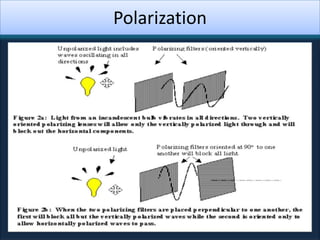
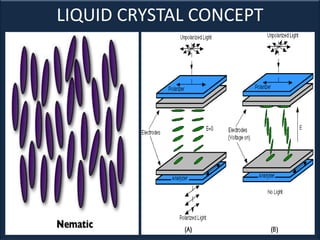
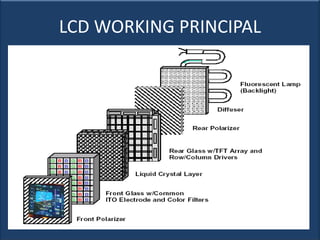
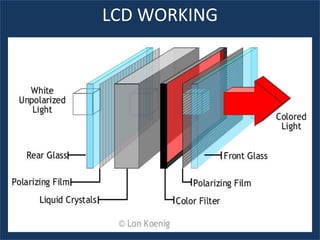
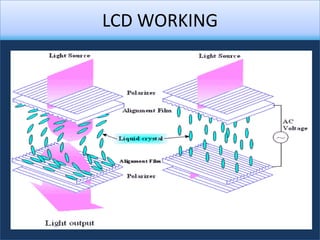
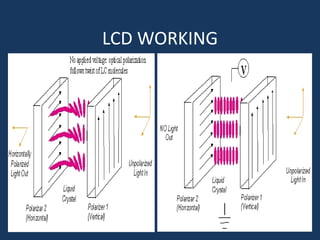
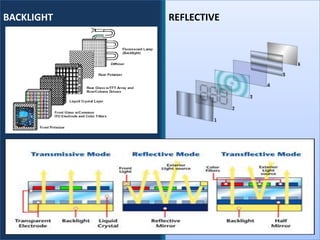
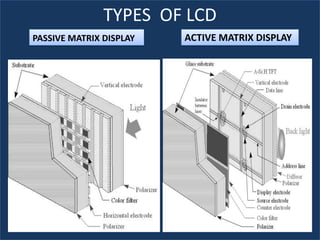
An LCD is a thin, flat panel that uses polarization of light to electronically display text, images, and video. It uses liquid crystals that shift polarization of light when voltage is applied. LCDs have transistors at each pixel to prevent crosstalk and allow higher resolutions, viewing angles, and response times than passive matrix displays. Color LCDs use red, green, and blue subpixels to display a wide range of colors.