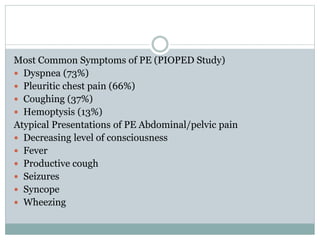
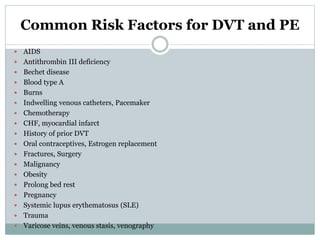
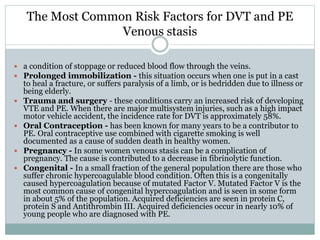
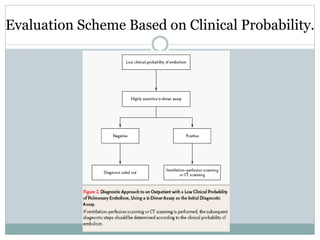
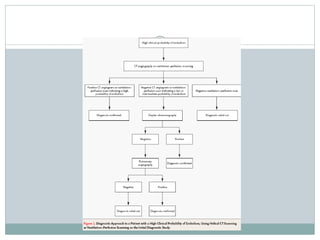
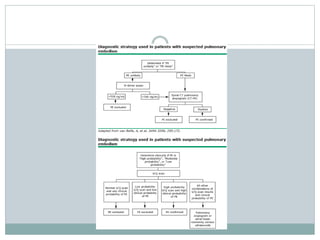
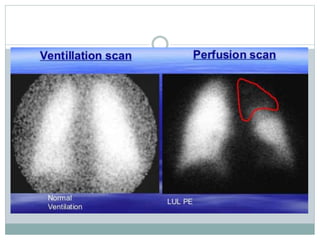
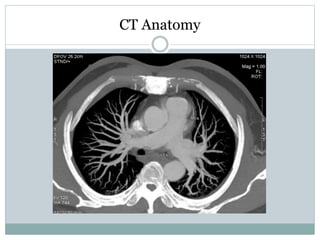
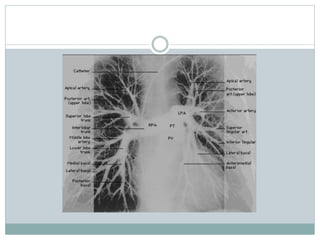
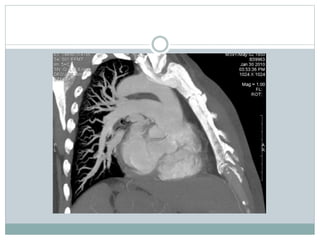
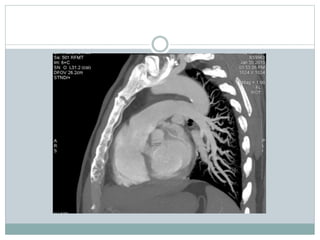
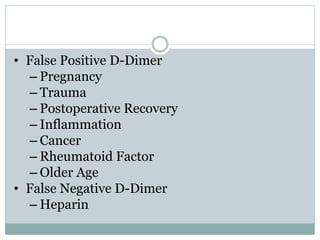
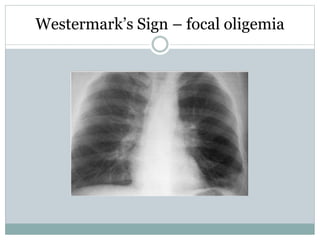
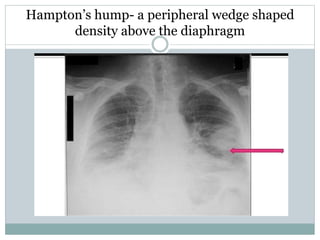
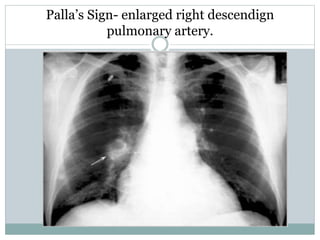
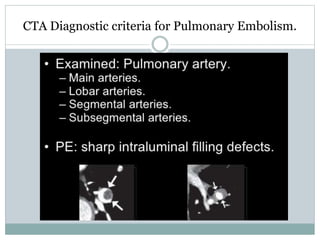
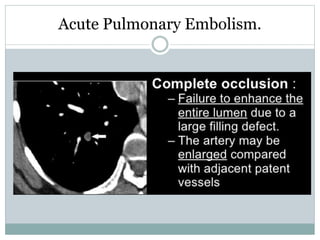
