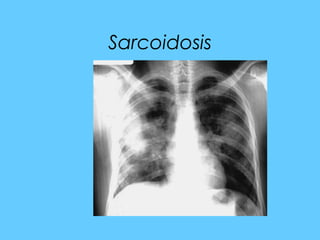
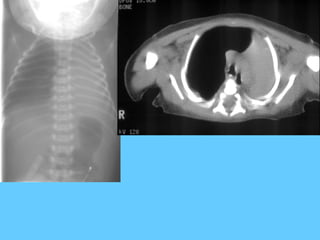
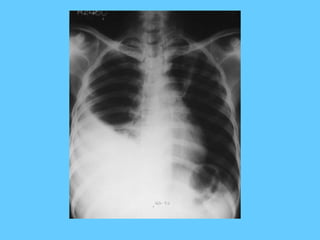
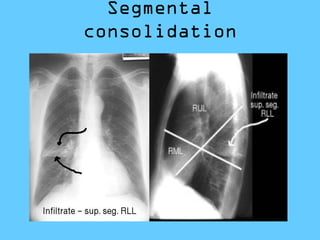
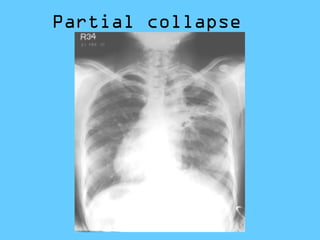
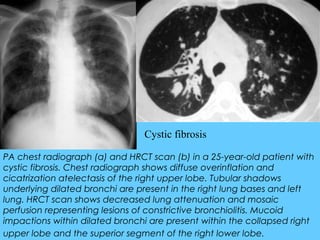
This document provides a classification and descriptions of various lung abnormalities visualized on radiography. It groups abnormalities according to their shape, size and distribution. Examples include bilateral total homogeneous shadows caused by conditions like pulmonary edema, bilateral opacity in the major part of the lung seen in diseases such as pulmonary edema and pneumonia, and unilateral total homogeneous opacity associated with pleural effusions or lung collapse. Circular or oval homogeneous shadows over 2cm may indicate tumors, infections or other pathologies. Multiple descriptions and radiologic findings of specific lung diseases are also provided.









































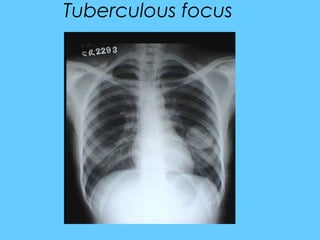
























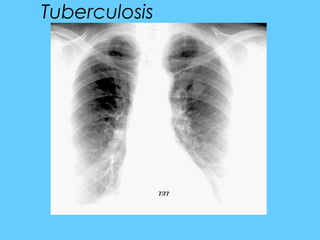















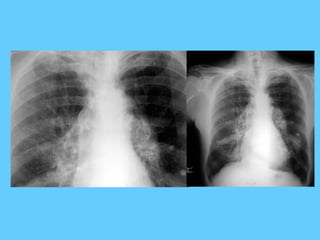
![Poorly defined small homogeneous
shadow
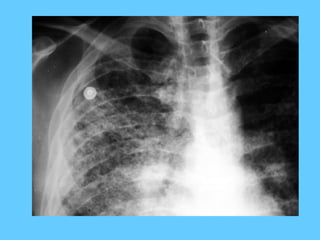
[ a smudge] < 2 cms
• Usually in the upper zones :
• Tuberculous focus
• If present in the lower ½ of the lung
near the pleura :
• Infract](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abnormallung1-150902234350-lva1-app6892/85/abnormal-chest-xray-ppt-90-320.jpg)
















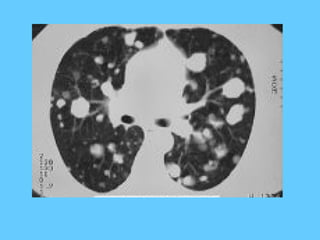
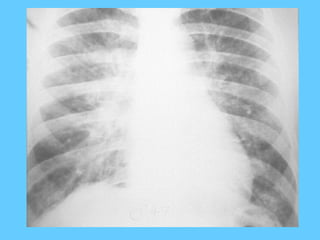
![Nodular shadows with ground
glass haze [pin point]
• Respiratory distress syndrome
• Fibrosing alveolitis
• Microlithiasis alveolaris](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abnormallung1-150902234350-lva1-app6892/85/abnormal-chest-xray-ppt-112-320.jpg)








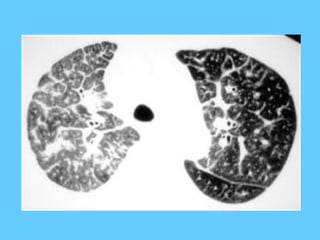


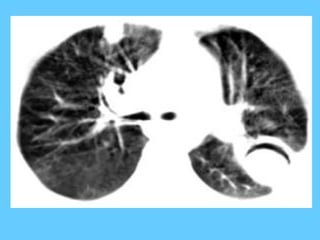
![Nodular shadows with small ring
shadows [ring diameter 3- 8 mm]
• Fibrosing alveolitis – late stage
cryptogenic form
• Asbestos induced fibrosis
• Systemic sclerosis
• Allergic alveolitis – farmers , bird fanciers ,
malt workers
• Xanthomatous lung disease
• Idiopathic Haemosiderosis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abnormallung1-150902234350-lva1-app6892/85/abnormal-chest-xray-ppt-125-320.jpg)