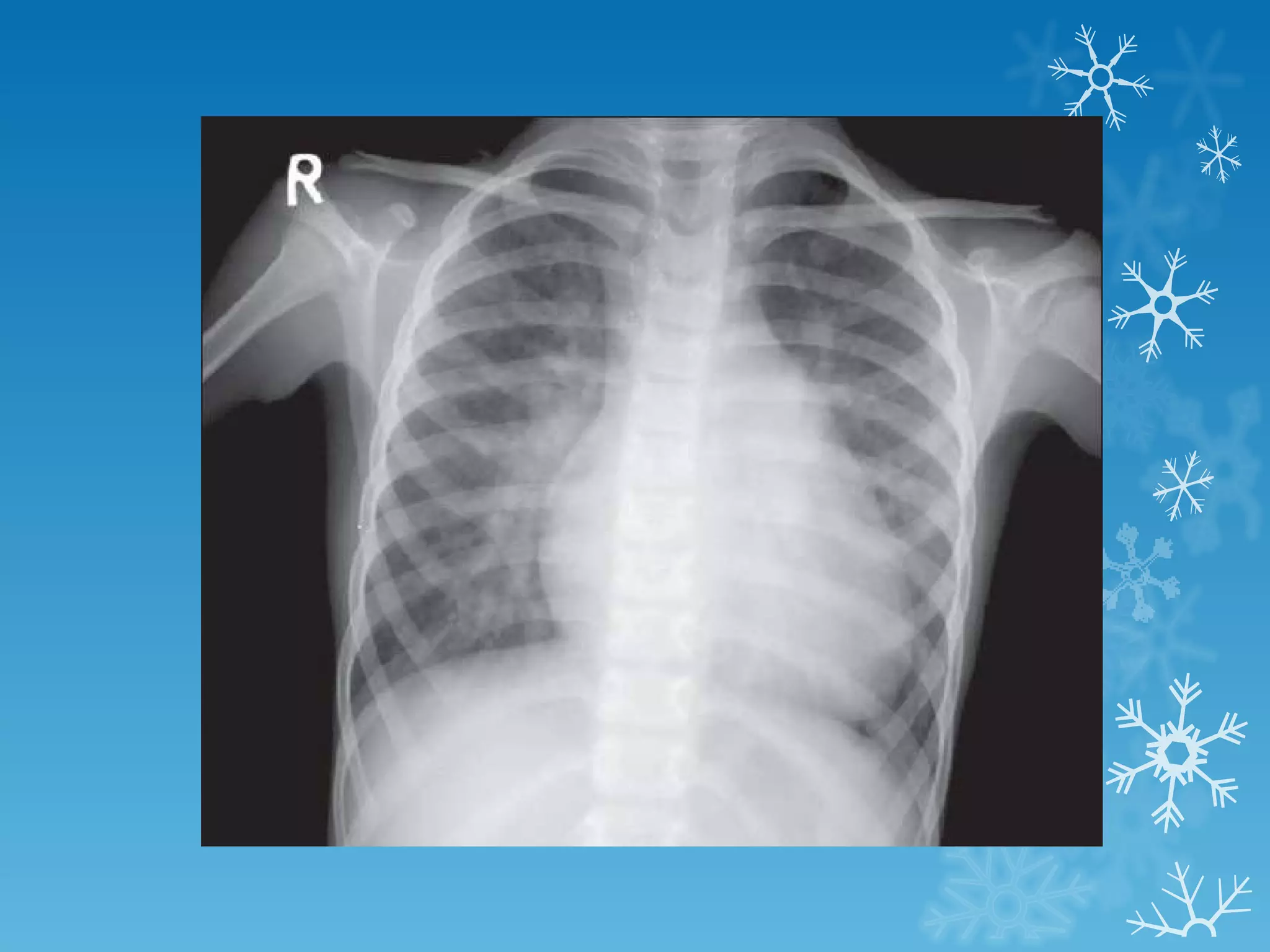
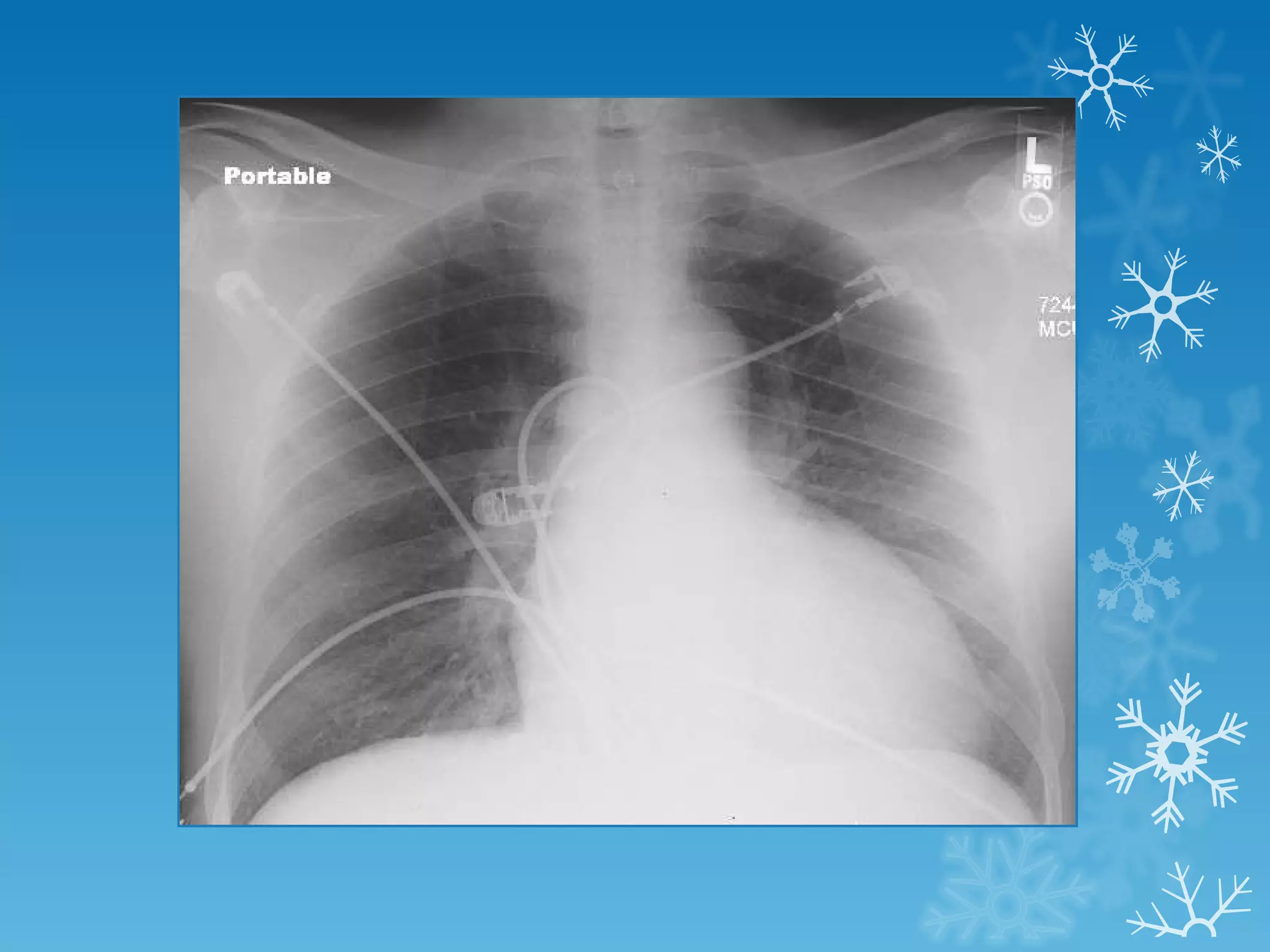
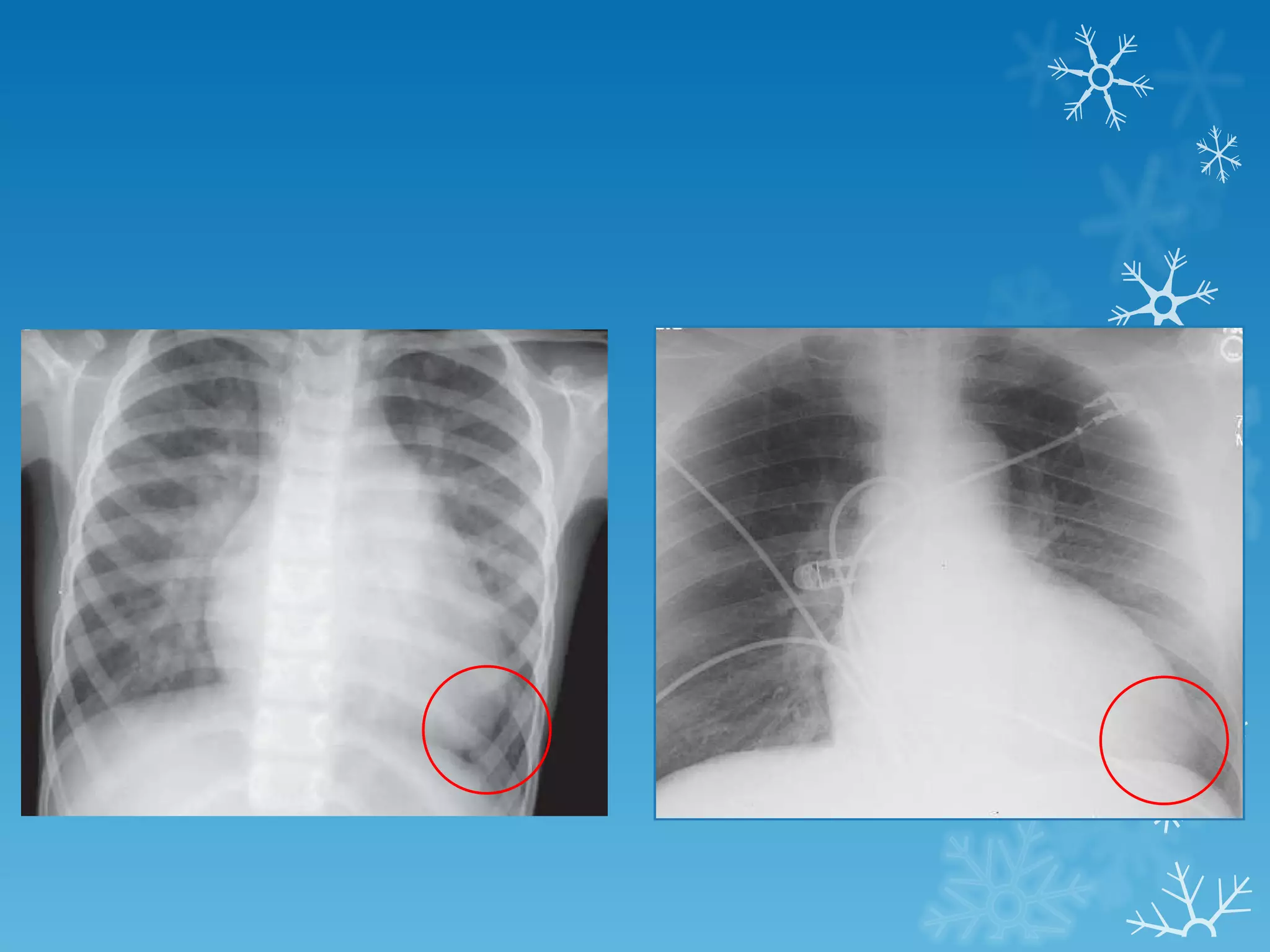
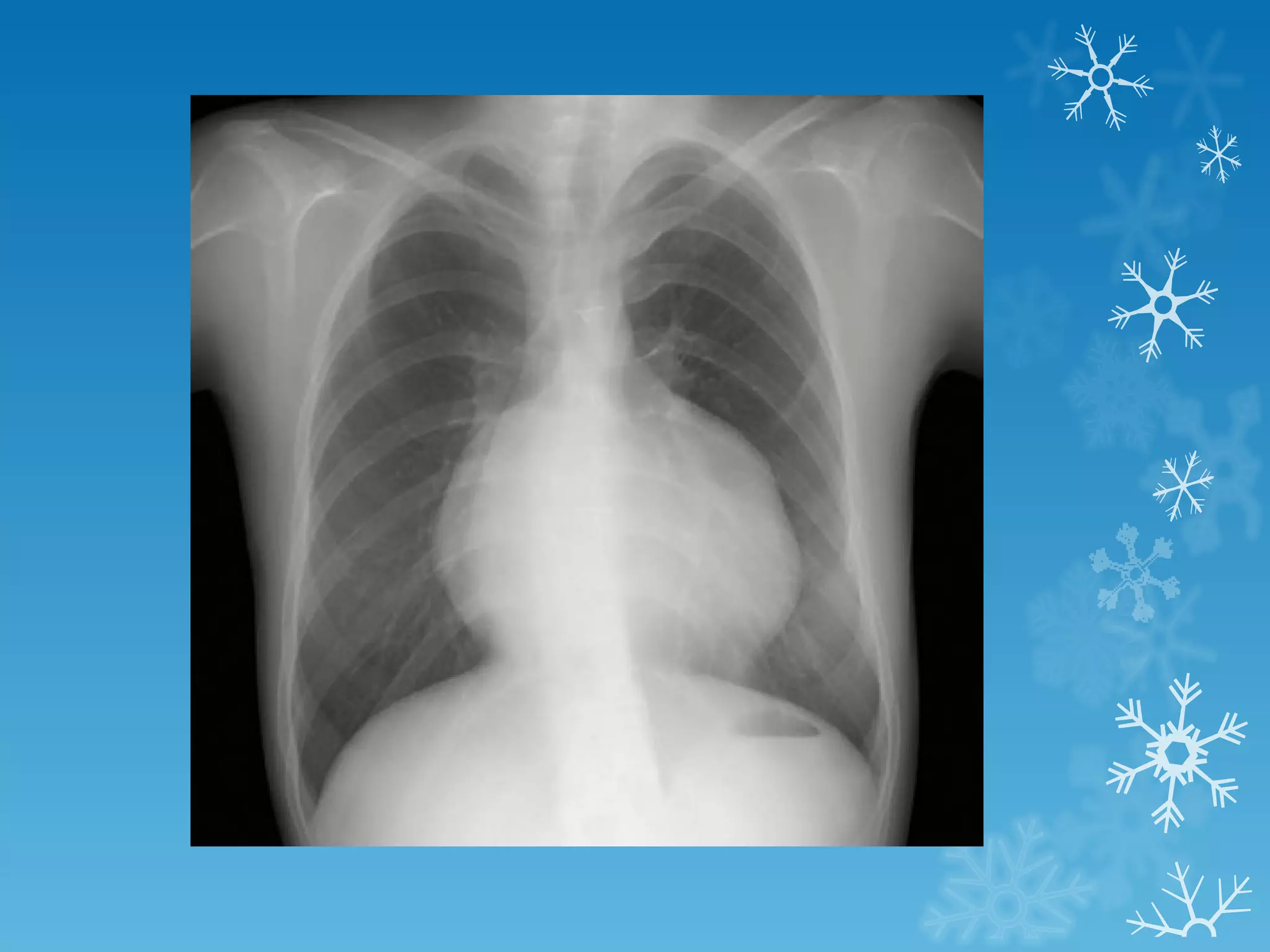
