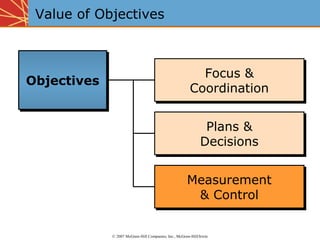
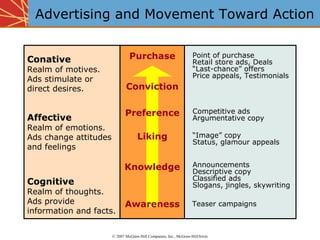
The document discusses establishing objectives and budgeting for promotional programs. It emphasizes that objectives should be specific, measurable, attainable, realistic and time-bound. Marketing objectives aim to achieve goals like sales and market share, while communication objectives are more narrow and focus on delivering messages to target audiences. Budgeting can be done through top-down or bottom-up approaches. Top-down uses a percentage of sales or competitive parity to set budgets, while bottom-up budgets activities to achieve predefined objectives. Marginal analysis is used to determine optimal spending by increasing, holding, or decreasing expenditures based on incremental returns.