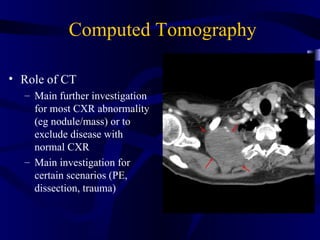
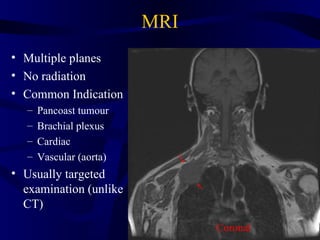
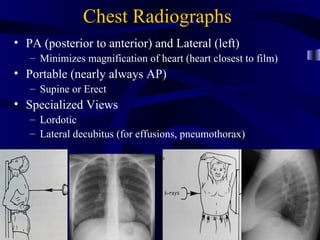
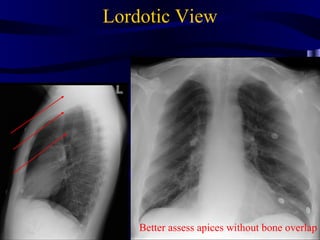
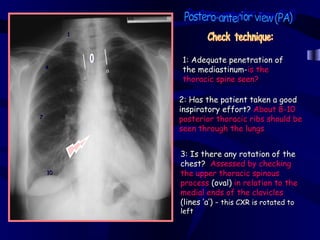
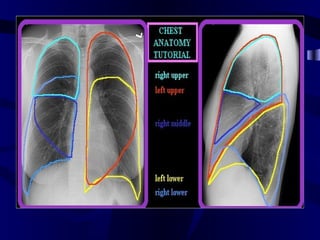
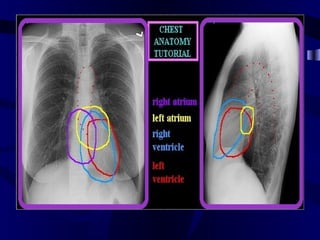
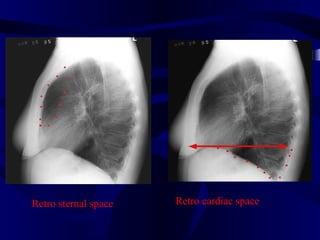
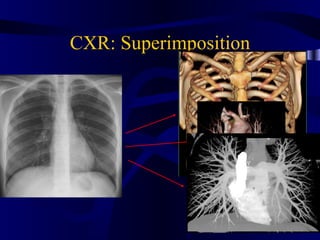
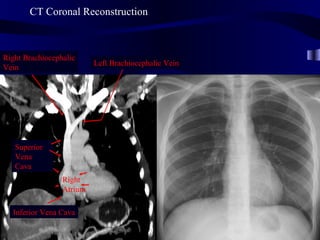
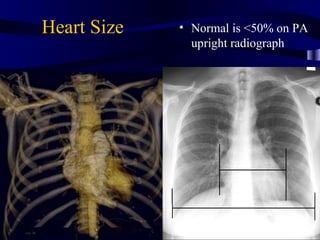
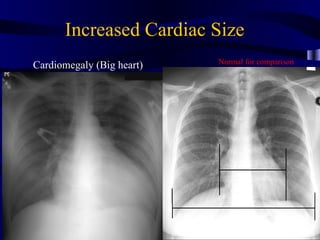
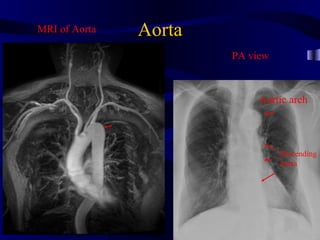
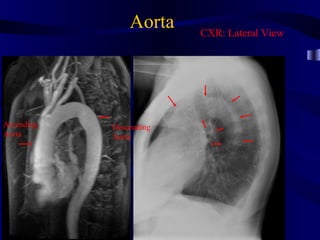
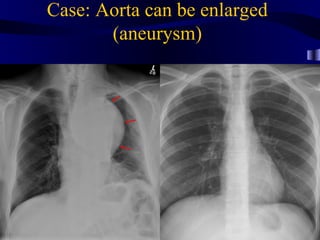
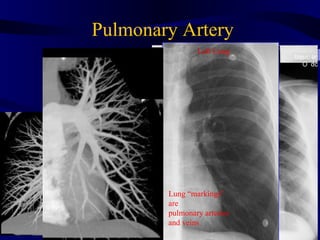