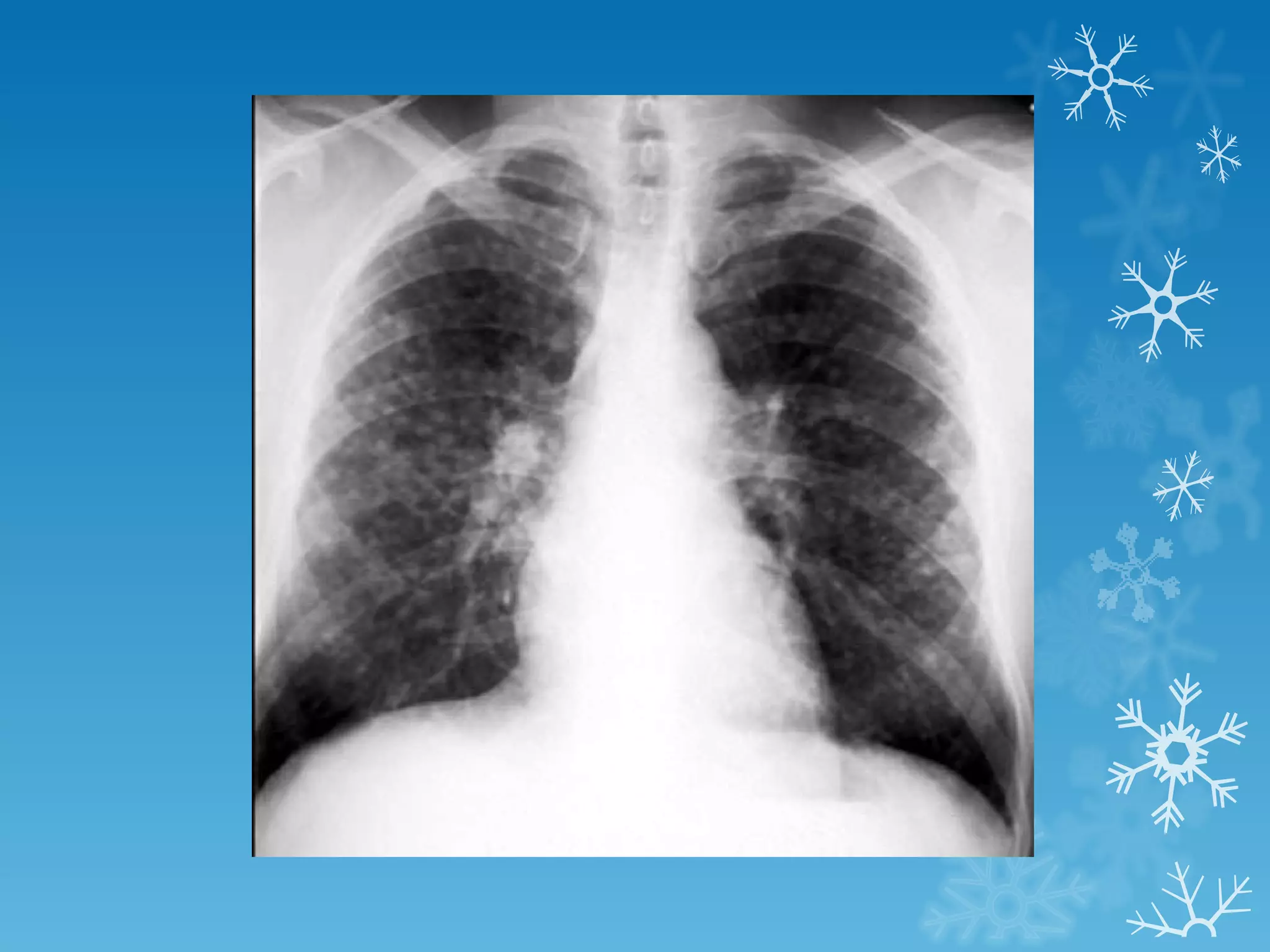
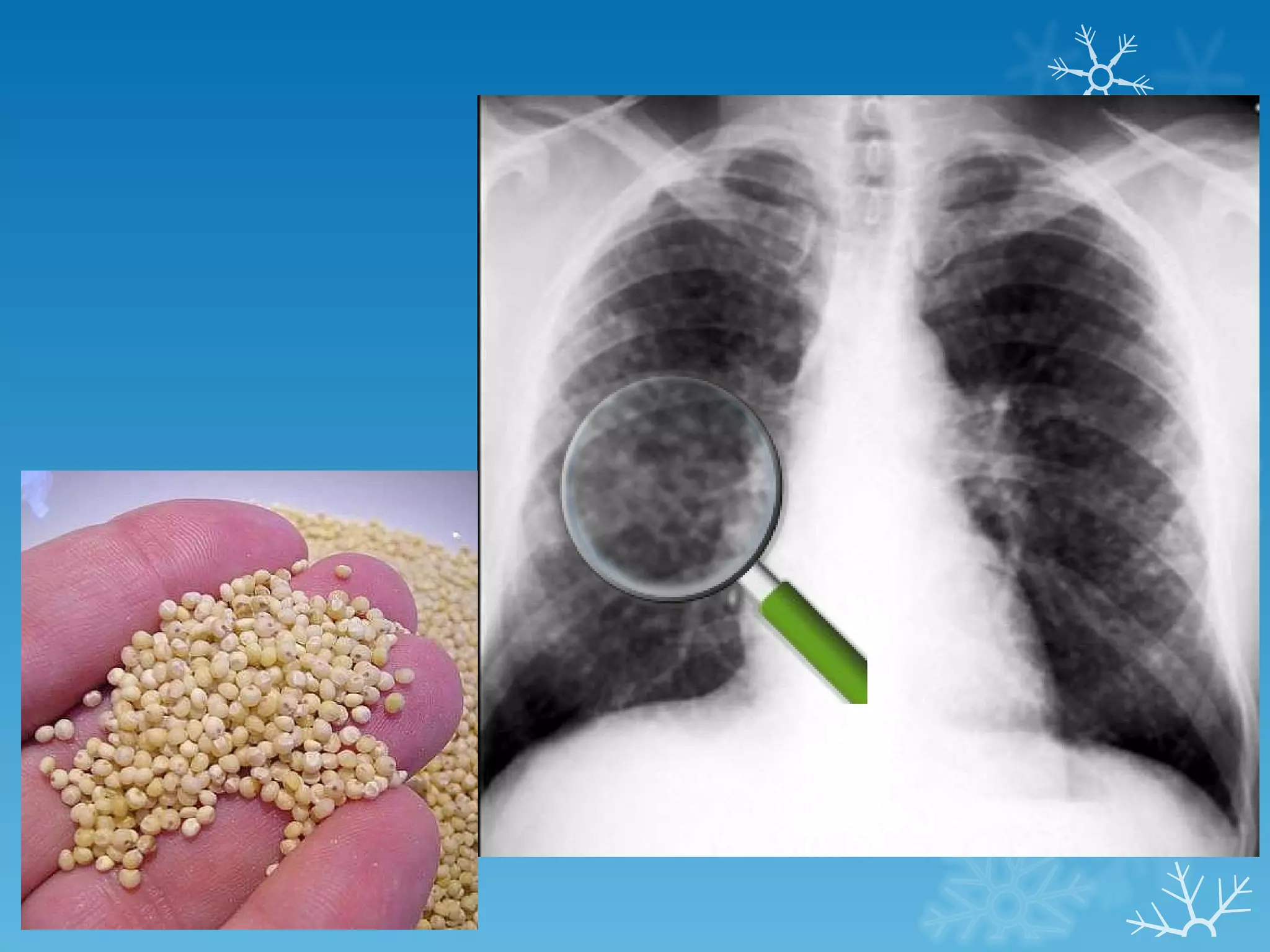
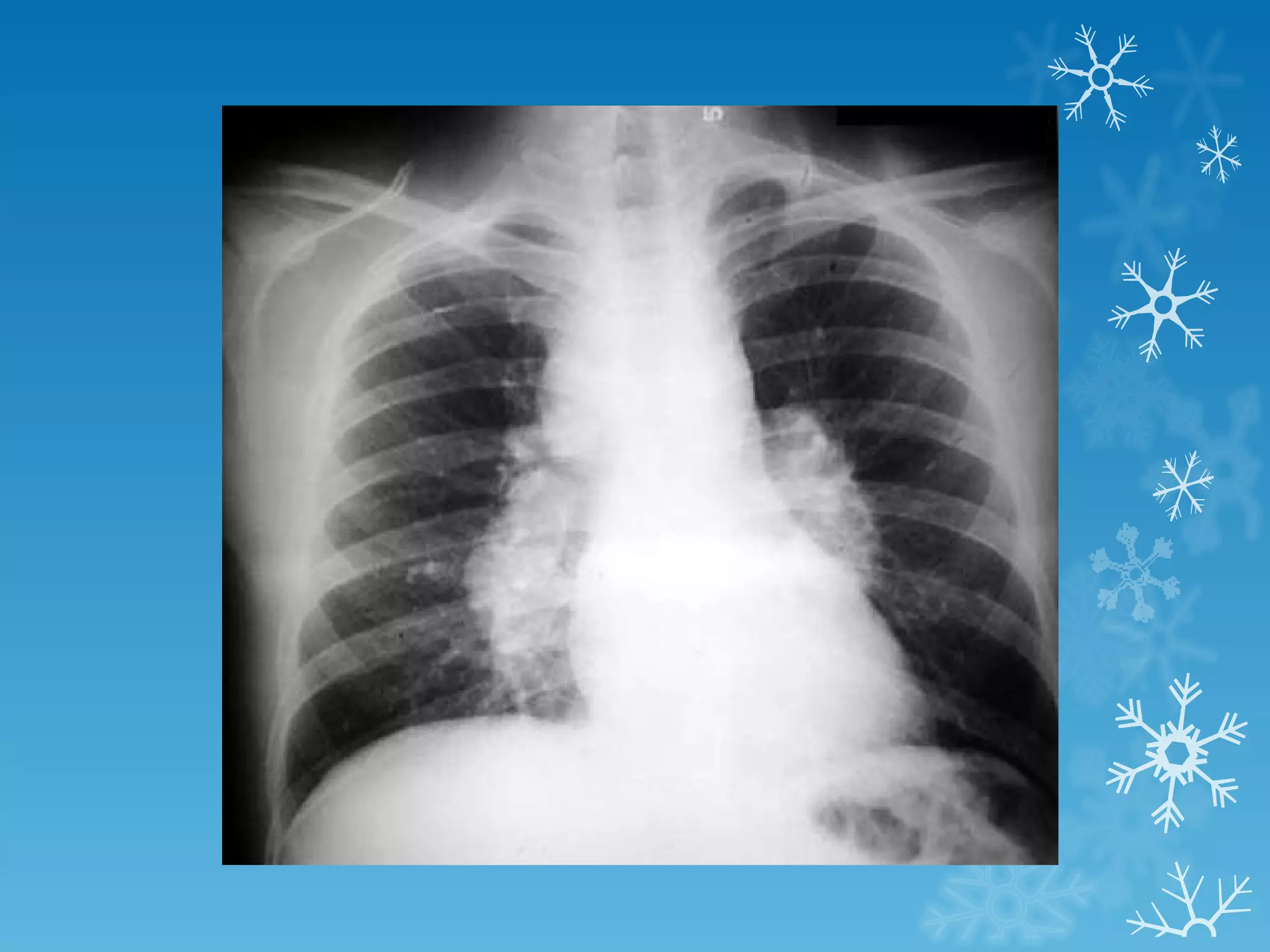
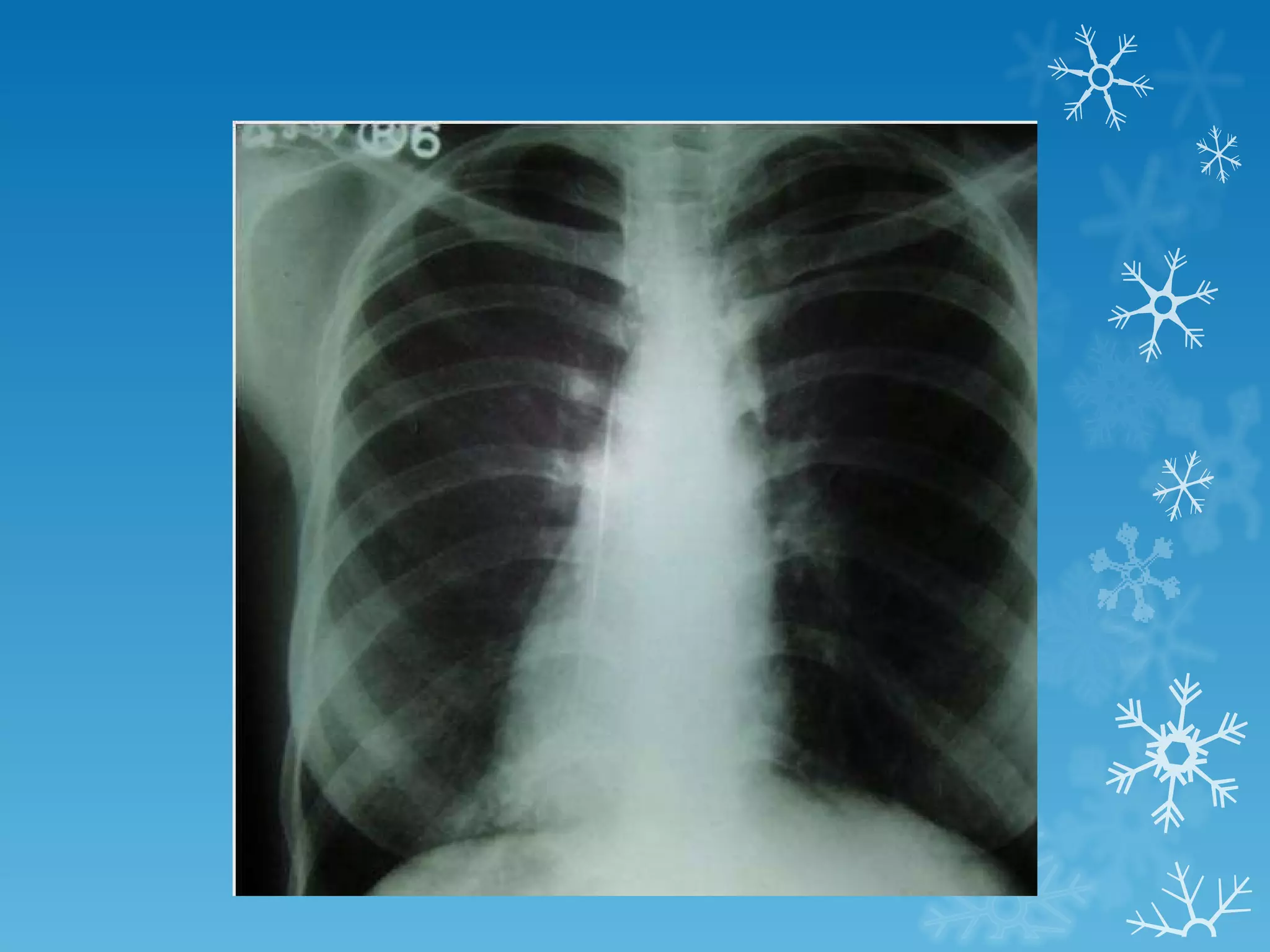