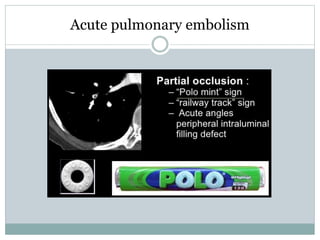
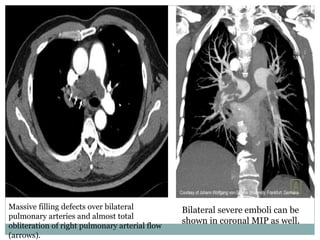
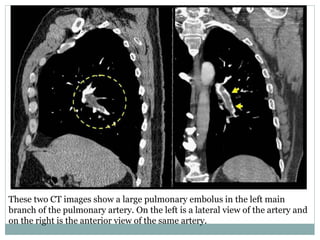
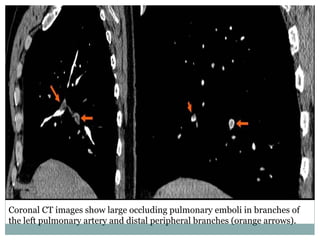
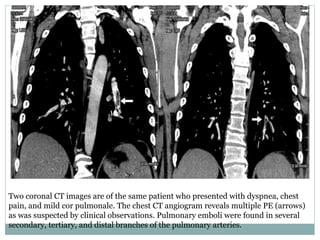
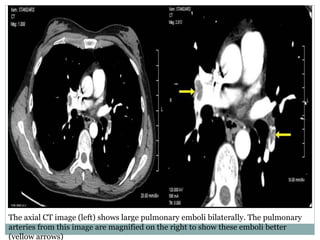
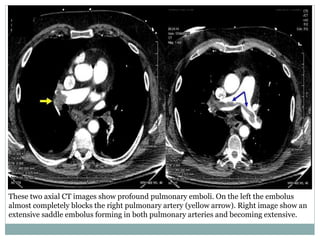
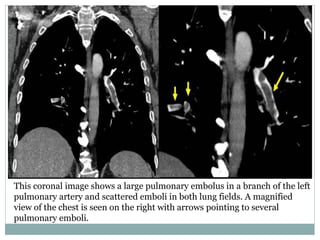
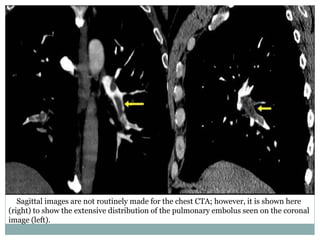
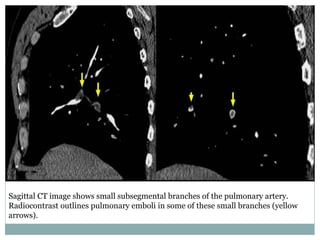
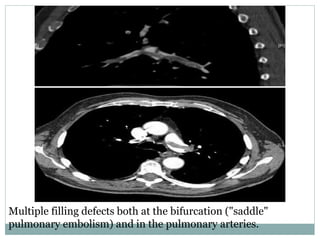
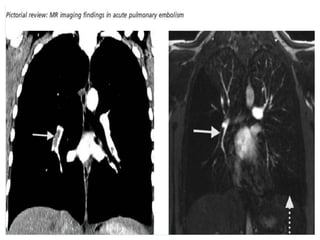
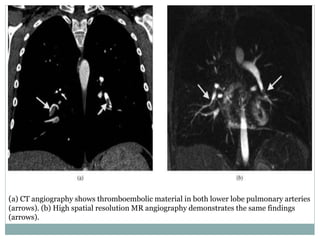
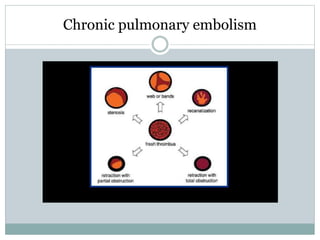
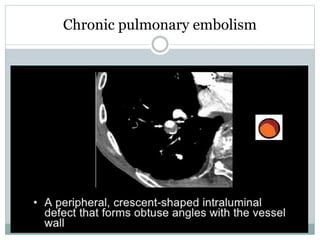
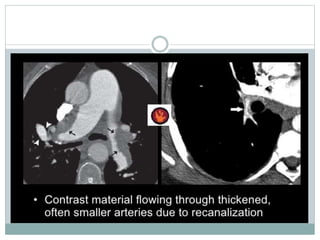
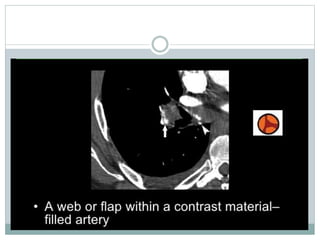