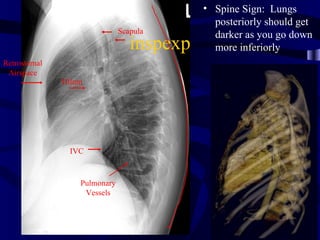
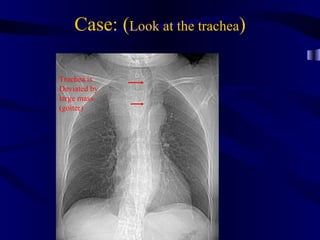
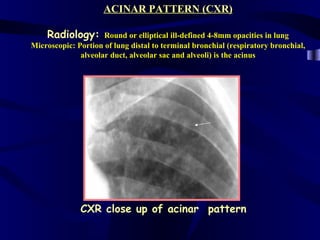
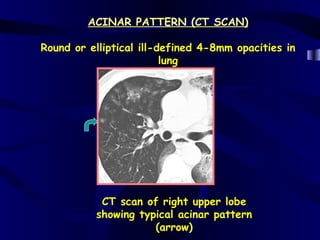
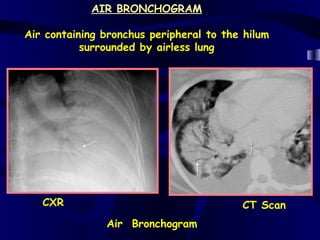
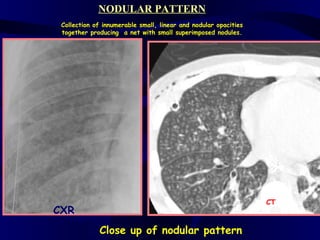
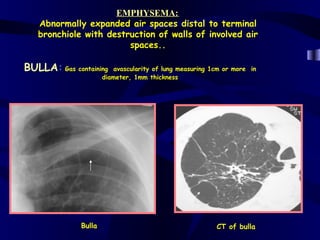
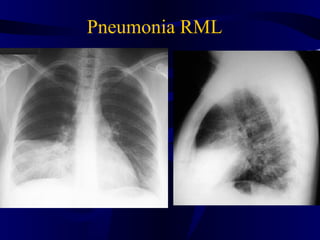
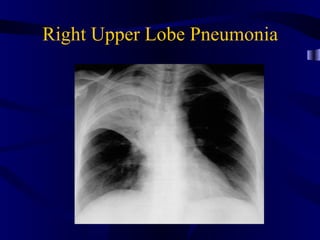
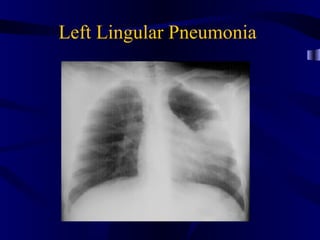
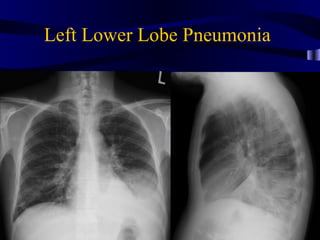
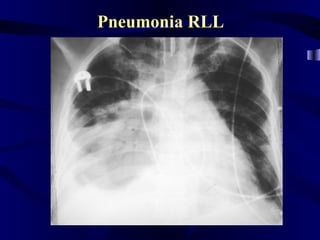
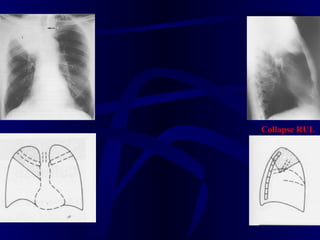
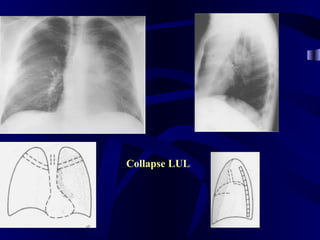
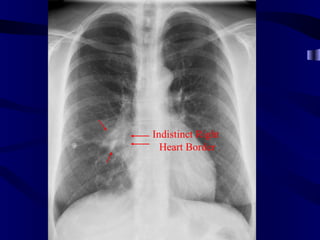
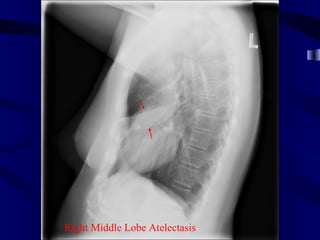