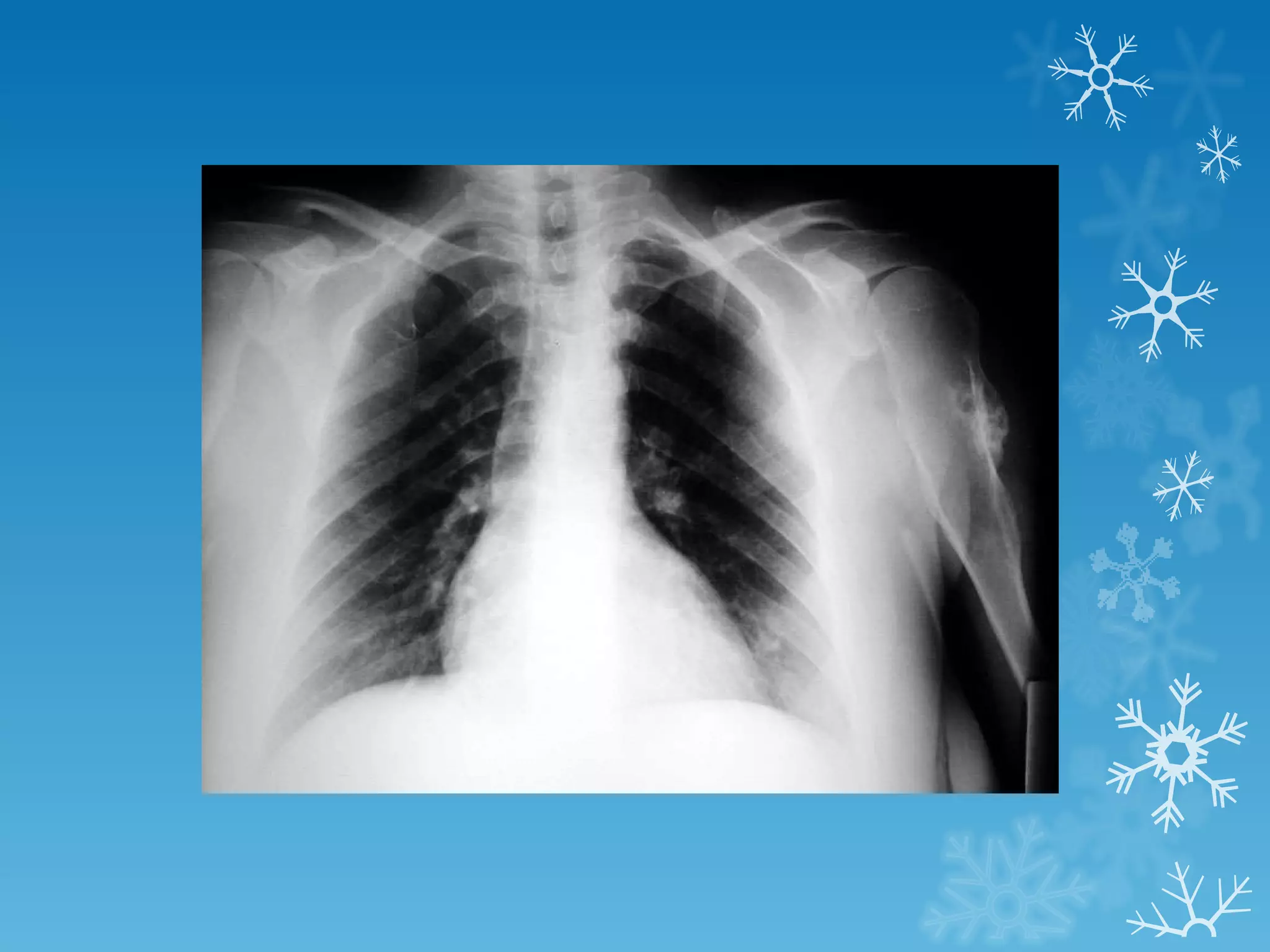
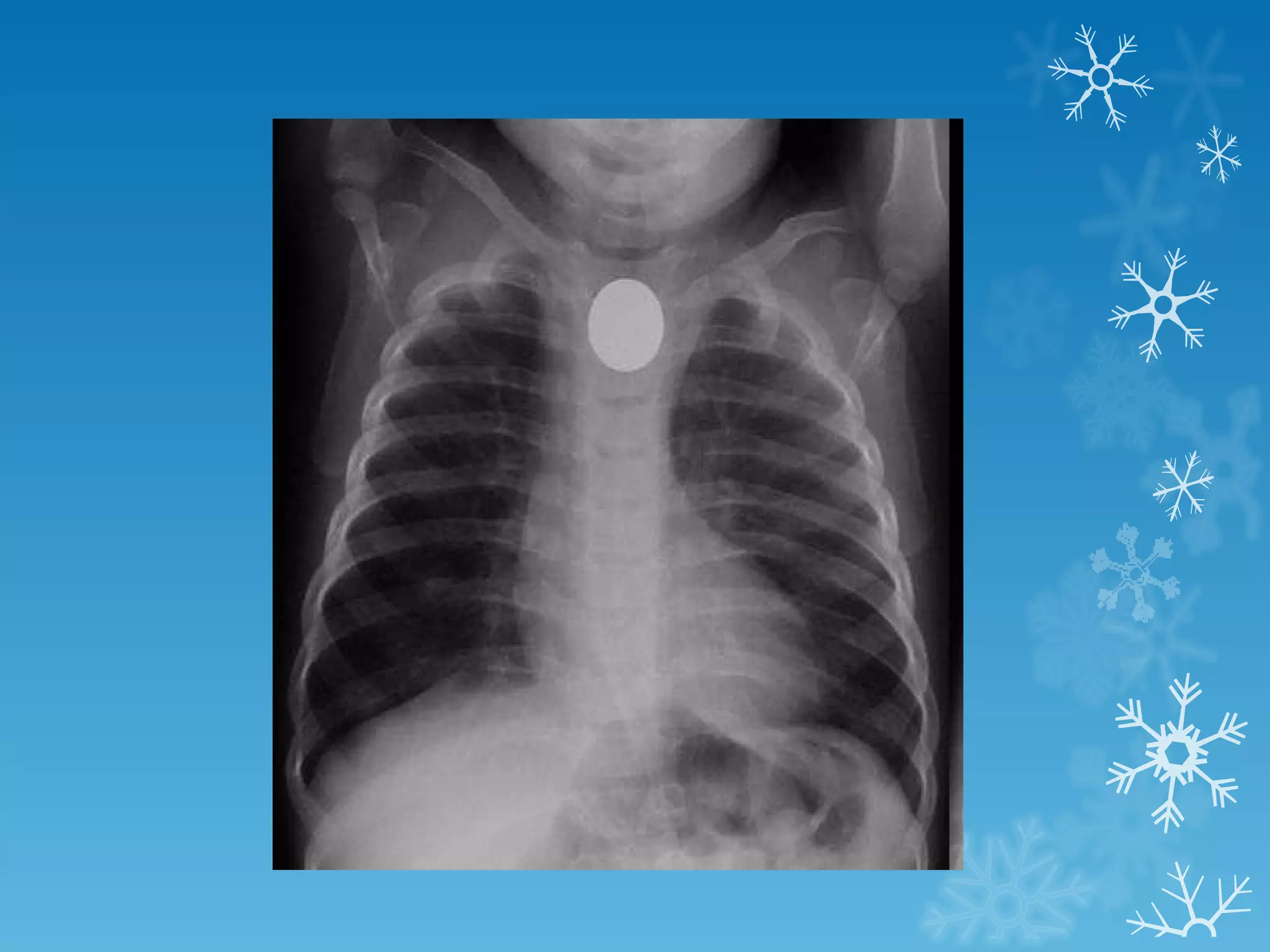
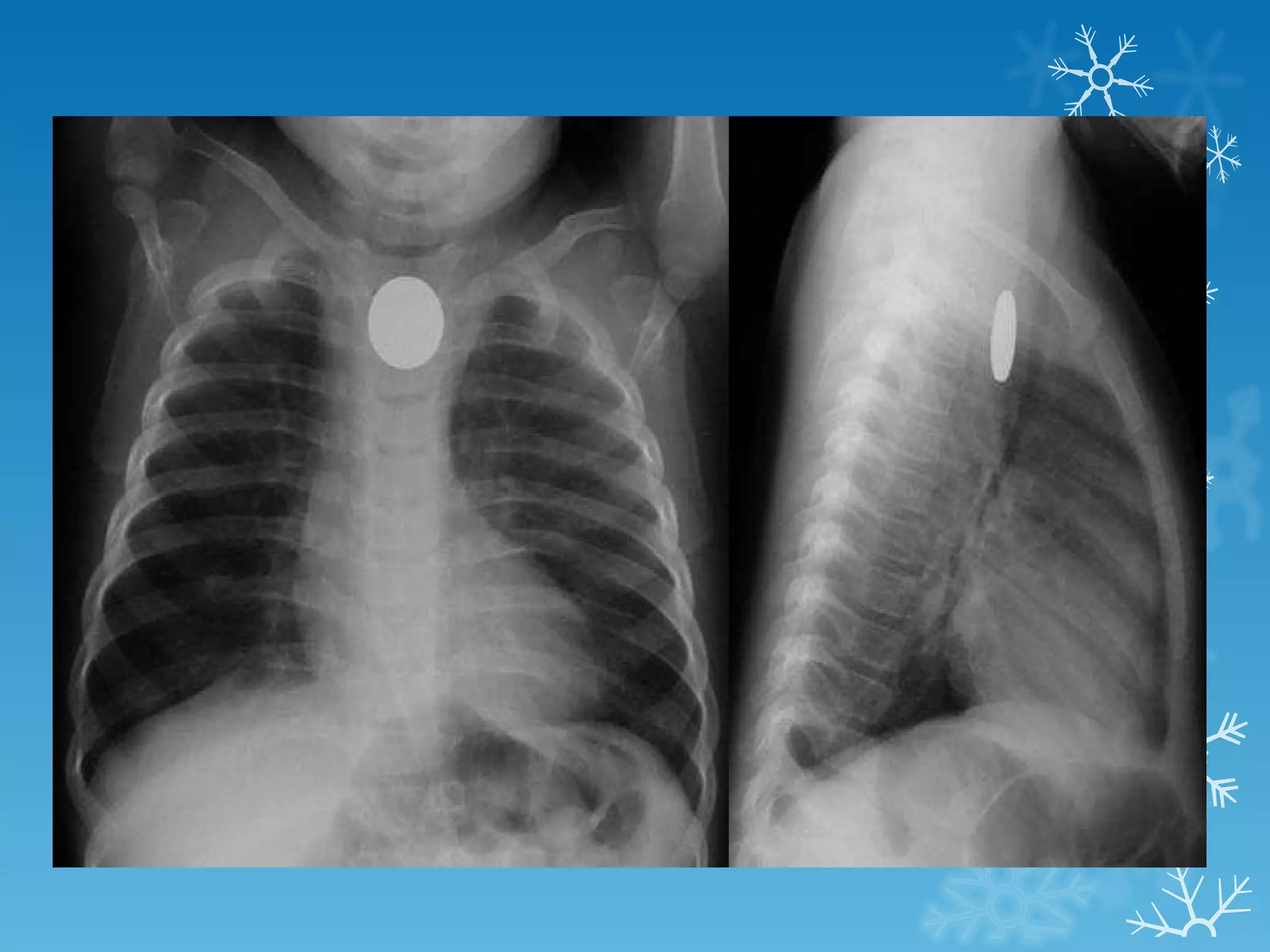
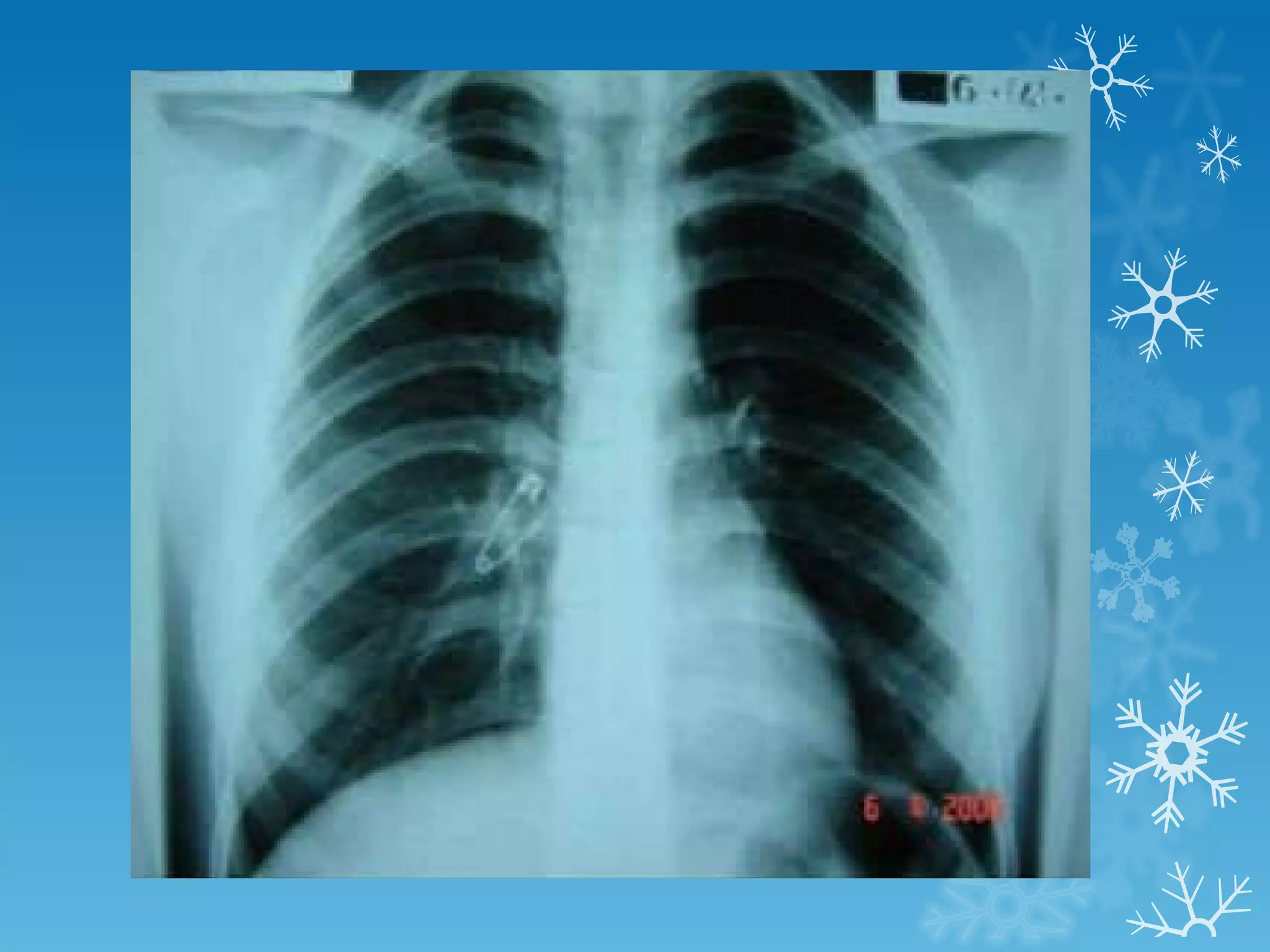
