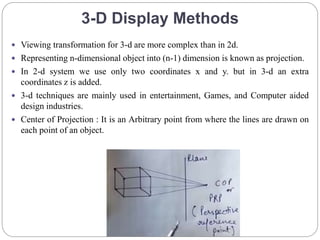
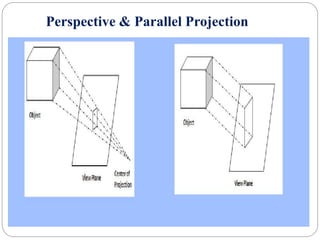
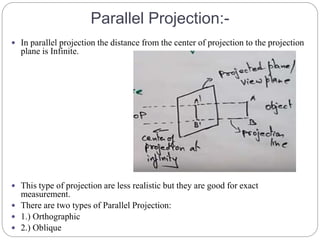
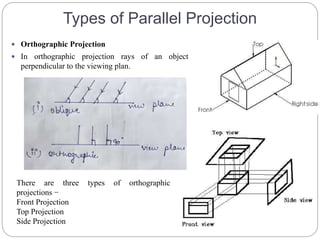
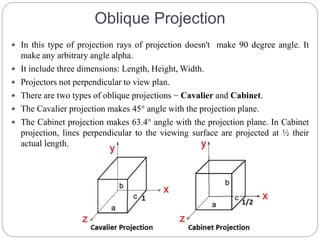
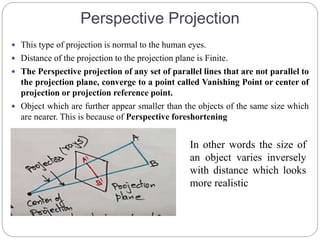
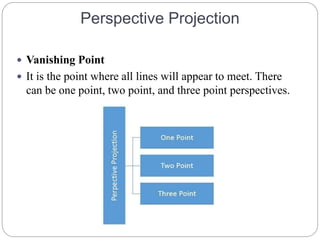
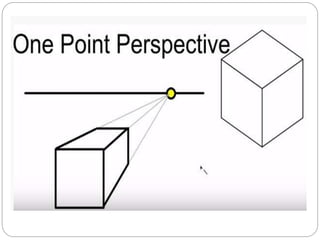
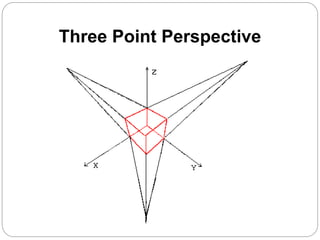
The document discusses different methods for 3D display and projection. It describes parallel projection, where lines of sight are parallel, and perspective projection, where lines converge at vanishing points. The key types of projection are outlined as parallel (orthographic and oblique) and perspective. Orthographic projection uses perpendicular lines, while oblique projection uses arbitrary angles. Perspective projection creates realistic size variation with distance and can have one, two, or three vanishing points.