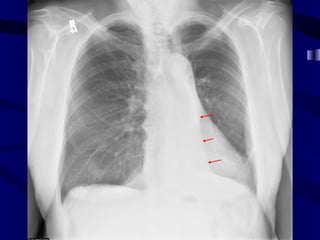
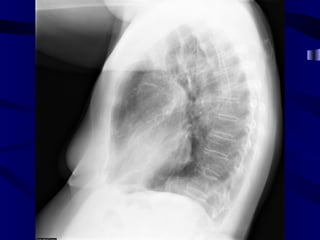
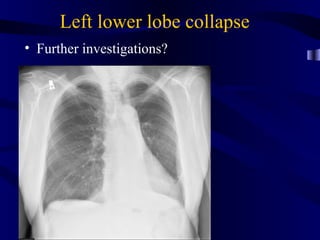
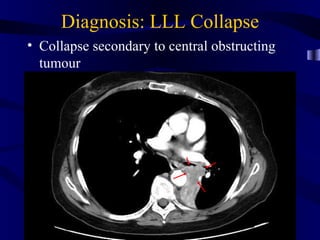
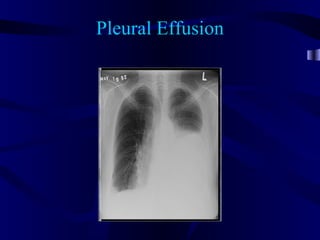
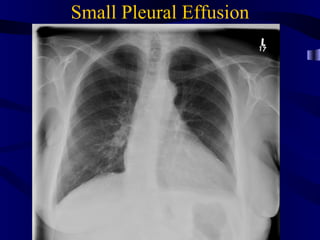
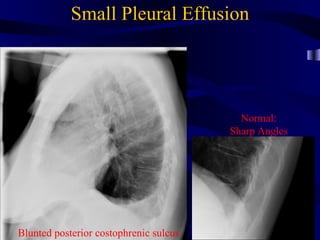
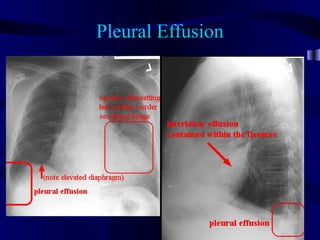
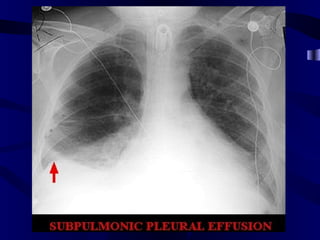
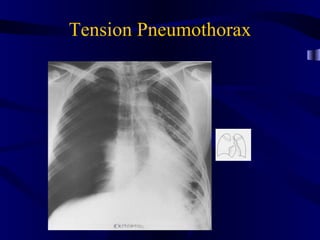
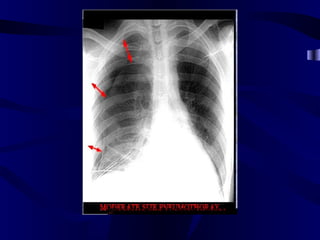
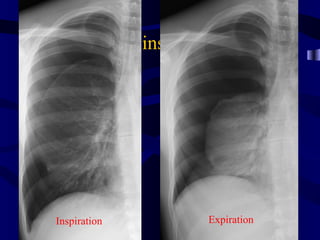
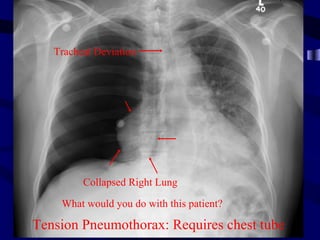
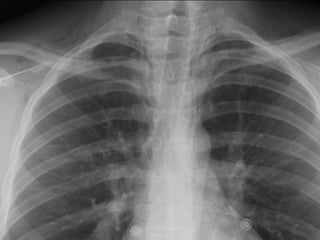
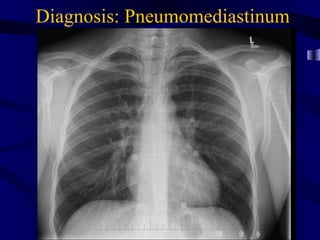
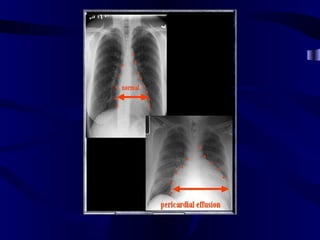