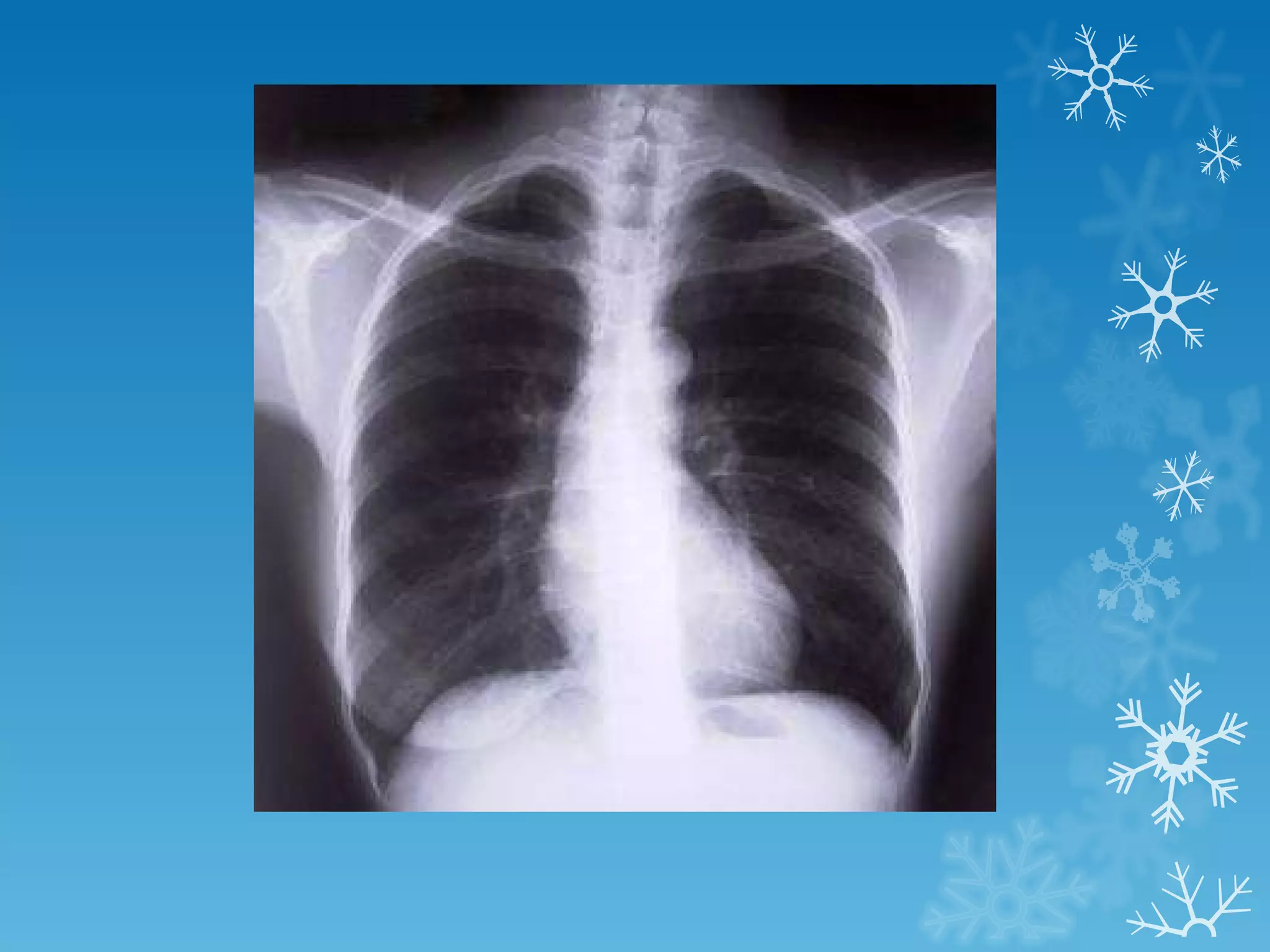
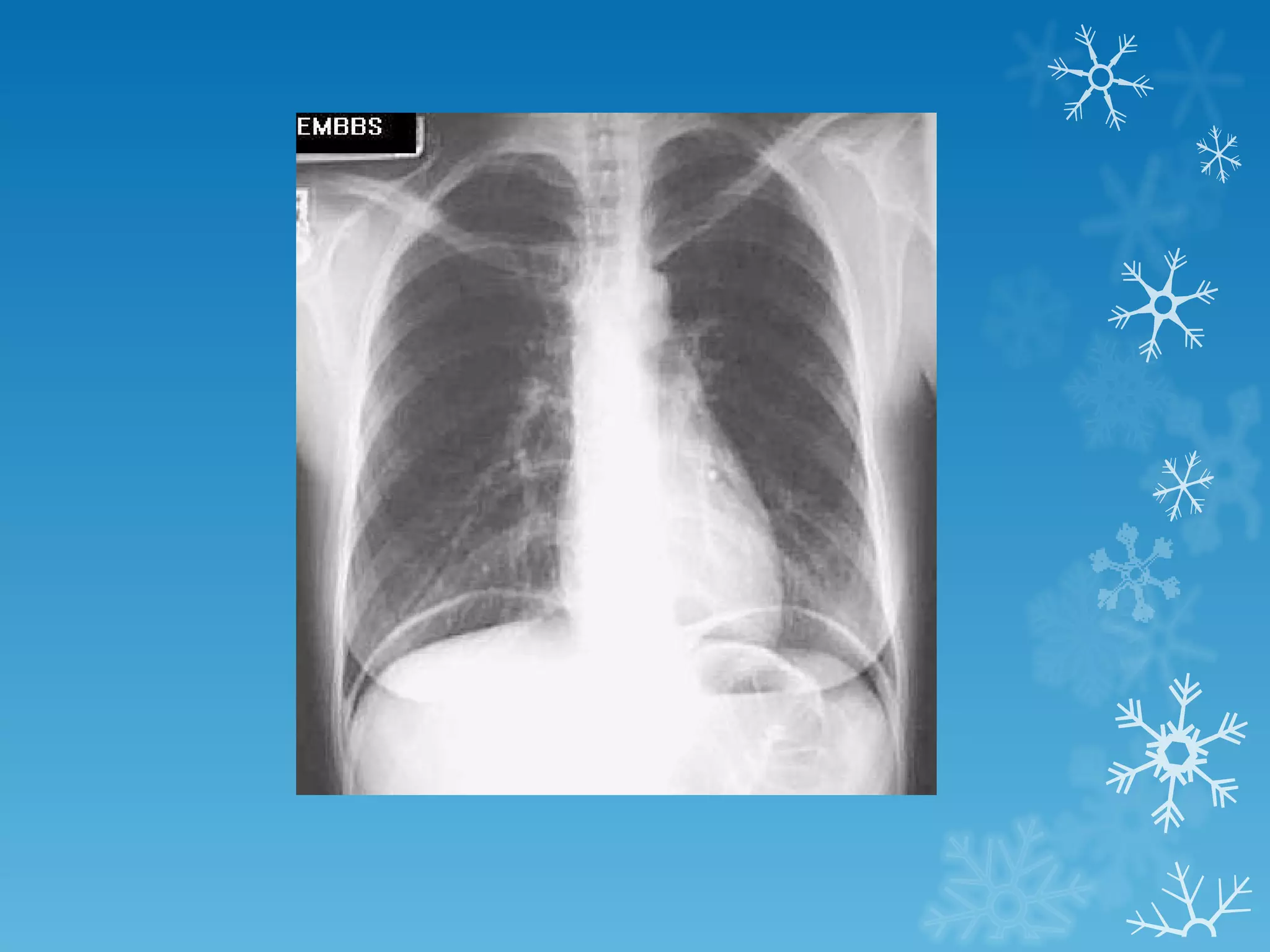
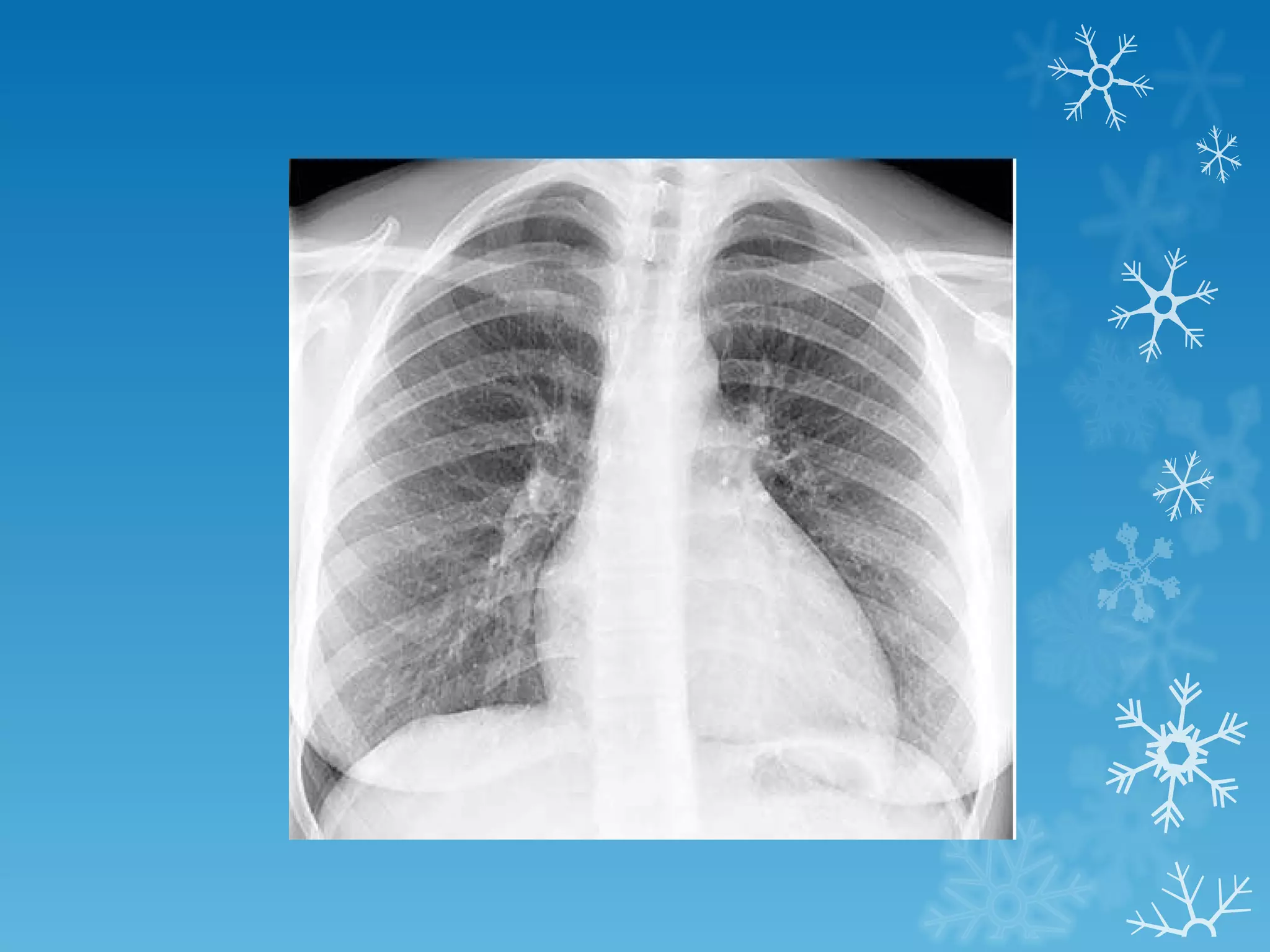

This document discusses chest x-ray interpretation and provides guidance on evaluating x-rays. It explains that tissue density determines how an x-ray beam penetrates, with denser tissues appearing whiter and less dense tissues appearing blacker. It also outlines different chest x-ray views and factors to consider like patient orientation, age, gender, and rotation. Abnormalities are described as appearing too white, too black, too large, or in the wrong place. The document stresses a systematic approach of identifying, localizing, describing lesions, and providing differential diagnoses.



































































