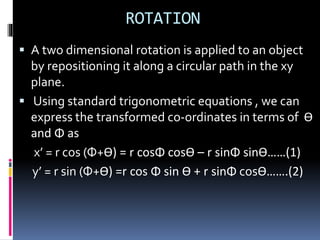
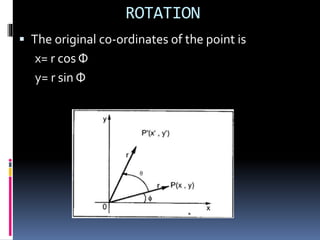
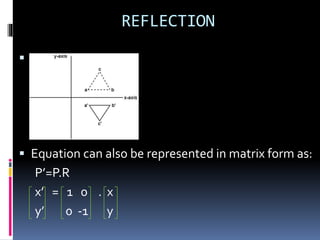
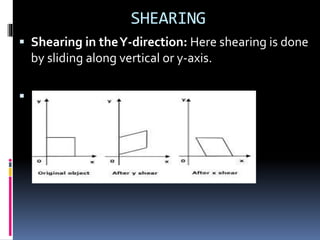
This document discusses 2D transformations in computer graphics, including rotation, reflection, and shearing. It explains rotation using trigonometric equations to express transformed coordinates in terms of an angle, and represents rotation using a rotation matrix. Reflection is described as rotating an object 180 degrees about an axis, and reflection about the x-axis is represented using a matrix. Shearing is defined as a transformation that changes an object's shape by sliding its layers, and shearing matrices for the x and y directions are provided.