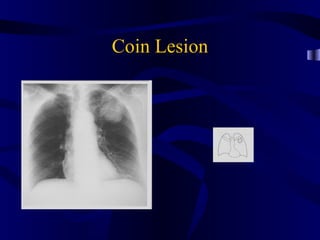
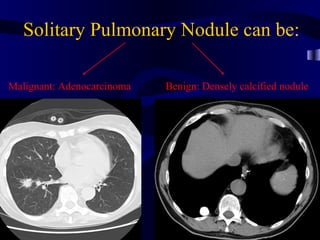
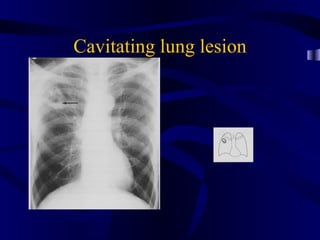
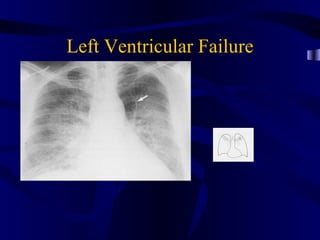
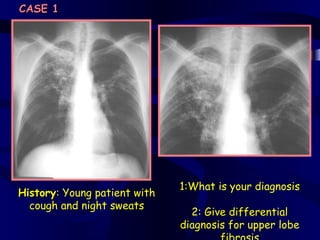
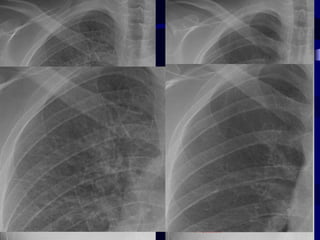
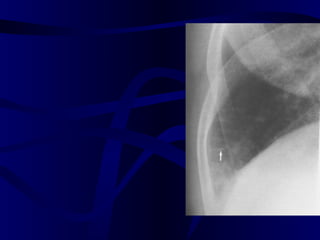
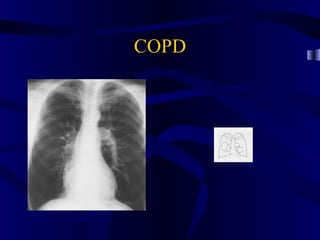
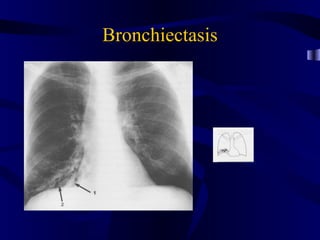
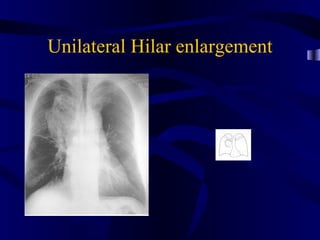
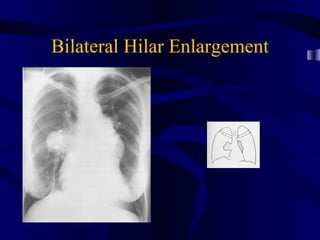
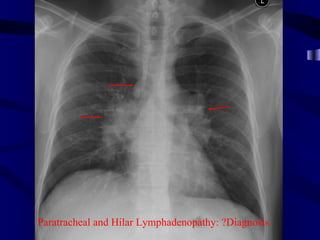
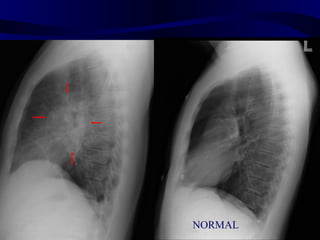
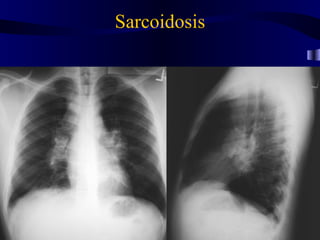
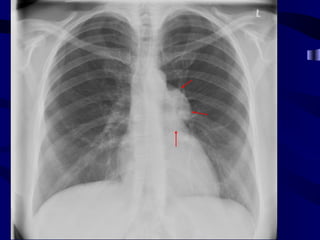
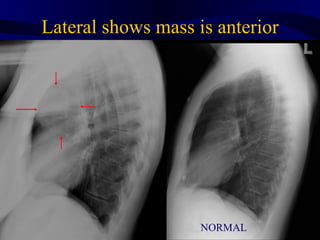
