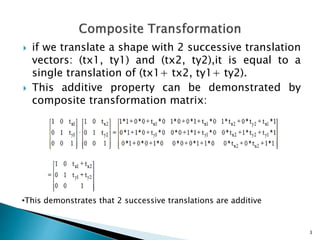
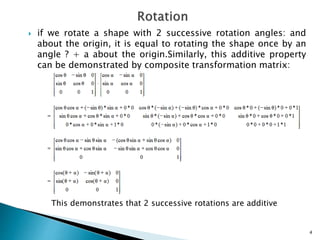
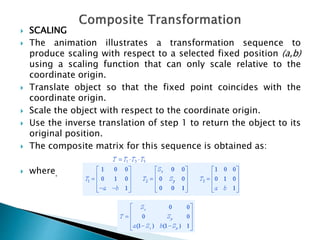
The document discusses composite transformations, which involve performing two or more transformations in sequence. It provides examples that two successive translations can be represented as a single translation, and two successive rotations can be represented as a single rotation. It also explains that scaling an object with respect to a fixed point can be achieved through a sequence of translations, scaling around the origin, and inverse translations, as represented by a composite matrix.