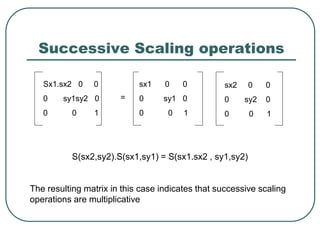
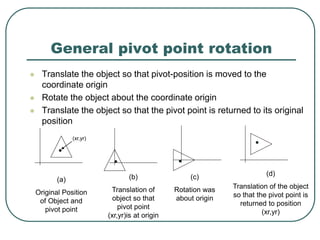
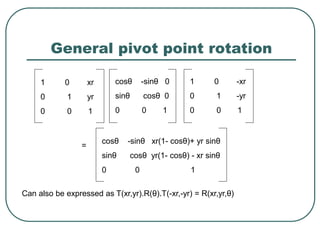
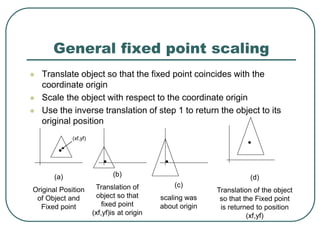
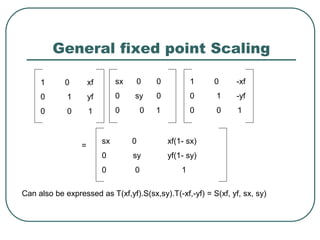
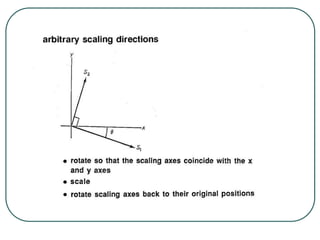
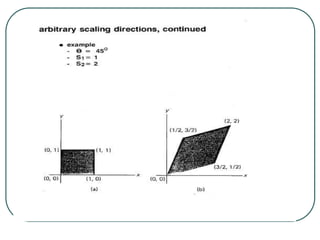
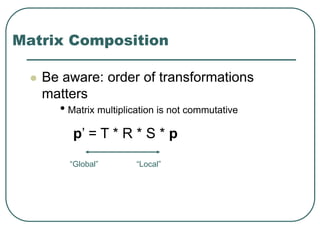
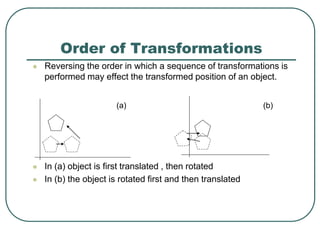
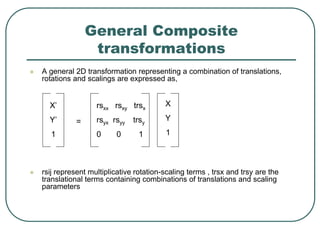
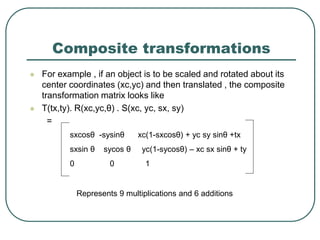
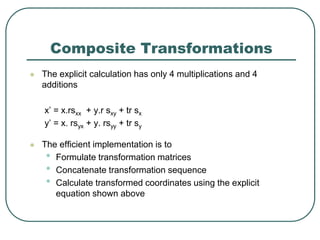
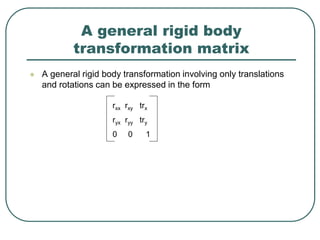
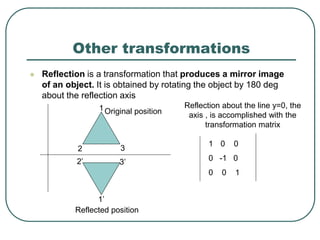
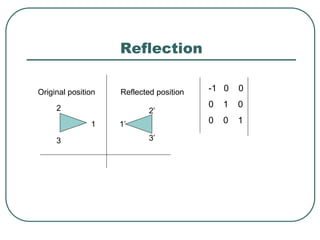
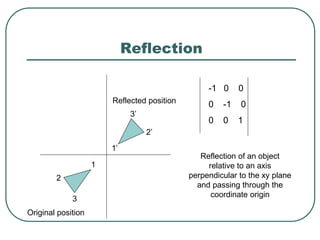
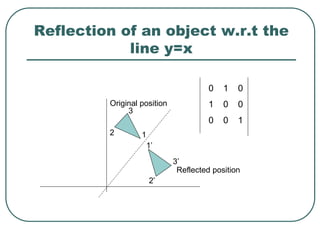
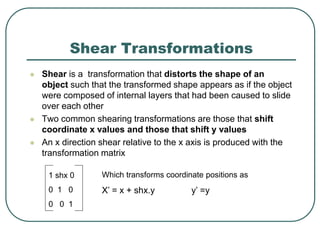
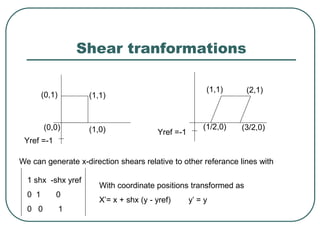
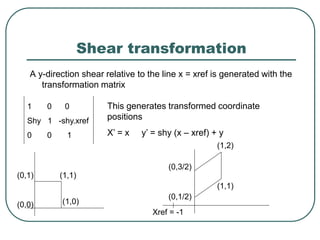
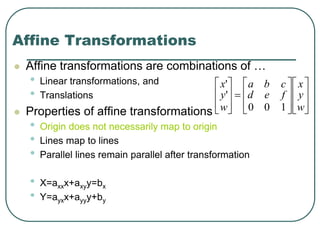
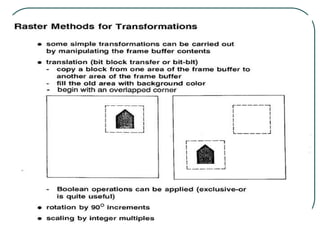