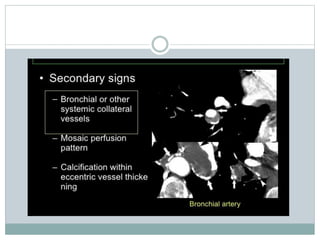
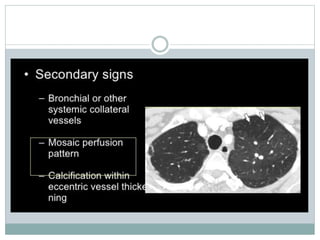
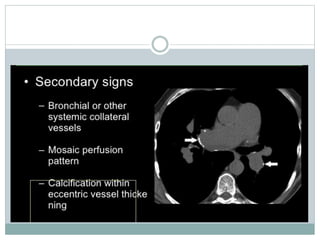
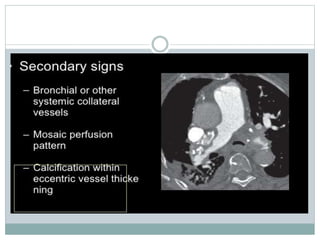
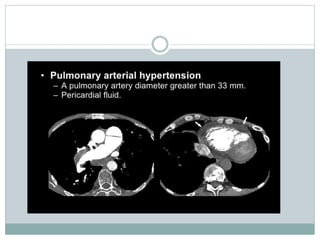
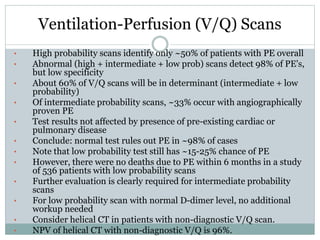
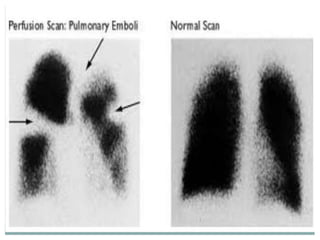
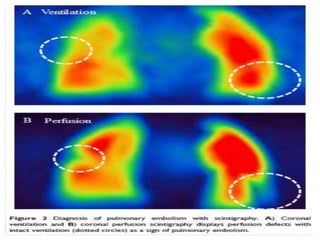
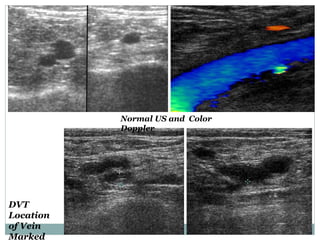
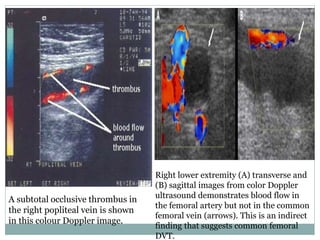
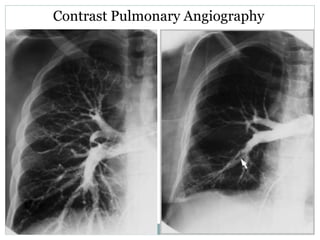
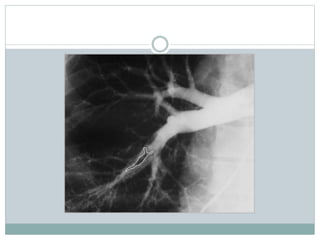
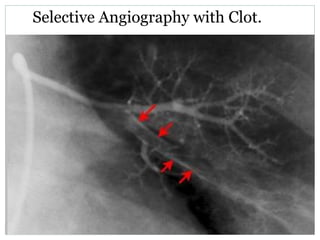
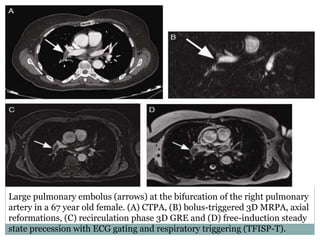
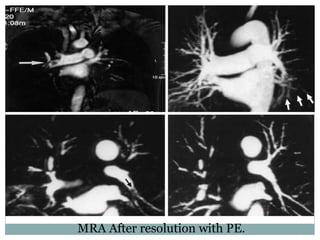
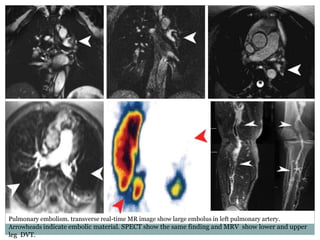
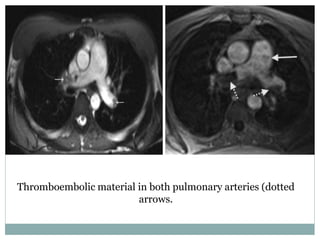
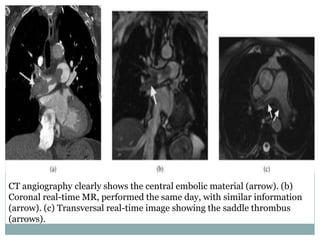
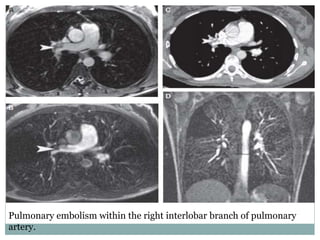
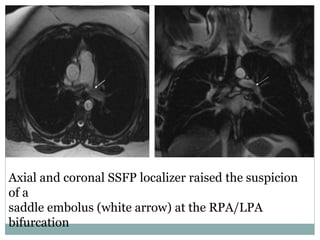
Pulmonary embolism is a blockage of the pulmonary artery or its branches by material that has traveled from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream. It is most commonly caused by deep vein thrombosis in the legs. Symptoms include dyspnea, chest pain, and cough. Risk factors include prolonged bed rest, cancer, oral contraceptives, and recent surgery or trauma. Diagnosis involves evaluating clinical probability and testing such as D-dimer, CT pulmonary angiography, ventilation-perfusion scanning, and pulmonary angiography. Treatment focuses on anticoagulation to prevent further clots.