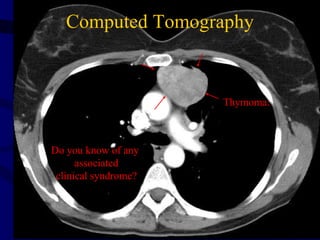
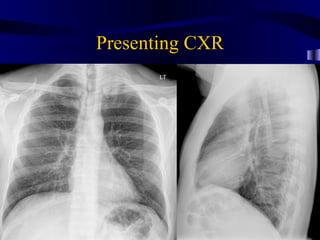
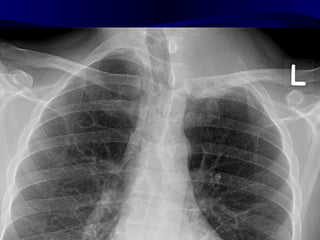
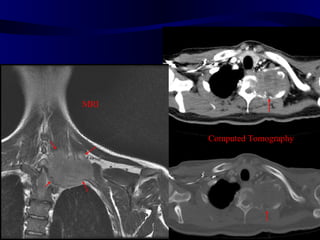
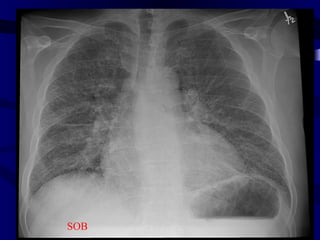
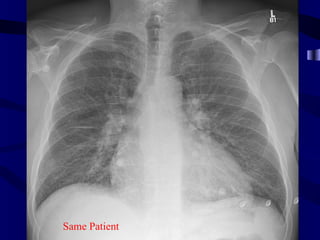
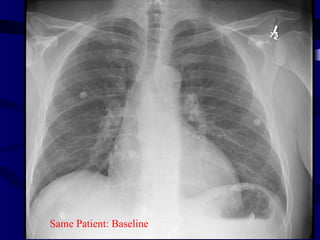
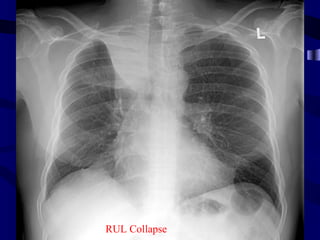
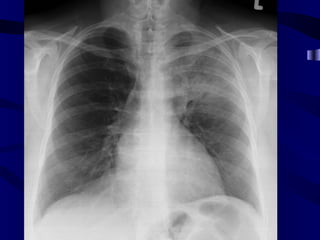
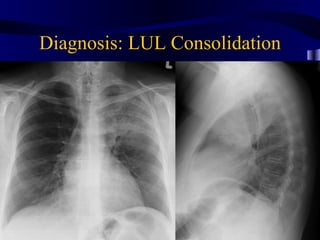
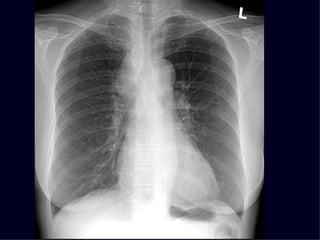
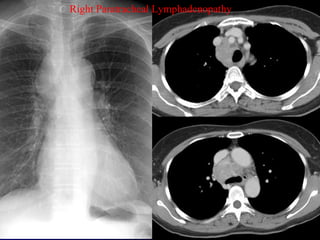
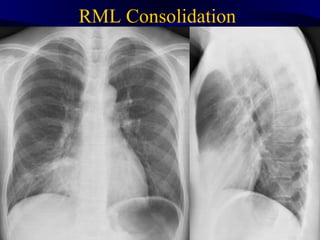
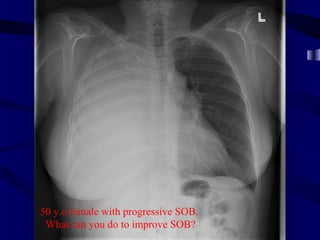
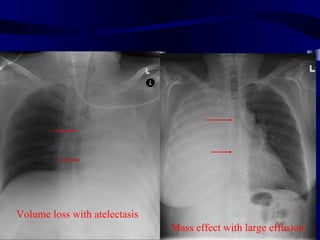
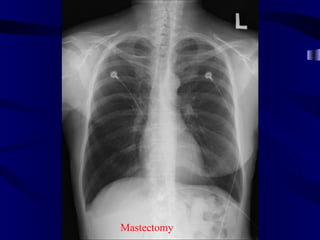
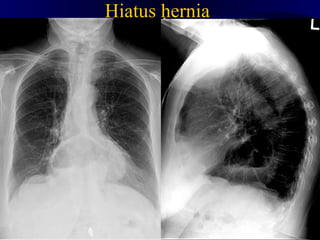
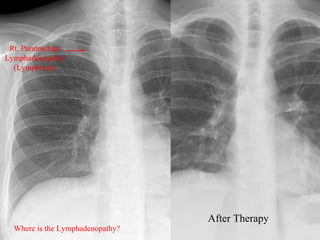
This document provides an overview of various imaging modalities used for chest imaging including plain chest radiographs, computed tomography, MRI, nuclear medicine scans, ultrasound, and pulmonary angiography. It describes the technical aspects and clinical applications of each modality. Key points covered include how plain chest radiographs remain diagnostic in 80% of cases and involve standard views, as well as how computed tomography is the main further investigation for most chest x-ray abnormalities and certain scenarios like pulmonary embolism.