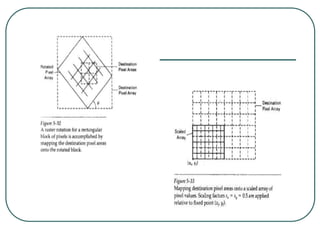
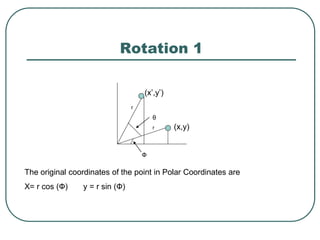
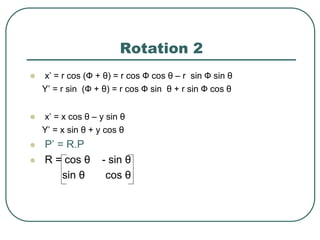
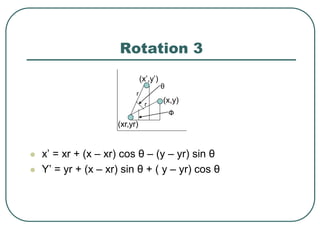
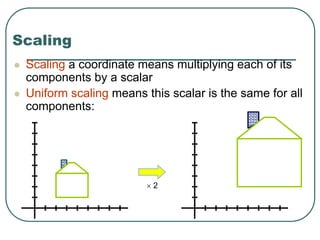
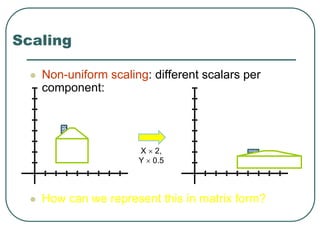
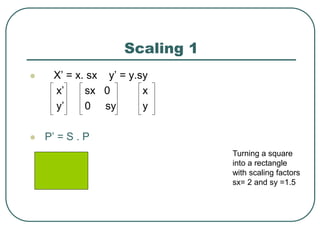
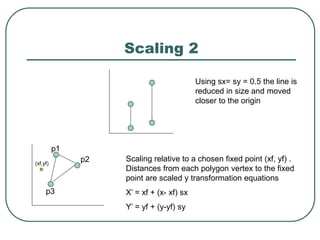
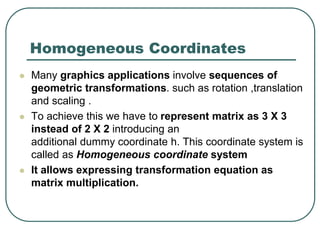
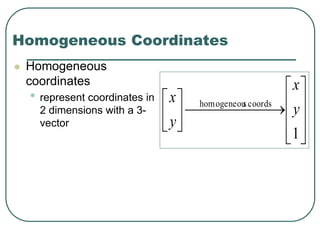
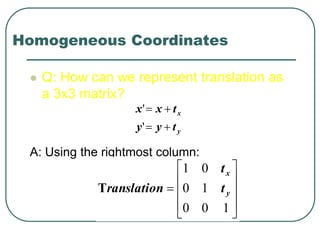
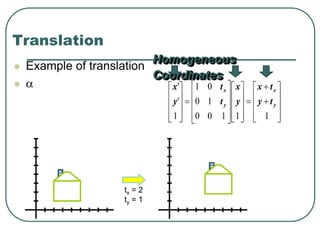
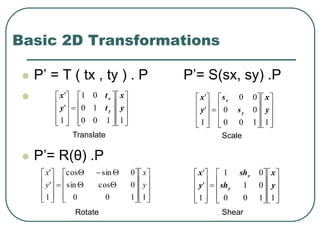
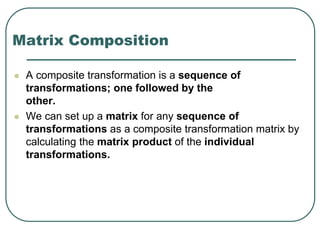
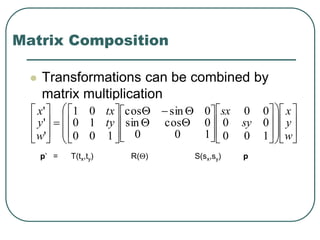
2D transformations can be represented by matrices and include translations, rotations, scalings, and reflections. Translations move objects by adding a translation vector. Rotations rotate objects around the origin by pre-multiplying the point