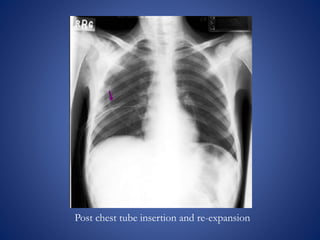
The document discusses chest x-rays and how to analyze them. It describes how densities appear on x-rays, with gas being darkest and bone being lightest. Proper inspiration, penetration, and rotation are needed for quality images. The lungs, heart, bones, and other structures are then analyzed systematically. Common findings like consolidation and air bronchograms are also explained.