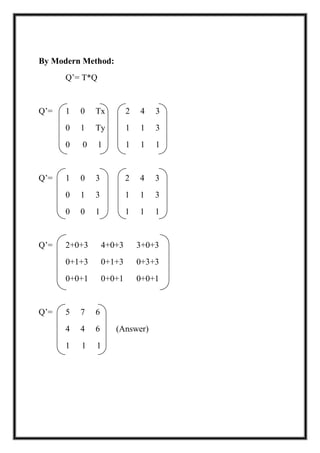
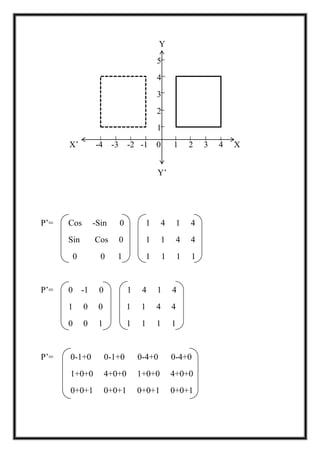
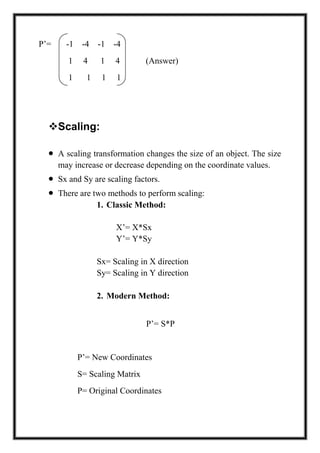
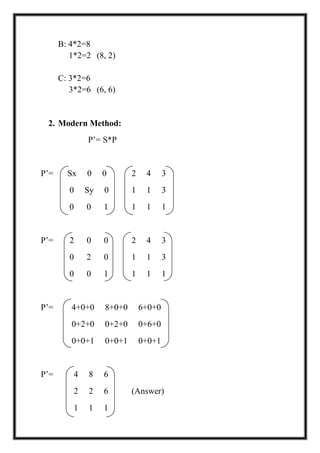
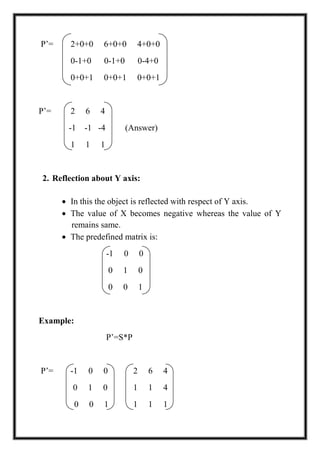
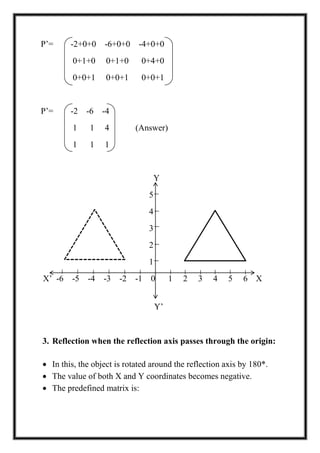
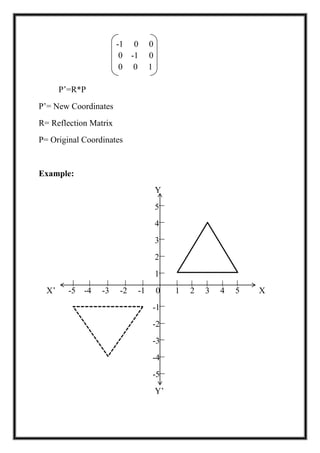
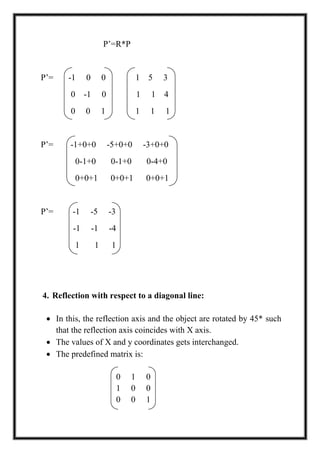
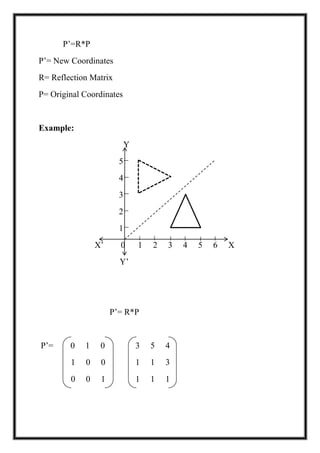
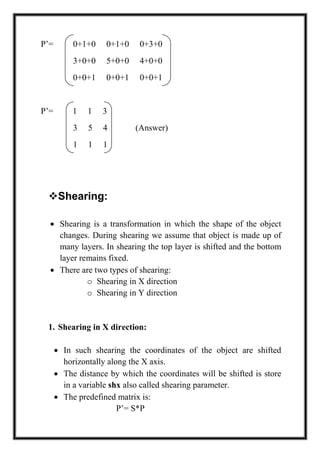
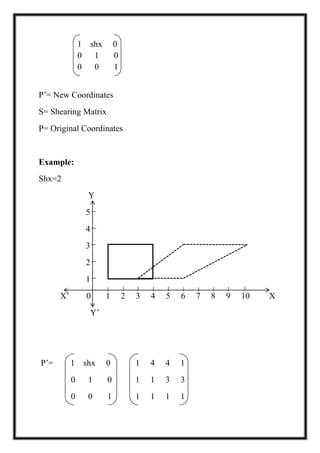
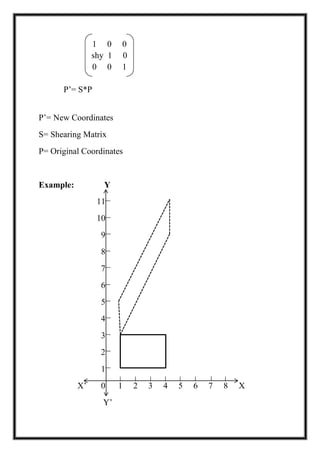
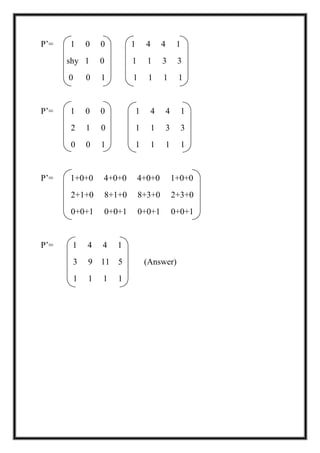
This document is a project report by Aditi Patni on 2-D transformations for her Bachelor's degree. It defines 2-D transformations as changes in orientation, shape, size or position of an object that alter its coordinate values. There are two types of 2-D transformations: basic transformations of translation, rotation, and scaling; and derived transformations of reflection and shearing. The report provides detailed explanations and examples of how to perform each of these transformations using matrix representations.