coordinates with a rotation matrix. Scaling enlarges or shrinks objects by multiplying the point coordinates with scaling factors. Composite transformations represent multiple transformations applied in sequence, with the overall transformation represented as the matrix product of the individual transformations. The order of transformations matters as matrix multiplication is not commutative.

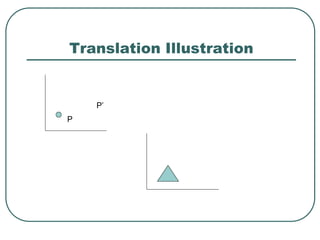
![Successive translations
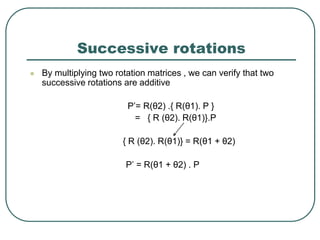
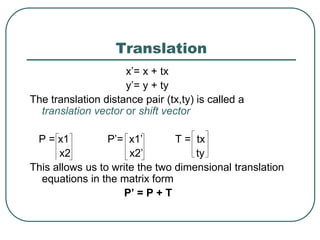
Successive translations are additive
P’= T(tx1, ty1) .[T(tx2, ty2)] P
= {T(tx1, ty1). T(tx2, ty2)}.P
T(tx1, ty1). T(tx2, ty2) = T(tx1+tx2 , ty1 + ty2)
1 0 tx1+tx2
0 1 ty1+ty2
0 0 1
1 0 tx1
0 1 ty1
0 0 1
1 0 tx2
0 1 ty2
0 0 1
=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2dtransformation-200226044408/85/2d-transformation-20-320.jpg)