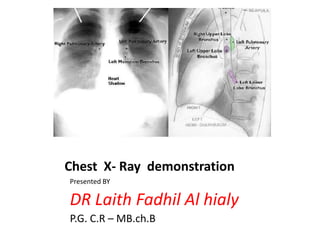
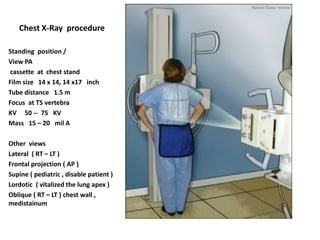
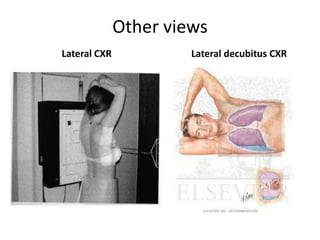
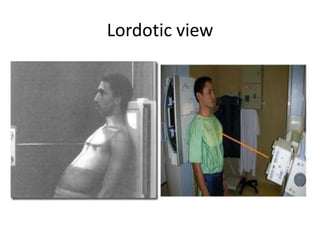
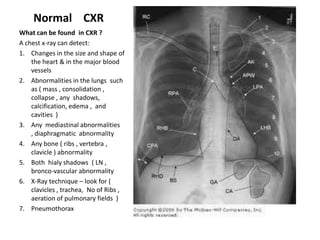
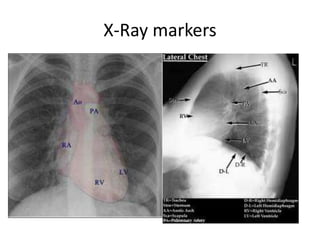
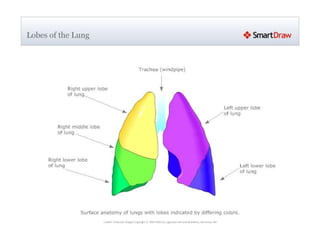
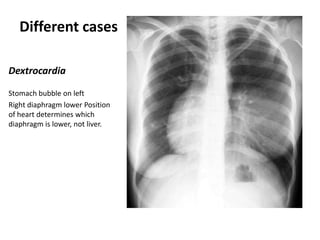
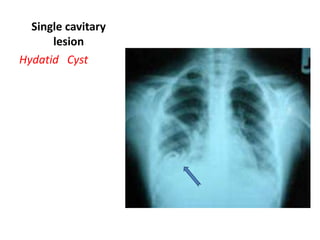
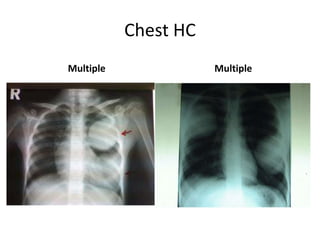
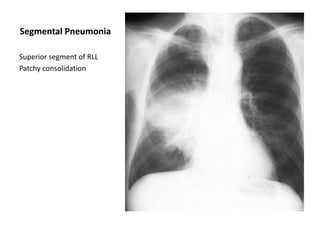
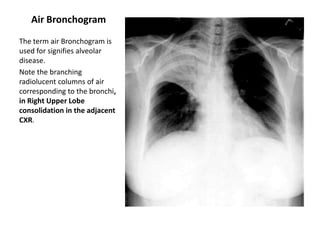
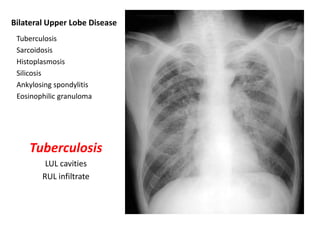
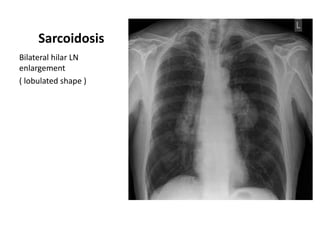
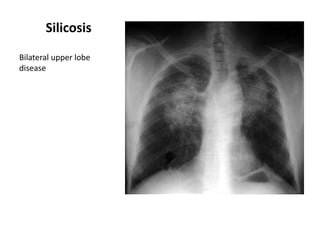
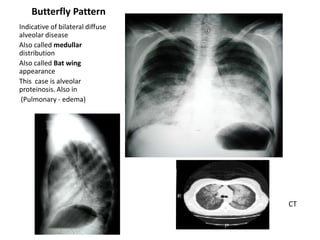
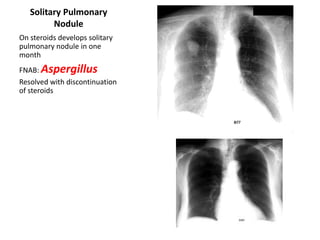
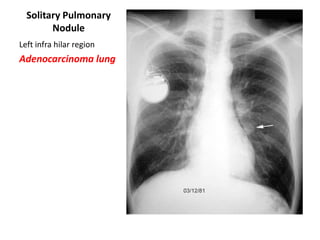
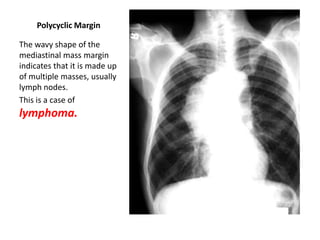
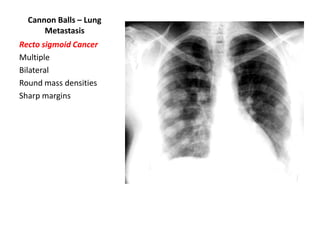
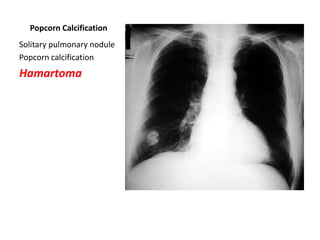
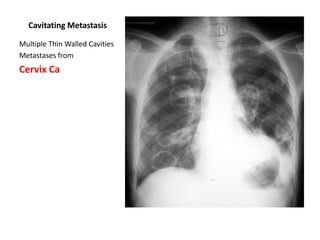
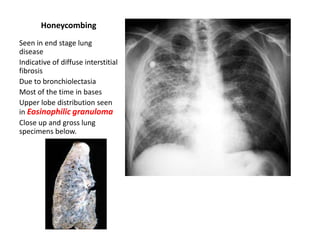
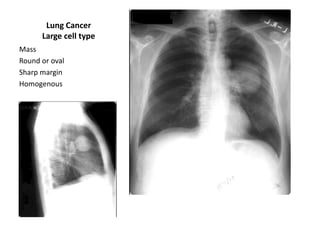
This document provides an overview of chest X-ray procedures and demonstrations of various chest X-ray images. It describes the standard positioning and views for chest X-rays, including posteroanterior, lateral, lordotic, and others. It then shows examples of normal chest X-ray findings and various pathologies that can be detected, such as heart and lung abnormalities, pneumothorax, cavitary lesions, pneumonia, and tumors. Specific disease examples include tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, silicosis, and lung cancer.